Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Magnetic Fridge Doors
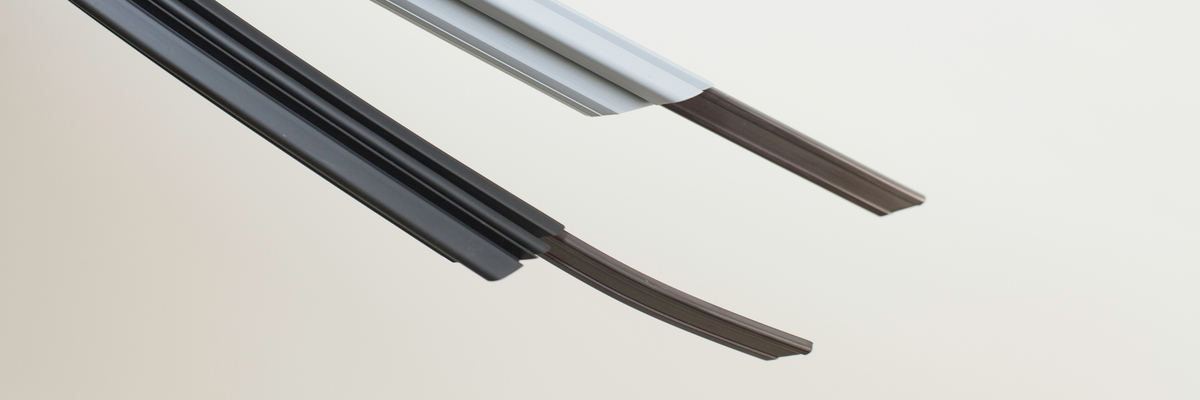

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Magnetic Fridge Door Seals
In the manufacturing of magnetic fridge doors, the performance, longevity, and energy efficiency of the final product are directly influenced by the material composition of the magnetic gasket. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize that off-the-shelf rubber solutions often fail to meet the rigorous demands of commercial and industrial refrigeration systems due to inadequate material engineering. The core issue lies in the mismatch between generic formulations and the specific environmental, mechanical, and magnetic requirements of high-duty-cycle applications.
Magnetic door seals function under continuous stress—repeated opening and closing, exposure to temperature fluctuations, and long-term compression. Standard EPDM or PVC-based seals may appear cost-effective initially but degrade prematurely under such conditions. Common failure modes include compression set, loss of magnetic retention, cracking at low temperatures, and microbial growth in high-humidity environments. These failures compromise door integrity, increase energy consumption, and lead to costly service interventions.
The optimal solution lies in precision-formulated thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV) or specialty EPDM compounds reinforced with strontium ferrite or barium ferrite magnetic strips. These materials offer superior elastic recovery, UV and ozone resistance, and stable magnetic flux retention over time. At Baoshida, our engineered compounds are tailored to balance Shore hardness (typically 60–70A), tensile strength (>9 MPa), and magnetic field strength (>800 Gauss surface field), ensuring consistent sealing force across thousands of cycles.
Moreover, material compatibility with cleaning agents and food-safe standards (such as FDA or NSF compliance) is non-negotiable in medical and foodservice refrigeration. Off-the-shelf seals often lack proper certification, posing contamination risks and violating regulatory requirements. Custom formulations allow for antimicrobial additives, color stability, and low outgassing—features rarely found in generic products.
The table below outlines key performance specifications differentiating engineered rubber solutions from standard alternatives:
| Property | Standard PVC/EPDM Seal | Baoshida Engineered TPV/EPDM-Magnetic Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 55–65 | 60–70 |
| Tensile Strength | 6–8 MPa | 9–12 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 250–300% | 350–450% |
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | 25–35% | <18% |
| Magnetic Field Strength (Surface) | 600–700 Gauss | 800–1000 Gauss |
| Low-Temp Flexibility | -20°C | -40°C |
| Cycle Life (Door Open/Close) | ~20,000 cycles | >50,000 cycles |
| Regulatory Compliance | Limited or None | FDA, NSF, RoHS, REACH |
In industrial refrigeration, reliability cannot be compromised. The magnetic door seal is not a passive component—it is a dynamic interface critical to thermal efficiency and operational safety. By investing in engineered rubber solutions, OEMs mitigate field failures, reduce warranty claims, and enhance brand reputation. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we partner with manufacturers to co-develop formulations that meet exact performance envelopes, ensuring every seal performs under real-world conditions.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Magnetic Refrigerator Door Seals
Selecting the optimal elastomer for magnetic refrigerator door seals is critical for ensuring energy efficiency, longevity, and compliance with food safety standards. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we prioritize materials that maintain consistent compression force over 100,000+ door cycles while resisting degradation from repeated exposure to moisture, cleaning agents, and temperature fluctuations. The seal must also accommodate embedded magnetic strips without compromising flexibility or adhesion. Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone represent the primary material solutions, each engineered for specific operational demands.
Viton fluoroelastomers excel in extreme environments, offering unparalleled resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and aggressive cleaning chemicals common in commercial kitchens. With a functional temperature range of -20°C to 230°C, Viton maintains structural integrity in blast freezers or high-heat display units where standard elastomers fail. Its low compression set (≤15% per ASTM D395) ensures persistent sealing force, though higher material costs position it for premium commercial applications. Nitrile rubber provides an optimal balance for standard household and light commercial refrigeration. Its exceptional resistance to oils and greases (volume swell <15% in IRM 903 per ISO 1817) prevents degradation from food spills and lubricants, while a -40°C to 120°C operating range covers most consumer use cases. Nitrile’s cost efficiency and robust tensile strength (15–20 MPa) make it the industry benchmark for mass production. Silicone stands out for ultra-low-temperature flexibility down to -60°C and superior biocompatibility, meeting FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 for direct food contact. Its inert nature resists mold growth in humid environments, though moderate oil resistance and higher compression set (≤20%) necessitate careful design validation for high-cycle doors.
The comparative analysis below details critical performance metrics guiding material selection:
| Material | Temp Range (°C) | Compression Set (%, 70h/70°C) | Key Chemical Resistance | Primary Applications | Cost Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton | -20 to 230 | ≤15 | Ozone, acids, solvents, steam | Commercial freezers, medical refrigeration | Premium |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 to 120 | ≤25 | Oils, greases, water | Household refrigerators, beverage coolers | Standard |
| Silicone | -60 to 200 | ≤20 | Water, alcohols, mild acids | Ultra-low-temp freezers, food-grade units | Moderate to Premium |
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering team validates all formulations against ISO 188 aging tests and EN 13090 seal force requirements. For magnetic door assemblies, we emphasize Shore A hardness optimization (65–75) to balance magnetic retention with low opening force. Nitrile remains the dominant solution for cost-sensitive OEMs, while Viton and Silicone address specialized thermal or regulatory constraints. Material certification dossiers, including REACH SVHC compliance and FDA letters, are provided for every production batch. Partner with us to align your seal specifications with lifecycle performance targets and regional market regulations.
Manufacturing Capabilities
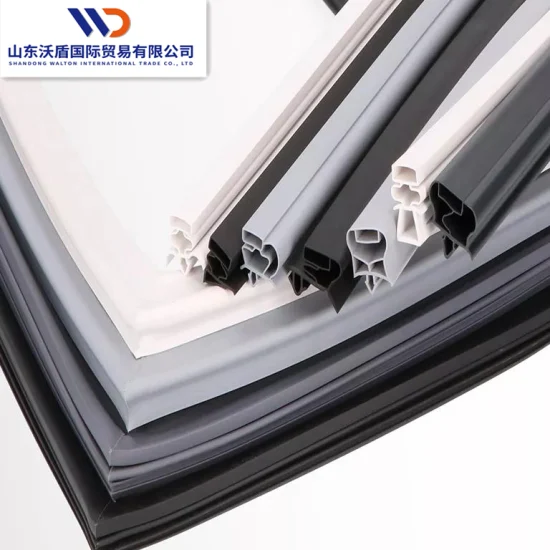
Engineering Capability
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability is anchored in deep technical expertise and a disciplined approach to industrial rubber formulation and mold design. We maintain a dedicated team of five certified mold engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, enabling us to deliver fully integrated OEM solutions for high-performance applications such as magnetic fridge doors. This cross-functional engineering team ensures that every product is optimized for material performance, sealing efficiency, durability, and manufacturability.
Our mold engineers bring over 15 collective years of experience in precision rubber molding, with specialization in compression, transfer, and injection molding techniques. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM software—including SolidWorks, AutoCAD, and UG NX—to develop robust mold designs that support tight tolerances, complex geometries, and high-cycle production demands. Each mold undergoes rigorous simulation and validation processes to ensure dimensional accuracy, uniform material flow, and minimal defect rates during mass production.
Complementing our mold engineering strength is our in-house rubber formulation capability. Our two formula engineers focus exclusively on elastomer chemistry, tailoring compound formulations to meet the functional requirements of refrigerator door seals. These include resistance to temperature cycling (-40°C to +80°C), ozone and UV exposure, compression set, and long-term elasticity retention. We formulate using EPDM, silicone, and specialty rubber blends, ensuring optimal sealing performance and energy efficiency in refrigeration systems.
Our OEM capabilities extend from concept to mass production. We support customers through every stage: technical consultation, 3D modeling, material selection, prototype development, DFM analysis, and final validation. This end-to-end control allows us to maintain consistency, reduce time-to-market, and meet stringent quality standards required by major appliance manufacturers.
We also maintain full traceability and compliance with ISO 9001 and RoHS standards. All formulations and mold designs are documented and archived, enabling seamless replication and scalability across production batches. Our facility is equipped with state-of-the-art mixing, curing, and testing equipment to ensure batch-to-batch consistency and performance reliability.
The integration of mold and material engineering under one roof positions Suzhou Baoshida as a strategic partner in the development of next-generation magnetic fridge door seals—delivering performance, precision, and reliability at scale.
Material and Performance Specifications
| Property | Test Standard | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 55 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 8 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 250% |
| Compression Set (24h @ 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 20% |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +80°C |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracking (200 pphm, 40°C, 96h) |
| Magnetic Flux Density | GB/T 32147 | ≥ 1.8 mT |
| Aging Resistance (70°C × 168h) | ASTM D573 | Tensile retention ≥ 80% |
Customization Process

Customization Process for Magnetic Refrigerator Door Seals
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. implements a rigorously controlled four-stage customization workflow for magnetic refrigerator door seals, ensuring optimal sealing performance, energy efficiency, and durability. This process begins with comprehensive Drawing Analysis, where engineering teams scrutinize client-provided CAD files and technical specifications. Critical parameters assessed include geometric tolerances per ISO 2768-mK standards, magnetic strip positioning relative to the rubber profile, and interference fit requirements against the refrigerator cabinet. Material constraints such as maximum cross-sectional thickness deviations (±0.15mm) and curvature radii are validated against manufacturing capabilities. Concurrently, environmental factors like operating temperature ranges (-40°C to +70°C) and chemical exposure risks are documented to inform formulation design.
The Formulation stage leverages Baoshida’s proprietary compound database and accelerated aging simulations. Engineers select base polymers (EPDM or silicone) based on ozone resistance and low-temperature flexibility requirements. Magnetic ferrite or rare-earth particles are dispersed at precise loadings (typically 35–45% by weight) to achieve target magnetic flux density while maintaining elastomer integrity. Cure kinetics are optimized via DSC analysis, balancing scorch safety (T₅ ≥ 12 minutes at 160°C) with efficient vulcanization (T₉₀ ≤ 8 minutes). Additives for UV stabilization, compression set resistance, and pigment matching undergo DOE-driven validation to ensure compliance with IEC 62552-3 energy efficiency standards.
Prototyping utilizes CNC-machined aluminum molds for rapid validation. Three functional prototypes undergo stringent testing: magnetic flux density mapping via gaussmeter (per ASTM F2213), compression force-deflection profiling (ISO 3384), and 500-cycle door slam durability trials. Seal integrity is quantified using helium leak testing (detection limit < 5×10⁻⁶ mbar·L/s) under simulated frost conditions. Client feedback on fitment and aesthetics triggers iterative refinements, with material lot traceability maintained via blockchain-secured batch records.
Mass Production deployment integrates real-time SPC monitoring. Each production run begins with first-article inspection against the approved prototype, followed by automated inline checks of magnetic strength, durometer (Shore A 55–65), and dimensional conformity via laser micrometers. Statistical process control charts track critical variables like cure state (MH-ML per ASTM D5289) with Cpk ≥ 1.67. All finished seals undergo 100% magnetic continuity verification and batch-level aging tests per ISO 188. Final shipment includes full material certification, RoHS/REACH compliance documentation, and traceable lot codes for end-of-life recycling.
Key Performance Specifications for Magnetic Door Seals
| Parameter | Target Range | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Flux Density | 1.8–2.2 kGauss | ASTM F2213 |
| Shore A Hardness | 55–65 | ISO 48-4 |
| Compression Set (22h) | ≤ 15% | ISO 815-B |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 8.0 MPa | ISO 37 |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +70°C | IEC 60068-2-1/2 |
| Magnetic Strip Pull Force | ≥ 4.5 N/cm | Internal BAOSHIDA-07 |
This systematic approach minimizes time-to-market while guaranteeing seals that prevent thermal leakage, reduce compressor load by 8–12%, and exceed 10-year service life under continuous operation. Suzhou Baoshida maintains full process ownership from specification finalization to bulk delivery, with all stages audited to IATF 16949 quality management protocols.
Contact Engineering Team

For manufacturers and OEMs seeking high-performance rubber components tailored for magnetic refrigerator door applications, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands as a trusted industrial partner. Specializing in precision-engineered rubber solutions, we deliver sealing systems that meet the rigorous demands of thermal efficiency, durability, and magnetic integration. Our expertise in material formulation, compression molding, and magnetic strip encapsulation ensures that every gasket performs reliably under repeated compression cycles, extreme temperature fluctuations, and long-term environmental exposure.
Our rubber profiles for magnetic fridge doors are designed to maintain consistent sealing force while accommodating embedded magnetic strips that ensure airtight closure. We utilize advanced elastomer compounds—including EPDM, silicone, and specialty NBR formulations—that provide excellent resistance to ozone, UV degradation, and temperature extremes from -40°C to +120°C. Each profile is manufactured under strict quality control protocols, ensuring dimensional accuracy, uniform durometer (Shore A hardness), and seamless integration with magnetic inserts. Whether you require custom cross-sectional geometries, co-extruded profiles, or multi-material bonding, our engineering team collaborates directly with clients to optimize performance and manufacturability.
Suzhou Baoshida supports global supply chains with scalable production capacity, ISO-certified processes, and full traceability across batches. Our technical team conducts comprehensive testing—including compression set analysis, tensile strength evaluation, and magnetic flux consistency checks—to validate product reliability prior to shipment. We also offer prototyping services, material certification packages (e.g., RoHS, REACH, FDA), and on-site technical audits upon request.
To ensure seamless integration into your production workflow, we provide detailed technical documentation, including 2D/3D drawings, tolerance analyses, and installation guidelines. Our logistics network enables just-in-time delivery to manufacturing hubs across Asia, Europe, and North America, minimizing inventory overhead while maintaining supply continuity.
For immediate technical consultation or quotation support, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. Mr. Boyce leads material development and client engineering initiatives, with over 12 years of experience in industrial sealing applications. He is available to review your design specifications, recommend optimal material configurations, and coordinate sample production.
Reach out via email at [email protected] to initiate a technical dialogue. Include your project requirements, performance criteria, and preferred materials (if applicable) to accelerate the evaluation process. Our team responds to all inquiries within 8 business hours.
Below are key technical specifications for our standard magnetic door gasket series:
| Parameter | Value / Range |
|---|---|
| Material Options | EPDM, Silicone, NBR, HNBR |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 45–75 ±5 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C (up to +150°C intermittent) |
| Magnetic Strip Type | Flexible Ferrite or Rare Earth (NdFeB) |
| Magnetic Flux Density | 800–1200 Gauss (adjustable) |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤20% |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8.0 MPa (EPDM) |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% |
| Standard Compliance | RoHS, REACH, FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 |
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for technically advanced, application-specific rubber solutions engineered for performance and longevity in magnetic refrigerator door systems. Contact Mr. Boyce today to begin the engineering process.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
