Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Neoprene Vs Viton
Engineering Insight: Neoprene vs Viton – The Critical Role of Material Selection in Industrial Applications
In the field of industrial sealing and rubber component design, selecting the appropriate elastomer is not merely a matter of cost or availability—it is a decisive engineering parameter that directly impacts system reliability, service life, and operational safety. Two of the most widely specified synthetic rubbers, neoprene and Viton, are often considered interchangeable in off-the-shelf applications. However, this assumption frequently leads to premature failure, especially in demanding environments where chemical exposure, temperature extremes, or long-term compression set resistance are critical.
Neoprene (polychloroprene) is valued for its good resistance to ozone, weathering, and moderate oils, making it a common choice for general-purpose industrial seals, gaskets, and weatherstripping. It offers a balanced performance profile with decent mechanical strength and flame resistance. However, its limitations become apparent in high-temperature environments or when exposed to non-polar hydrocarbons, fuels, or chlorinated solvents. Neoprene begins to degrade above 100°C and exhibits poor resistance to many industrial fluids, leading to swelling, hardening, or cracking over time.
In contrast, Viton (a fluoroelastomer, or FKM) is engineered for extreme conditions. With continuous service temperatures up to 230°C and exceptional resistance to a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals—including aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons, acids, and jet fuels—Viton is the preferred material in aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing industries. Its molecular structure provides superior thermal stability and low gas permeability, ensuring long-term sealing integrity under pressure and heat.
The failure of off-the-shelf rubber components often stems from the use of neoprene in applications that unknowingly demand Viton-level performance. Standardized parts, while economical, are typically designed for generic conditions and do not account for specific fluid compatibility, temperature cycling, or regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA, UL, or MIL-SPEC). When such components are deployed in high-stress environments without proper material validation, the result is accelerated aging, seal extrusion, leakage, or catastrophic system failure.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize application-specific material engineering. Our industrial rubber solutions are not selected from catalog defaults but are rigorously matched to operational parameters through fluid immersion testing, thermal profiling, and compression set analysis. This precision approach ensures that whether neoprene or Viton is specified, the choice is based on performance data—not assumptions.
Below is a comparative summary of key physical and chemical properties:
| Property | Neoprene (CR) | Viton (FKM) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +100 (short-term +120) | -20 to +230 (special grades to +250) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 250–400 | 150–300 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–80 | 60–90 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Moderate | Excellent |
| Resistance to Acids | Fair | Excellent |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set (after heat aging) | Moderate to Poor | Very Good |
Material selection is not a commodity decision—it is a core engineering function. Choosing between neoprene and Viton requires a detailed understanding of the operational envelope. At Baoshida, we partner with OEMs to move beyond off-the-shelf compromises and deliver rubber solutions engineered for real-world performance.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Critical Industrial Sealing Applications
Selecting the optimal elastomer requires precise evaluation of chemical exposure, thermal demands, and mechanical stress. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our technical team validates material performance against ASTM D2000 standards to ensure reliability in OEM manufacturing. Chloroprene (commonly referenced as neoprene), Viton® (FKM fluorocarbon rubber), and nitrile (NBR) exhibit distinct molecular structures dictating their operational boundaries. Chloroprene offers balanced resistance to ozone, weathering, and moderate oils but degrades under prolonged aromatic hydrocarbon exposure. Viton® excels in extreme chemical and thermal environments due to its high fluorine content, while nitrile provides cost-effective resilience against petroleum-based fluids within limited temperature ranges. Silicone (VMQ) remains indispensable for ultra-high/low-temperature applications despite lower tensile strength.
The comparative analysis below details critical specifications for informed material selection:
| Property | Chloroprene (CR) | Viton® (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +120 | -20 to +230 | -40 to +120 | -60 to +200 |
| Fuel Resistance (ASTM D471) | Poor | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Oil Resistance (ASTM D471) | Fair | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Poor | Good |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 7–15 | 10–20 | 5–10 |
| Compression Set (ASTM D395) | 20–30% | 15–25% | 25–40% | 20–35% |
| Key Industrial Uses | HVAC hoses, weatherstripping | Aerospace seals, chemical valves | Fuel lines, gaskets | Medical tubing, cryogenic seals |
Chloroprene’s moderate chemical resistance suits outdoor applications where UV and ozone stability are paramount, though its vulnerability to ketones and esters necessitates careful fluid compatibility testing. Viton®’s superiority in aggressive media—such as jet fuels, acids, and steam—makes it non-negotiable for aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing, despite higher raw material costs. Nitrile remains the workhorse for automotive fuel systems due to its abrasion resistance and rapid compression set recovery below 100°C, but fails in oxygenated biofuels or high-temperature transmissions. Silicone’s biocompatibility and extreme temperature tolerance support medical and food-grade applications, yet its low tear strength requires design compensation for dynamic seals.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. emphasizes that material selection must align with actual service conditions, not theoretical maximums. For instance, Viton®’s 230°C rating assumes static, non-abrasive environments; dynamic seals in reciprocating pumps may require derating by 30°C. Similarly, nitrile’s acrylonitrile content (typically 33–50%) directly impacts oil resistance—higher ACN grades sacrifice low-temperature flexibility. Our OEM partners achieve optimal lifecycle performance by cross-referencing fluid compatibility charts with real-world aging data. We provide certified material test reports (MTRs) for all compounds, ensuring traceability from raw polymer to finished component. Consult our engineering team to validate material suitability against your specific operational parameters before prototyping.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Excellence in Industrial Rubber Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our industrial rubber manufacturing expertise. With a dedicated team of five mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we combine material science with precision tooling to deliver high-performance elastomer components tailored to demanding OEM applications. Our focus spans the full product development lifecycle—from compound formulation and mold design to prototyping and mass production—ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-efficiency.
Our formula engineers possess deep expertise in polymer chemistry, enabling precise customization of neoprene (polychloroprene) and Viton (fluoroelastomer) compounds to meet exact environmental and mechanical requirements. Whether the application demands resistance to ozone, UV exposure, and moderate oils (neoprene), or extreme heat, aggressive chemicals, and hydrocarbons (Viton), our team formulates rubber compounds that deliver consistent, reliable performance. This scientific approach allows us to fine-tune hardness, tensile strength, compression set, and low-temperature flexibility—critical parameters in industrial sealing, gasketing, and vibration damping applications.
Complementing our formulation capabilities, our five mould engineers specialize in precision tool design and manufacturing for compression, transfer, and injection molding processes. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM software and coordinate closely with our formula team to ensure mold geometry, material flow, and curing characteristics are fully synchronized. This integrated engineering workflow minimizes defects, reduces cycle times, and ensures dimensional accuracy across production runs.
As an OEM partner, we offer full turnkey solutions, including design validation, material selection, tooling fabrication, and batch traceability. Our facility supports low-volume prototyping and high-volume manufacturing, with strict quality control per ISO standards. We work directly with clients to reverse-engineer legacy parts, optimize existing designs, and accelerate time-to-market through rapid sampling and testing.
The following table highlights key performance characteristics of neoprene and Viton to guide material selection:
| Property | Neoprene (CR) | Viton (FKM) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +120 | -20 to +230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 250–500 | 150–300 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40–90 | 50–90 |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Excellent |
| Resistance to Aliphatic Oils | Good | Excellent |
| Resistance to Aromatic Oils | Fair | Excellent |
| Resistance to Acids/Bases | Moderate to Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set (after heat aging) | Moderate | Low |
| Cost Level | Medium | High |
By integrating advanced rubber formulation with precision mold engineering, Suzhou Baoshida delivers technically superior, application-specific elastomer solutions. Our OEM partnerships are built on engineering rigor, material intelligence, and a commitment to solving complex industrial challenges.
Customization Process
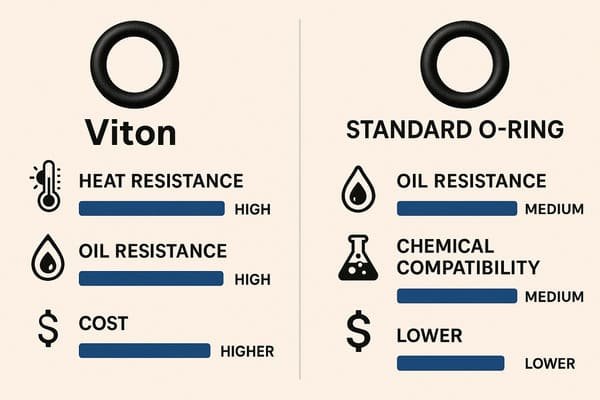
Customization Process: Precision Engineering for Neoprene and Viton Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our industrial rubber customization follows a rigorously defined sequence to ensure optimal performance for neoprene (polychloroprene) and Viton (fluoroelastomer) applications. This process begins with Drawing Analysis, where engineering teams dissect client specifications against material capabilities. Critical factors include dimensional tolerances per ISO 3302, environmental exposure (e.g., ozone, UV, fluids), and mechanical stress points. For neoprene, we prioritize resilience in moderate chemical environments like hydraulic systems; for Viton, we focus on extreme conditions such as aerospace fuel seals or semiconductor manufacturing. Misalignment here risks premature failure—thus, we validate seal geometry against material elongation limits (neoprene: 250–600%; Viton: 200–400%) early.
Formulation leverages Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary compound databases. Neoprene formulations emphasize sulfur-cure systems for tear strength (≥18 MPa) and flame resistance (ASTM D412), while Viton requires peroxide curing to achieve chemical inertness. Key adjustments include:
Neoprene: Adding antidegradants for ozone resistance in outdoor gaskets.
Viton: Incorporating low-temperature additives (e.g., GBL-S types) to extend operational range below -40°C.
We simulate cure kinetics via MD+Rheometer data to avoid scorch during molding, ensuring Viton compounds meet stringent AMS 7251 standards for aerospace.
Prototyping employs rapid compression molding with client-approved tooling. Each neoprene or Viton sample undergoes accelerated aging (ASTM D573) and fluid immersion tests (e.g., ASTM D471). For instance, Viton prototypes for oilfield seals endure 72-hour exposure to H₂S at 150°C, while neoprene variants for automotive weatherstripping undergo 1,000-cycle flex testing. Dimensional checks via CMM verify shrinkage compliance—neoprene typically exhibits 1.5–2.5% linear shrinkage versus Viton’s 2.0–3.0%. Revisions target compression set reduction; Viton must achieve ≤20% at 200°C (per ASTM D395) to prevent seal leakage.
Mass Production integrates real-time SPC monitoring. Neoprene extrusion lines maintain ±0.1mm tolerance for hose profiles, while Viton injection molding uses cavity pressure sensors to eliminate voids. All batches undergo 100% visual inspection and lot sampling for tensile strength (neoprene: 15–28 MPa; Viton: 7–15 MPa). Suzhou Baoshida’s ISO 13485-certified facility ensures traceability via blockchain-linked material certificates, guaranteeing Viton’s FKM type (e.g., FKM-GBL) matches OEM fluid compatibility matrices.
Critical material properties directly influence process success, as summarized below:
| Property | Neoprene | Viton | Critical Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C | -20°C to +230°C | Formulation |
| Fuel/Oil Resistance | Moderate (swell ≤30%) | Excellent (swell ≤5%) | Prototyping Validation |
| Compression Set (22h/100°C) | 25–40% | 15–25% | Mass Production QC |
| Base Compound Cost | $2.50–$3.50/kg | $25–$40/kg | Drawing Analysis |
This structured approach minimizes iteration cycles by 30% and ensures Suzhou Baoshida delivers mission-critical rubber components with zero field failures. Our engineers collaborate at every phase to align material science with your operational reality.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida – Your Trusted Partner in Industrial Rubber Solutions
When it comes to selecting the right elastomer for demanding industrial applications, the decision between neoprene and Viton® is more than a material choice—it’s a critical engineering consideration that impacts performance, longevity, and safety. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering high-performance rubber materials tailored to the exacting standards of global OEMs and industrial manufacturers. Our expertise in neoprene and fluorocarbon (Viton®) compounds ensures that your sealing, gasketing, and protective components perform reliably under extreme conditions.
Understanding the operational environment is key. Neoprene offers excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and moderate oils, making it ideal for outdoor applications, automotive hoses, and HVAC systems. In contrast, Viton® excels in high-temperature environments and aggressive chemical exposure, commonly used in aerospace, semiconductor processing, and oil & gas industries. The right selection depends on temperature range, chemical compatibility, compression set, and cost-efficiency—all factors our engineering team evaluates with precision.
We invite you to contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager at Suzhou Baoshida, to discuss your specific application requirements. Whether you are prototyping a new component or scaling up production, our technical team provides full material consultation, custom compounding, and precision manufacturing support. We work closely with clients to ensure material compatibility, regulatory compliance, and consistent quality across batches.
Our facility in Suzhou is equipped with advanced testing equipment and adheres to ISO 9001 standards, guaranteeing that every product meets international performance benchmarks. From durometer control to aging resistance, we validate every parameter to deliver rubber solutions you can trust.
Below is a comparative overview of key physical and chemical properties for standard grades of neoprene and Viton® to guide your preliminary assessment.
| Property | Neoprene (CR) | Viton® (FKM) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +120 | -20 to +230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 12–20 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 250–400 | 150–300 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–80 | 60–90 |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 150°C) | 20–35% | 15–25% |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good |
| Resistance to Aliphatic Oils | Good | Excellent |
| Resistance to Aromatic Oils | Fair | Excellent |
| Resistance to Acids | Moderate | Excellent (diluted) |
| Resistance to Ketones | Poor | Poor |
For applications requiring long-term reliability in dynamic environments, partnering with an experienced supplier is essential. Mr. Boyce and the Suzhou Baoshida team are ready to support your project with technical data sheets, sample provisioning, and OEM-specific formulation development.
Contact Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] to initiate a technical consultation. Let us help you make the right elastomer choice—engineered for performance, built for industry.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
