Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Non Latex Meaning

Engineering Insight: Defining Non-Latex in Industrial Rubber Applications
The term non-latex is frequently misinterpreted in industrial contexts, leading to critical material selection errors. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we clarify that non-latex specifically denotes synthetic elastomers engineered without natural rubber latex (NRL) components. This distinction is non-negotiable for performance-critical applications where NRL’s inherent limitations—protein-induced biocompatibility risks, poor ozone resistance, and temperature instability—compromise reliability. Off-the-shelf “non-latex” solutions often fail because they prioritize cost over precision engineering, using generic formulations that ignore application-specific stressors like chemical exposure, dynamic fatigue, or regulatory compliance.
Industrial failures commonly originate from overlooking polymer backbone architecture. For example, a standard nitrile rubber (NBR) seal marketed as “non-latex” may lack acrylonitrile content optimization for hydraulic fluid resistance, causing premature swelling in automotive systems. Similarly, silicone alternatives with inadequate platinum-cure systems degrade under steam sterilization in medical devices. These failures stem from suppliers treating non-latex as a binary checkbox rather than a tailored material science challenge. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM process mandates accelerated aging protocols and finite element analysis to validate performance under exact operational parameters, ensuring molecular crosslink density aligns with compression set requirements.
The table below contrasts critical properties of common non-latex synthetics versus NRL, highlighting why generic substitutions fail:
| Material | Key Properties | Industrial Failure Modes (Generic Substitutes) | Typical Validated Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (High ACN) | Tensile: 25-30 MPa; Temp: -30°C to +120°C | Swelling in phosphate ester fluids; ozone cracking | Fuel hoses; printing rollers |
| EPDM | Tensile: 15-25 MPa; Temp: -50°C to +150°C | Compression set >40% after 72h at 100°C; steam degradation | HVAC seals; semiconductor wafer carriers |
| Silicone (VMQ) | Tensile: 6-10 MPa; Temp: -60°C to +230°C | Tear strength <15 kN/m; extractables in USP Class VI tests | Biopharma tubing; aerospace gaskets |
| Natural Latex (NRL) | Tensile: 20-30 MPa; Temp: -20°C to +60°C | Protein leaching; rapid ozone degradation; thermal aging | NOT industrial-grade critical components |
Material selection must address the entire lifecycle: chemical resistance indices, dynamic fatigue thresholds, and regulatory traceability (e.g., FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 for food contact). A semiconductor OEM using off-the-shelf EPDM for wafer-handling seals experienced $220,000 in wafer loss due to unvalidated outgassing—a failure preventable through peroxide-cure optimization and ASTM D2000 classification rigor.
Suzhou Baoshida’s value lies in transcending commodity specifications. We co-engineer non-latex solutions by mapping application stressors to polymer chemistry, ensuring each formulation undergoes OEM-specific validation. This precision prevents the cascading costs of field failures: unplanned downtime, regulatory non-conformance, and brand erosion. For mission-critical rubber components, non-latex is not a label—it is a commitment to engineered resilience. Contact our formulation team to transform your material challenges into competitive advantage.
Material Specifications
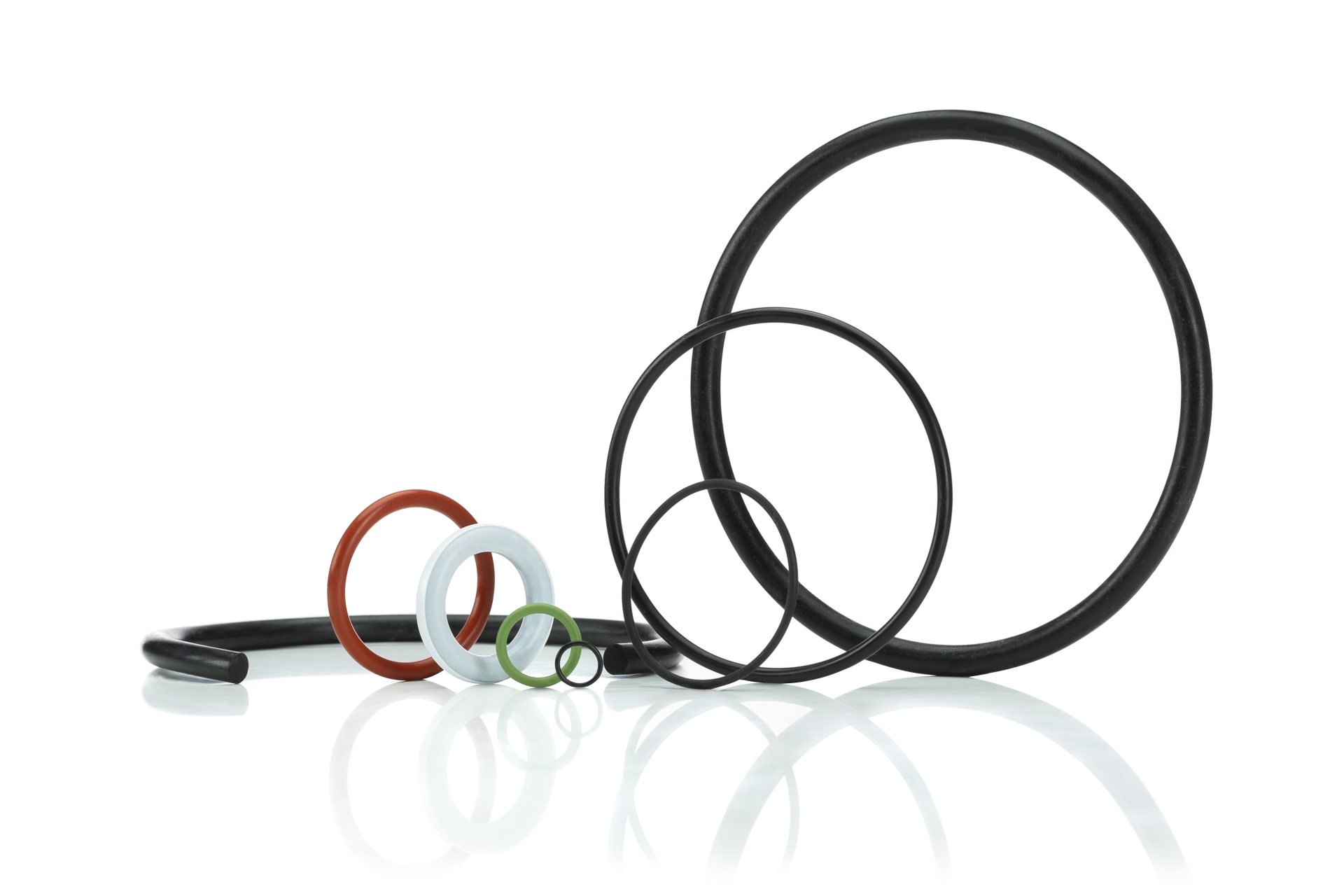
Understanding the term “non latex” in industrial rubber applications is critical for ensuring material compatibility, performance reliability, and safety in manufacturing environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we define non latex not merely as the absence of natural rubber latex, but as the strategic selection of synthetic elastomers engineered for superior resistance to heat, oils, chemicals, and environmental degradation. This specification is particularly vital in industries such as automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, where latex proteins can trigger allergic reactions or compromise product integrity.
Our core non latex materials—Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone—represent advanced synthetic alternatives tailored for demanding operational conditions. Each material exhibits a unique performance profile, enabling precise matching to application requirements. Viton, a fluorocarbon rubber (FKM), delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures (up to 250°C), aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons, and aggressive acids. Its molecular stability ensures long-term sealing performance in fuel systems and chemical processing equipment.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, offers excellent resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels, making it a preferred choice for hydraulic systems, oil seals, and gaskets in industrial machinery. With a continuous service temperature range of -30°C to 120°C, Nitrile balances cost efficiency with robust mechanical properties, including high abrasion resistance and tensile strength.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) stands apart for its extreme temperature resilience from -60°C to 200°C, coupled with outstanding UV and ozone resistance. While not suitable for dynamic applications involving high mechanical stress, silicone excels in static sealing, medical devices, and food-grade applications due to its inertness, transparency, and compliance with FDA and USP Class VI standards.
The following table summarizes the key physical and chemical properties of these non latex materials:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Resistance to Acids/Bases | Excellent | Fair | Good |
| FDA Compliance | Select Grades | Limited | Yes (Standard) |
Selecting the appropriate non latex material requires a comprehensive evaluation of operating environment, media exposure, mechanical stress, and regulatory standards. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we support OEMs and industrial partners with precision-formulated rubber compounds and technical documentation to ensure optimal material performance and compliance.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capabilities for Non-Latex Industrial Rubber Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers precision-engineered non-latex rubber components for demanding industrial applications. Non-latex formulations exclude natural rubber latex (NRL), eliminating allergenic proteins while providing superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and longevity. Our engineering team specializes in synthetic elastomer systems including NBR, EPDM, silicone, CR, and IIR, ensuring optimal material selection for mission-critical environments where NRL fails.
Our core strength lies in integrated material and mold engineering. Five dedicated mold engineers collaborate with two advanced formula engineers to solve complex challenges from concept to量产. This synergy enables rapid prototyping of intricate geometries—such as seals for semiconductor manufacturing or hydraulic gaskets for heavy machinery—while maintaining strict dimensional tolerances (±0.05mm). Formula engineers optimize compound formulations for specific operational parameters, including resistance to oils, acids, ozone, and extreme temperatures. This dual-expertise model prevents costly mismatches between material behavior and mold functionality, a common pitfall in outsourced rubber manufacturing.
OEM partnerships benefit from our end-to-end technical ownership. We manage the entire process: material sourcing from ISO-certified suppliers, finite element analysis (FEA) for stress prediction, mold flow simulation, and accelerated lifecycle testing. Clients receive full traceability documentation, including compound certificates and mold validation reports, ensuring compliance with ISO 9001 and industry-specific standards. Our engineers conduct on-site failure analysis to refine designs, reducing time-to-market by up to 30% compared to conventional suppliers.
Critical non-latex material properties are summarized below for industrial selection guidance.
| Material | Key Properties | Temperature Range | Chemical Resistance | Typical Industrial Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | High oil/fuel resistance, abrasion-resistant | -30°C to 120°C | Oils, fuels, aliphatic hydrocarbons | Automotive fuel systems, hydraulic seals |
| EPDM | Exceptional ozone/weathering resistance, electrical insulation | -50°C to 150°C | Water, steam, alkalis, oxygenated solvents | HVAC components, electrical enclosures |
| Silicone | Biocompatible, extreme temp stability, low compression set | -60°C to 230°C | Water, mild chemicals, UV radiation | Medical devices, aerospace seals, food processing |
| CR | Flame retardancy, good mechanical strength | -40°C to 100°C | Ozone, weathering, moderate chemicals | Conveyor belts, marine hardware, roofing membranes |
| IIR | Very low gas permeability, vibration damping | -40°C to 120°C | Acids, alkalis, polar solvents | Pharmaceutical stoppers, shock absorbers |
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering rigor transforms non-latex rubber from a compliance requirement into a performance advantage. By embedding formula science within mold design workflows, we eliminate iterative rework and deliver components that withstand 50,000+ operational cycles in aggressive media. Our OEM clients—from semiconductor equipment manufacturers to renewable energy system integrators—leverage this capability to enhance product reliability while meeting stringent global regulatory frameworks. Partner with us for engineered non-latex solutions where failure is not an option.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis: Precision Engineering as the Foundation
The customization process for industrial rubber components begins with comprehensive drawing analysis, a critical phase that establishes the technical blueprint for all subsequent development stages. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team conducts a meticulous review of client-provided CAD drawings, 2D technical schematics, and dimensional specifications. This assessment includes tolerance verification, geometric feature validation, and functional intent interpretation. We evaluate critical parameters such as sealing surfaces, load-bearing zones, and environmental exposure zones to ensure the final product meets exact operational requirements. Our engineers also perform Design for Manufacturability (DFM) checks to identify potential production challenges early, minimizing rework and accelerating time-to-market. This phase serves as the technical anchor, aligning material science with mechanical design.
Formulation: Tailoring Rubber Chemistry to Application Demands
Following drawing validation, the formulation phase translates mechanical requirements into precise rubber compound development. Understanding “non latex meaning” is essential here—our industrial solutions are inherently non-latex, utilizing synthetic elastomers to avoid allergenic proteins and ensure compatibility with sensitive environments such as medical devices, food processing, and electronics. We select base polymers—such as Nitrile (NBR), EPDM, Silicone (VMQ), or Fluorocarbon (FKM)—based on thermal stability, chemical resistance, compression set, and mechanical strength. Additives including reinforcing fillers, antioxidants, plasticizers, and curing agents are proportioned with laboratory-grade precision. Each formulation is documented under strict batch traceability protocols, ensuring repeatability and compliance with ISO 9001 and RoHS standards. The resulting compound is optimized not only for performance but also for process efficiency during molding.
Prototyping: Validating Design and Material Synergy
Prototyping transforms theoretical design and chemistry into physical performance. Using the approved drawing and formulated compound, we produce small-batch prototypes via injection molding, compression molding, or extrusion, depending on geometry and volume expectations. These samples undergo rigorous in-house testing, including tensile strength, hardness (Shore A), elongation at break, and environmental aging (e.g., heat, ozone, fluid immersion). Dimensional inspection is conducted using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify conformity within specified tolerances. Client feedback is integrated at this stage, allowing for iterative refinement of both form and function before committing to full-scale production.
Mass Production: Scalable Precision with Quality Assurance
Upon prototype approval, the project transitions to mass production. Our manufacturing lines operate under strict process control, with real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and cure time. Every batch is subject to statistical process control (SPC) and final inspection before shipment. This seamless progression from drawing to delivery ensures that each rubber component meets the highest standards of reliability and performance.
| Property | Test Method | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 40–90 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 8–20 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | 200–600% |
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Operating Temperature | — | -40°C to +250°C (varies by compound) |
Contact Engineering Team
Precision Non-Latex Rubber Solutions for Demanding Industrial Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. specializes in advanced non-latex rubber formulations engineered for critical industrial environments where natural rubber latex is unsuitable. Our technical expertise addresses the precise definition and implementation of non-latex materials—synthetic polymers such as Nitrile (NBR), Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), Silicone (VMQ), and Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR)—which eliminate latex protein allergens while delivering superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical performance. Unlike natural latex, these synthetics provide consistent repeatability in high-volume OEM manufacturing, essential for automotive seals, medical device components, semiconductor handling, and chemical processing equipment. We rigorously validate each compound against ASTM D2000 and ISO 37 standards to ensure dimensional integrity under extreme compression, ozone exposure, and fluid immersion.
Key performance differentiators of our non-latex formulations are quantified below for immediate technical evaluation:
| Property | Nitrile (NBR) | EPDM | Silicone (VMQ) | Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -30 to +120 | -50 to +150 | -60 to +230 | -40 to +180 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 7–20 | 5–12 | 20–30 |
| Oil/Fuel Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Moderate | Exceptional |
| Compression Set (%) | 15–25 | 10–20 | 20–40 | 10–15 |
| Key Industrial Use Case | Fuel hoses | Weather seals | Medical tubing | High-temp O-rings |
These specifications reflect baseline capabilities; our engineering team tailors formulations to exceed client-specific fluid compatibility, fatigue life, and regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA 21 CFR 177.2600, USP Class VI). Suzhou Baoshida operates ISO 9001-certified compounding facilities with in-house rheometry, DMA, and accelerated aging testing, enabling rapid iteration from prototype to full-scale production. We mitigate supply chain volatility through strategic raw material partnerships and dual-sourcing protocols for critical monomers.
For immediate technical consultation on non-latex rubber selection, compounding, or OEM manufacturing, contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated Technical Account Manager. Specify your application’s critical parameters—including fluid exposure, temperature extremes, dynamic stress conditions, and regulatory certifications—to receive a data-driven compound recommendation within 24 business hours. Mr. Boyce coordinates direct access to our formulation chemists and production schedulers, ensuring seamless transition from engineering inquiry to validated batch delivery. Avoid costly material misselection or production delays by leveraging our 15-year heritage in mission-critical elastomer solutions.
Initiate your non-latex rubber project today: [email protected]
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. — Where molecular precision meets industrial resilience.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
