Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Measure Ring Size With Calipers
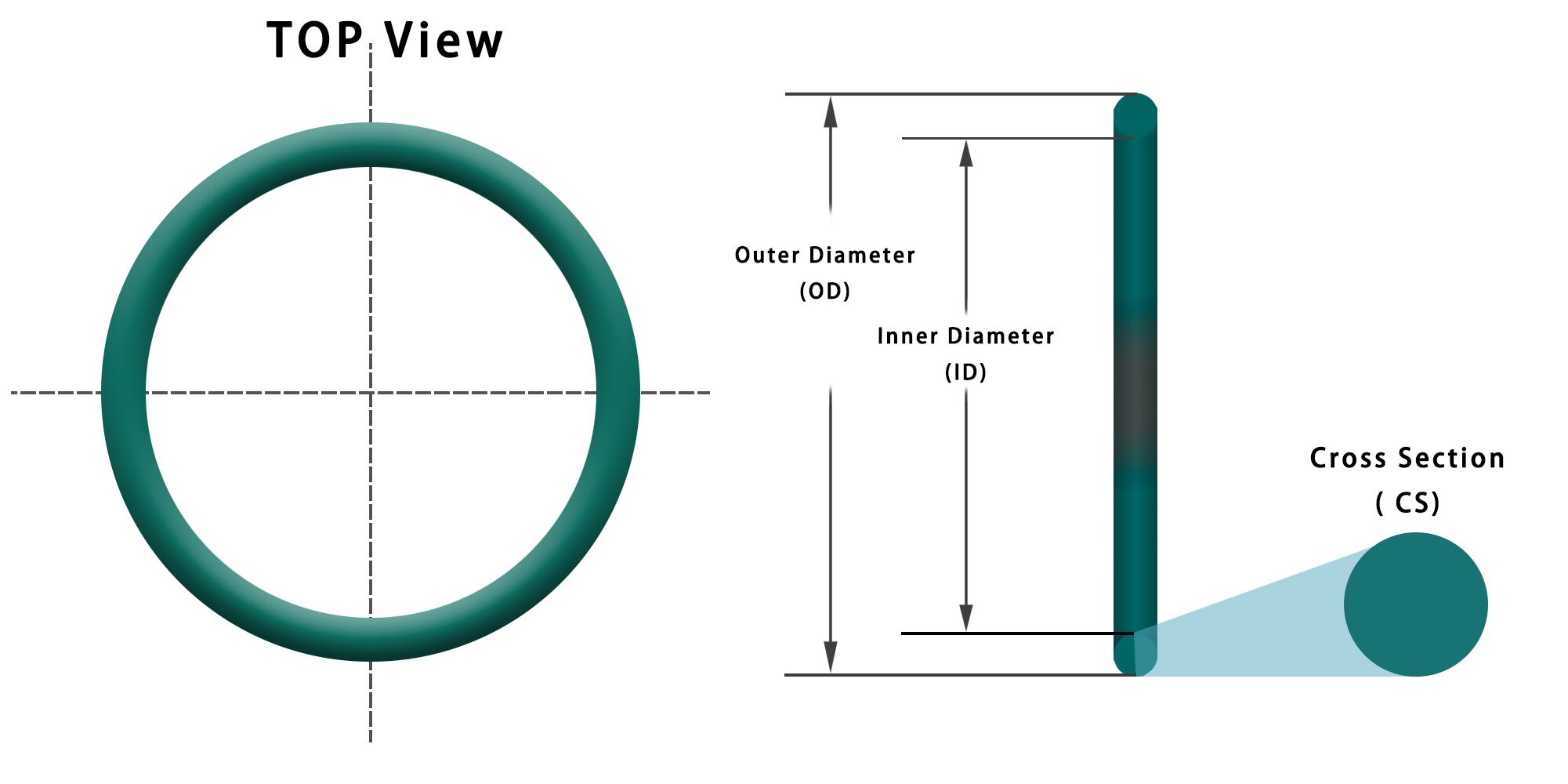
Engineering Insight: Measure Ring Size with Calipers – The Critical Role of Material Selection in Precision Rubber Seals
Accurate dimensional measurement of rubber seals using precision calipers is a fundamental step in quality assurance, yet it represents only one component of a far more complex engineering challenge. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize that while precise measurement ensures conformity to geometric specifications, the long-term performance of a rubber seal is predominantly governed by material selection. Off-the-shelf solutions often fail not due to dimensional inaccuracy, but because the base elastomer is mismatched to the operational environment.
When measuring ring size with calipers, engineers capture outer diameter (OD), inner diameter (ID), and cross-sectional (CS) dimensions. These values must align with ISO 3601 or AS568 standards, depending on application. However, rubber is a viscoelastic material—its dimensions can temporarily shift under handling, temperature, or pressure. A seal may measure within tolerance at room temperature but contract or swell beyond acceptable limits when exposed to hydraulic fluid or extreme heat. This behavior underscores why material compatibility must be evaluated alongside dimensional precision.
Common off-the-shelf seals are typically manufactured from generic Nitrile (NBR) or silicone (VMQ), chosen for cost efficiency rather than performance. While suitable for benign environments, these materials degrade rapidly under aggressive media such as phosphate esters, aromatic hydrocarbons, or hot air above 200°C. For example, NBR swells significantly in non-polar solvents, leading to extrusion and seal failure, even if initial caliper measurements were flawless. Similarly, silicone exhibits poor abrasion resistance and low tensile strength, making it unsuitable for dynamic sealing applications despite dimensional accuracy.
In contrast, engineered elastomers such as Fluorocarbon (FKM), Ethylene Acrylate (AEM), or Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) offer superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals. These materials maintain dimensional stability under stress and exhibit minimal compression set—critical for long-term sealing integrity. At Suzhou Baoshida, we custom-formulate compounds based on OEM fluid exposure, temperature range, and mechanical load, ensuring that both measured dimensions and material behavior align with real-world demands.
The table below outlines key elastomer properties relevant to precision seal applications:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Fluid Resistance | Compression Set | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | -30 to +100 | Good (aliphatic oils) | Moderate | Hydraulic systems, pneumatic seals |
| VMQ | -55 to +200 | Fair (water, oils) | Poor | Static seals, low-stress environments |
| FKM | -20 to +230 | Excellent (fuels, acids) | Low | Aerospace, automotive, chemical processing |
| AEM | -40 to +175 | Good (hot oil, coolant) | Low | Automotive transmission seals |
| FFKM | -15 to +325 | Exceptional (all media) | Very Low | Semiconductor, ultra-high-purity systems |
Ultimately, measuring ring size with calipers is a necessary but insufficient step in seal validation. True reliability emerges when dimensional precision is paired with intelligent material selection. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. partners with OEMs to move beyond off-the-shelf compromises, delivering seals engineered for performance, not just measurement.
Material Specifications
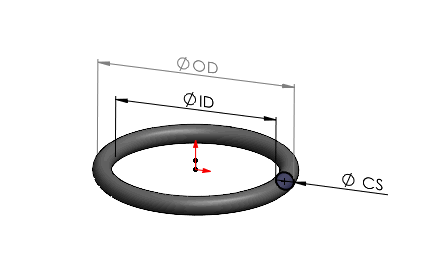
Precision Ring Size Measurement Protocol for Rubber Seal Materials
Accurate dimensional verification of rubber seals using digital calipers is non-negotiable for OEM validation and failure prevention. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we enforce strict measurement protocols aligned with ISO 3601 and ASTM D3767 standards to ensure seal integrity under operational stress. Rubber compounds exhibit unique behaviors during measurement due to elasticity, compression set, and thermal sensitivity. Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) each require material-specific handling to avoid misinterpretation of critical dimensions like inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and cross-section (CS).
Measurement must occur after 72 hours of post-cure conditioning at 23°C ±2°C and 50% ±5% RH per ASTM D573. Premature measurement induces elastic recovery errors. Calipers must be certified to ISO 130:2017 (Class 0.01mm resolution) and zeroed against gauge blocks immediately before use. Apply consistent 0.5N ±0.1N force during measurement—excessive pressure deforms softer compounds like Silicone, while insufficient force fails to overcome Viton’s stiffness. Measure three times at 120° intervals around the ring circumference; record the median value. Reject any seal with cross-sectional variance exceeding ±0.05mm, as this indicates molding inconsistency leading to extrusion or leakage.
Material composition directly impacts measurement stability. Nitrile’s susceptibility to plasticizer migration causes gradual shrinkage, demanding immediate post-conditioning measurement. Viton’s low compression set minimizes elastic recovery but requires extended conditioning to stabilize fluoropolymer chains. Silicone’s high thermal expansion coefficient (200–300 x 10⁻⁶/°C) necessitates temperature-controlled environments—0.1°C fluctuation alters dimensions by 0.002mm/mm. Chemical exposure history (e.g., fuel swell in NBR) must be documented, as residual swelling distorts baseline dimensions.
Material Performance and Measurement Specifications
| Material | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Continuous Temp Range (°C) | Key Chemical Resistances | Critical Measurement Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | 60–90 | -20 to +230 | Fuels, oils, acids, ozone | Minimal elastic recovery; measure after 96h conditioning. High stiffness requires precise force control to avoid under-compression. |
| Nitrile (NBR) | 50–90 | -30 to +120 | Aliphatic hydrocarbons, water, hydraulic fluids | Prone to plasticizer loss; measure within 1h of conditioning. Susceptible to swelling in aromatic fuels—account for 5–15% swell in design. |
| Silicone (VMQ) | 30–80 | -60 to +200 | Water, ozone, UV, steam | High elasticity demands slow, steady caliper application. Thermal drift critical—measure at exactly 23°C. Avoid fingerprint oils causing surface tack. |
Traceability is mandatory: record caliper serial number, operator ID, temperature, humidity, and measurement timestamps in the Certificate of Conformance. Suzhou Baoshida implements dual-operator verification for aerospace and medical seals where dimensional tolerances fall below ±0.03mm. This protocol prevents field failures caused by undetected dimensional drift—common in NBR seals exposed to biodiesel or Silicone in high-vacuum applications. Consistent adherence ensures our seals achieve 15,000+ hour service life in critical OEM assemblies.
Manufacturing Capabilities
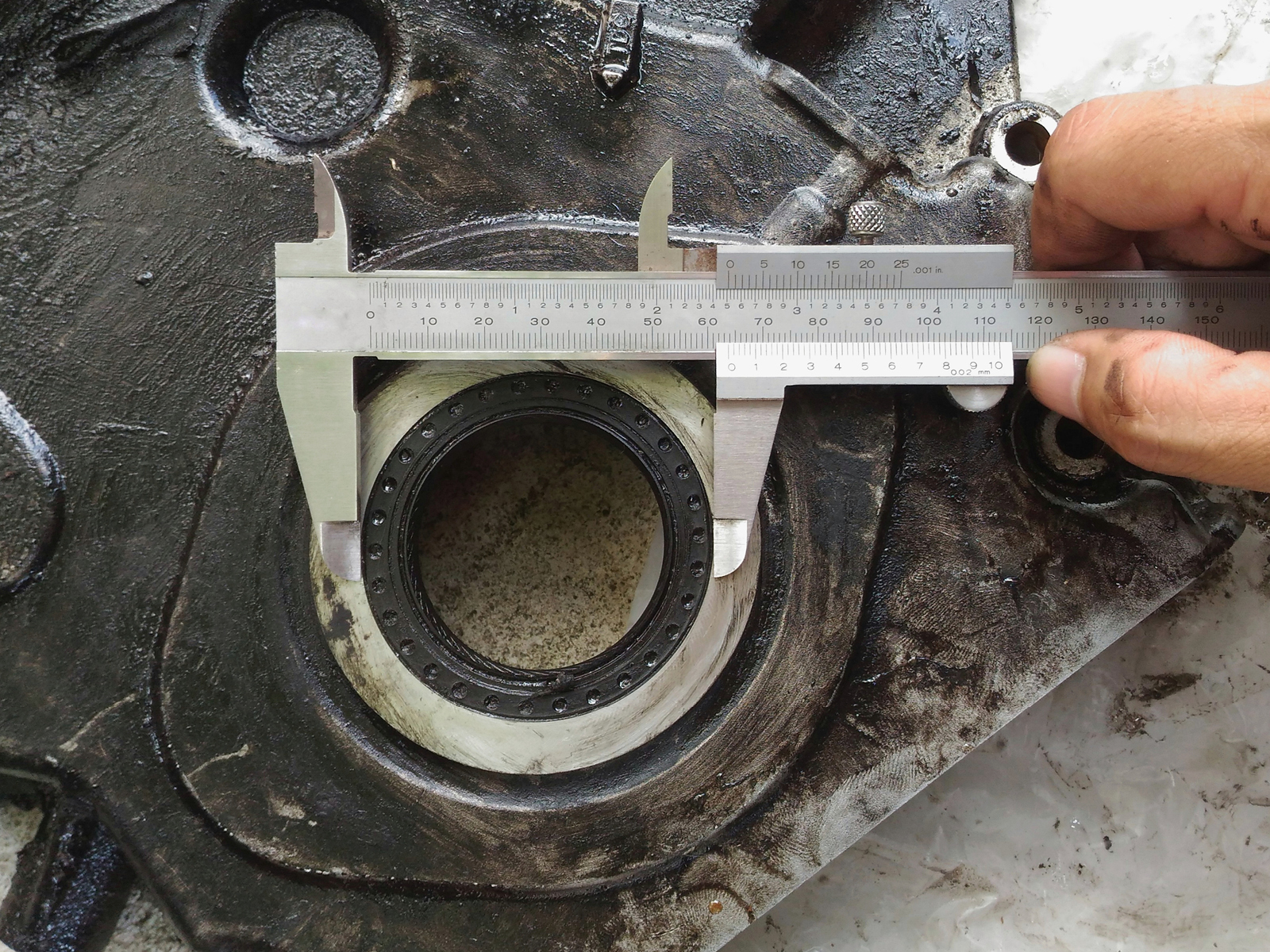

Precision Measurement of Rubber Seal Ring Dimensions Using Digital Calipers
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., dimensional accuracy in rubber seal manufacturing begins with precise measurement protocols. One of the foundational steps in quality assurance is the accurate determination of ring size using digital calipers. This process is critical for ensuring that every precision rubber seal meets exact OEM specifications, particularly in applications involving dynamic sealing, fluid control, and mechanical integrity under pressure and temperature extremes.
Our engineering team employs high-precision digital calipers calibrated to ISO 9001 standards to measure inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and cross-sectional (CS) dimensions of rubber rings. These measurements are conducted at multiple points around the circumference to account for any minor ovality or flash remnants from the molding process. All readings are recorded and cross-verified to ensure consistency within tolerance bands as tight as ±0.05 mm for critical applications.
The measurement procedure follows a standardized protocol. The rubber ring is placed gently between the caliper jaws without compression that could deform the elastomer. For soft compounds (Shore A hardness below 60), we apply controlled pressure using calibrated force gauges to avoid over-compression. Temperature stabilization of samples at 23°C ±2°C for 24 hours prior to measurement ensures dimensional stability, in accordance with ASTM D395 and ISO 37 standards.
Our in-house engineering capability supports this precision. With five dedicated mold engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we maintain full control over the entire product lifecycle—from compound development and mold design to final dimensional validation. This integrated approach allows us to anticipate and correct potential shrinkage variances during curing, adjusting formulations and tooling parameters proactively.
Our OEM manufacturing services are built on this foundation of metrological rigor. Clients benefit from custom formulation development tailored to media resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical performance, all validated through precise dimensional and physical testing. Whether producing standard O-rings or custom-profiled seals, our caliper-based measurement system serves as the first checkpoint in a multi-stage quality control process that includes hardness testing, tensile analysis, and volume swell evaluation.
The table below outlines typical dimensional tolerances achievable for common rubber seal types, based on ISO 3601 and AS568 standards, and validated using digital caliper measurement.
| Seal Type | Inner Diameter (mm) | Cross Section (mm) | Standard Tolerance (± mm) | Material Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-Ring (Standard) | 10 – 100 | 1.5 – 5.0 | 0.05 – 0.10 | Nitrile (NBR), 70 Shore A |
| Custom Rectangular | 20 – 150 | 2.0 – 6.0 | 0.08 – 0.15 | EPDM, 60 Shore A |
| High-Pressure O-Ring | 5 – 80 | 2.5 – 4.0 | 0.05 | FKM (Viton®), 75 Shore A |
This technical discipline ensures that every rubber seal produced under our OEM program meets the highest standards of dimensional fidelity and performance reliability.
Customization Process
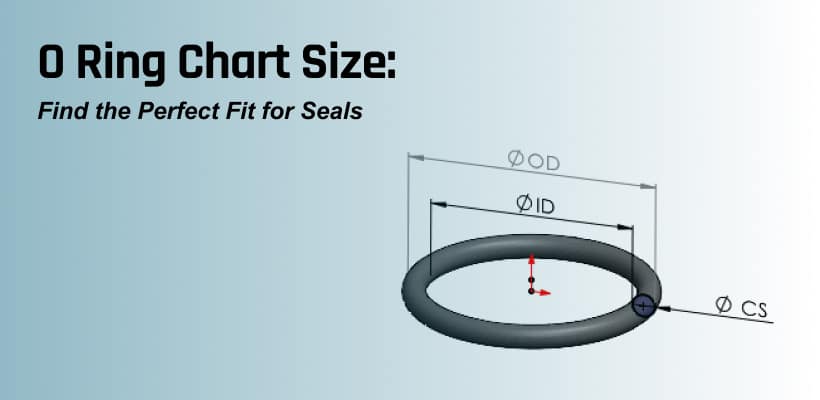
Precision Ring Dimension Measurement Protocol for Rubber Seal Customization
Accurate dimensional verification is the critical bridge between drawing analysis and rubber formulation development at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. During the customization process for precision rubber seals, measuring ring geometry with calibrated calipers establishes the foundation for material selection and process validation. This step occurs immediately after engineering drawing review and before compound formulation begins, ensuring theoretical specifications align with physical reality. Operators must utilize digital calipers traceable to ISO 17025 standards, zeroed at 23°C ±2°C to mitigate thermal expansion effects inherent in elastomeric materials.
Measurement requires strict adherence to ASTM D3767 Method A protocols. The internal diameter (ID) and cross-section (CS) must be recorded at three equidistant points around the ring circumference, with the average value used for analysis. Apply consistent, minimal pressure—0.5N maximum—to prevent elastomer deformation during measurement. Surface imperfections or flash exceeding 0.05mm must be noted, as these directly influence effective sealing diameter and compression behavior. For critical applications like hydraulic or aerospace seals, wall thickness uniformity must be verified within ±0.03mm tolerance to prevent asymmetric stress distribution during compression set testing.
The following dimensional parameters dictate subsequent formulation adjustments:
| Parameter | Symbol | Measurement Method | Critical Tolerance Range | Impact on Formulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Diameter | ID | Average of 3-point caliper | ±0.05 mm | Determines stretch ratio & compound modulus |
| Cross-Section | CS | Average of 3-point caliper | ±0.03 mm | Governs compression force & durometer selection |
| CS Roundness | ΔCS | Max-min CS deviation | ≤0.04 mm | Affects flash control in molding |
| ID Ovality | ΔID | Max-min ID deviation | ≤0.06 mm | Influences material flow in cavity |
| Surface Roughness | Ra | Optical comparator | ≤1.6 μm | Dictates mold polish requirements |
Inaccurate ring measurement propagates errors into prototyping, causing premature seal extrusion or insufficient sealing force. For instance, a 0.1mm oversize ID measurement may lead to underestimating required compound tensile strength, resulting in 15% higher extrusion failure rates during validation testing. Conversely, undersized CS readings trigger unnecessary hardness increases, elevating compression set by 8–12% in dynamic applications. All data is cross-referenced against the client’s GD&T drawing in our PLM system, with deviations triggering engineering change orders before compound mixing begins.
This metrology phase directly informs our rubber chemists during formulation. Measured dimensions determine the precise elongation-at-break requirements and filler loading percentages needed to achieve target compression stress relaxation. Only after dimensional validation is complete do we proceed to prototype molding, where the first-article inspection compares physical samples against these baseline caliper measurements. Consistent execution here prevents costly rework in mass production by ensuring the rubber compound’s viscoelastic properties are engineered for the actual geometry—not theoretical dimensions. This disciplined approach has reduced Suzhou Baoshida’s prototype iteration cycles by 30% across OEM automotive and industrial fluid power projects.
Contact Engineering Team

Precision Measurement of Rubber Seal Ring Size Using Digital Calipers
Accurate dimensional verification is critical in the production and application of precision rubber seals. A minor deviation in inner diameter, outer diameter, or cross-section can lead to seal failure, system leakage, or premature wear. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize metrological consistency and provide technical support to ensure that every rubber component meets OEM specifications. One of the most reliable methods for verifying ring dimensions is the use of high-precision digital calipers. This method is widely adopted in quality control laboratories and production floors due to its repeatability, speed, and accuracy.
To measure a rubber O-ring or sealing ring correctly, begin by ensuring the caliper is calibrated and zeroed. Use a digital caliper with a resolution of at least 0.01 mm and a measurement range suitable for your component size. Place the ring on a flat, clean surface and gently stretch it into a circular form without distorting the cross-section. For inner diameter (ID) measurement, position the caliper jaws across the center of the ring, ensuring alignment with the geometric axis. Do not compress the material; light contact is sufficient. Repeat the measurement at multiple orientations (e.g., 90° intervals) and average the results to account for any ovality.
For outer diameter (OD), open the caliper jaws and encircle the ring at multiple points, again ensuring consistent alignment. Cross-sectional thickness (CS) is determined by measuring the width of the rubber profile using the caliper’s outside jaws. Take at least three measurements around the circumference and calculate the mean value. All readings must be recorded under controlled environmental conditions (23°C ±2°C, 50% RH) as per ISO 3601 standards to minimize material expansion or contraction effects.
Below are the recommended caliper specifications for reliable rubber seal measurement:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Measurement Range | 0–150 mm (standard), up to 300 mm optional |
| Resolution | 0.01 mm |
| Accuracy | ±0.02 mm |
| Jaw Type | Flat, carbide-tipped |
| Units | mm/in selectable |
| Data Output | RS-232 or USB (for SPC integration) |
| Calibration Standard | Traceable to NIST or CNAS |
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we supply not only high-performance rubber seals but also the metrology guidance to ensure their correct implementation. Our engineering team supports clients in dimensional validation, material selection, and compliance with international sealing standards.
For technical assistance in measuring rubber sealing components or to request custom measurement protocols, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager, directly at [email protected]. We respond to all inquiries within 12 business hours and offer on-demand consultation for high-volume manufacturing partners. Trust Suzhou Baoshida for precision, consistency, and expert-backed rubber sealing solutions.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
