Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: O Ring Size Specifications
Engineering Insight: O Ring Size Specifications and the Critical Role of Material Selection
Precision in o ring size specifications extends beyond dimensional accuracy—it fundamentally intersects with material science. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize that successful sealing performance in industrial applications is not achieved through generic dimensions alone, but through the strategic alignment of material properties with operational conditions. While off-the-shelf o rings may conform to standard size charts such as AS568 or ISO 3601, their failure in real-world environments often stems from inappropriate material selection rather than dimensional inaccuracy.
Common elastomers such as Nitrile (NBR), Fluorocarbon (FKM), Silicone (VMQ), and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) exhibit vastly different chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical behavior. For example, NBR offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels but degrades rapidly when exposed to ozone or polar solvents. In contrast, FKM provides superior resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals but at a higher cost and reduced low-temperature flexibility. Selecting the wrong compound—even within the correct size group—can lead to premature seal failure, system contamination, and unplanned downtime.
Off-the-shelf o rings are typically manufactured using standardized materials optimized for broad compatibility rather than specific application demands. This one-size-fits-all approach neglects variables such as fluid compatibility, compression set under prolonged load, dynamic friction, and exposure to UV or sterilization cycles. In hydraulic systems operating above 100°C, for instance, a standard NBR o ring may harden and crack, whereas an FKM variant of identical dimensions would maintain sealing integrity. Similarly, in pharmaceutical or food processing equipment, EPDM’s resistance to steam and water-based cleaning agents makes it preferable, despite its incompatibility with hydrocarbons.
Furthermore, dimensional tolerances must be evaluated in conjunction with material behavior. Swelling due to fluid absorption or shrinkage under thermal cycling can shift an o ring out of its functional specification, even if initially within tolerance. Therefore, material selection directly influences the effective size and performance envelope of the seal.
At Suzhou Baoshida, we support OEMs and system engineers with application-specific formulation guidance, ensuring that both size and material meet the exacting demands of modern industrial environments. Our technical team conducts fluid immersion testing, thermal aging analysis, and compression set evaluation to validate material suitability before production.
Below is a comparison of common o ring materials and their key performance characteristics:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Fluid Resistance | Compression Set | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | -30 to +100 | Oil, fuel, water | Good | Hydraulics, pneumatics |
| FKM | -20 to +200 | Acids, oils, steam | Excellent | Automotive, chemical processing |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | Water, steam, brake fluid | Very Good | HVAC, pharmaceutical |
| VMQ | -60 to +180 | Ozone, UV | Fair | Medical devices, aerospace |
Understanding the synergy between size specifications and material properties is essential for achieving long-term sealing reliability.
Material Specifications
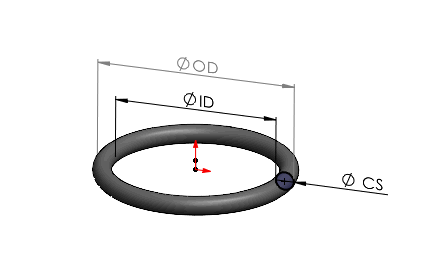
Material Specifications for Precision O-Ring Performance
Material selection directly governs O-ring dimensional stability, sealing integrity, and service life under operational stress. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we prioritize polymer chemistry alignment with fluid exposure, temperature extremes, and mechanical demands. Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) represent industry-standard elastomers for critical sealing applications, each exhibiting distinct molecular properties that influence size retention and functional reliability. Precise material specification ensures O-rings maintain cross-sectional compression within ISO 3601 or AS568 tolerances across dynamic cycles.
Viton fluorocarbon elastomers deliver exceptional resistance to high-temperature degradation and aggressive chemicals, including jet fuels, hydraulic fluids, and aromatic hydrocarbons. With a continuous service range of -20°C to +230°C (dry) and intermittent peaks to 300°C, Viton maintains compression set resistance below 25% after 70 hours at 200°C per ASTM D395. Its fluorine content provides inertness against oxygen and ozone, critical for aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing where seal failure risks catastrophic contamination. Viton O-rings require strict control of durometer (typically 70–90 Shore A) to balance extrusion resistance with low-temperature flexibility.
Nitrile butadiene rubber remains the cost-effective solution for petroleum-based hydraulic and lubrication systems. Operating effectively from -40°C to +120°C (short-term to 150°C), NBR offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength. Standard grades withstand aliphatic hydrocarbons, water, and glycols but degrade with exposure to ozone, ketones, or phosphate esters. Compression set values range from 15–30% after 70 hours at 100°C, necessitating careful groove design to compensate for moderate elastic recovery. High-acrylonitrile variants (48% ACN) enhance fuel resistance but reduce low-temperature performance, requiring dimensional recalibration per SAE AS568 standards.
Silicone elastomers excel in extreme-temperature environments where thermal stability is paramount. With a functional range spanning -60°C to +230°C, VMQ retains flexibility at cryogenic temperatures while resisting thermal oxidation. Its low compression set (<20% at 200°C) ensures long-term sealing force in static applications like medical devices and food processing equipment. However, silicone exhibits poor resistance to concentrated acids, steam, and petroleum derivatives, limiting use in hydraulic systems. Tear strength and tensile properties are inherently lower than Viton or NBR, demanding precise control of cross-section tolerances to prevent nipping during installation.
The following comparative analysis details critical physical properties per ASTM D2000 classification:
| Material | Base Polymer | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Temp Range (°C) | Key Chemical Resistances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | Vinylidene Fluoride-Hexafluoropropylene | 10–18 | 150–300 | -20 to +230 | Jet fuels, acids, aromatics, hydraulic fluids |
| Nitrile (NBR) | Acrylonitrile-Butadiene | 15–25 | 200–500 | -40 to +120 | Aliphatic hydrocarbons, water, glycols |
| Silicone (VMQ) | Polydimethylsiloxane | 5–10 | 200–700 | -60 to +230 | Ozone, UV, steam, food oils |
Material choice must correlate with dimensional tolerances specified in ISO 3601-1. Viton’s low gas permeability suits vacuum applications requiring minimal outgassing, while NBR’s cost efficiency supports high-volume automotive production. Silicone’s biocompatibility aligns with FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 for pharmaceutical seals. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. validates all formulations through rigorous compression set, volume swell, and accelerated aging testing to guarantee O-rings perform within micron-level size specifications throughout their operational lifecycle.
Manufacturing Capabilities
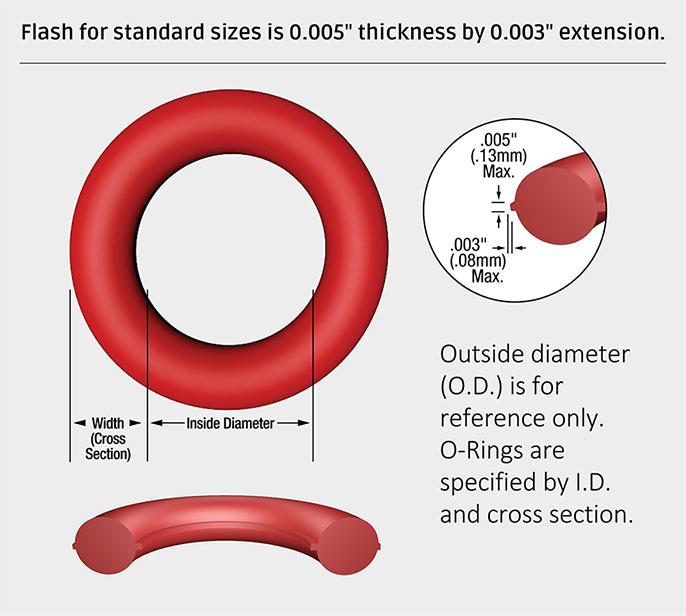
Engineering Capability: Precision in Every O Ring Specification
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability is anchored in deep technical expertise and a systematic approach to precision rubber seal manufacturing. With a dedicated team of five mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we deliver OEM-grade O rings that meet exacting international standards and application-specific demands. Our integrated engineering workflow ensures seamless transitions from design to material selection, prototyping, and mass production—each phase rigorously controlled to guarantee dimensional accuracy, material integrity, and long-term performance.
Our mould engineers utilize advanced CAD/CAM software and CNC machining technologies to develop high-precision tooling tailored to customer drawings or samples. Each O ring mould is engineered with attention to cavity alignment, venting, and runner design to minimize flash and ensure consistent part quality. This precision is critical in meeting tight tolerance requirements, especially for applications in automotive, medical, and industrial hydraulic systems where failure is not an option.
Complementing our tooling expertise, our two in-house rubber formula engineers specialize in elastomer compounding for optimal physical and chemical resistance. They formulate custom rubber compounds based on NBR, EPDM, FKM, silicone, and other specialty materials, adjusting hardness, compression set, and temperature resilience to match operational environments. This dual-engineering synergy—mould design and material science—enables us to solve complex sealing challenges and support clients in highly regulated industries.
We are fully equipped to manage OEM projects from concept to delivery. Our team collaborates directly with clients to interpret AS568, ISO 3601, or custom size specifications, ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Rapid prototyping, material validation, and first-article inspection reports (FAIR) are standard in our development cycle, reducing time-to-market and minimizing design risks.
The following table outlines our standard O ring size specifications and material capabilities:
| Parameter | Specification Range |
|---|---|
| Inside Diameter (ID) | 3.0 mm – 500.0 mm |
| Cross Section (CS) | 1.0 mm – 10.0 mm |
| Tolerance (AS568 Standard) | ±0.05 mm (CS), ±0.15 mm (ID) |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 40 – 90 |
| Standard Materials | NBR, EPDM, FKM, Silicone, CR, ACM, AEM |
| Custom Compounds | Available (fuel-resistant, FDA-compliant, etc.) |
| Production Capacity | 500,000 – 2,000,000 units/month |
Our engineering framework is built on continuous improvement and technical ownership. By maintaining full control over both formulation and tooling, Suzhou Baoshida ensures repeatability, traceability, and scalability across every production batch. This capability positions us as a trusted OEM partner for global manufacturers requiring precision, reliability, and responsive technical support in rubber seal solutions.
Customization Process
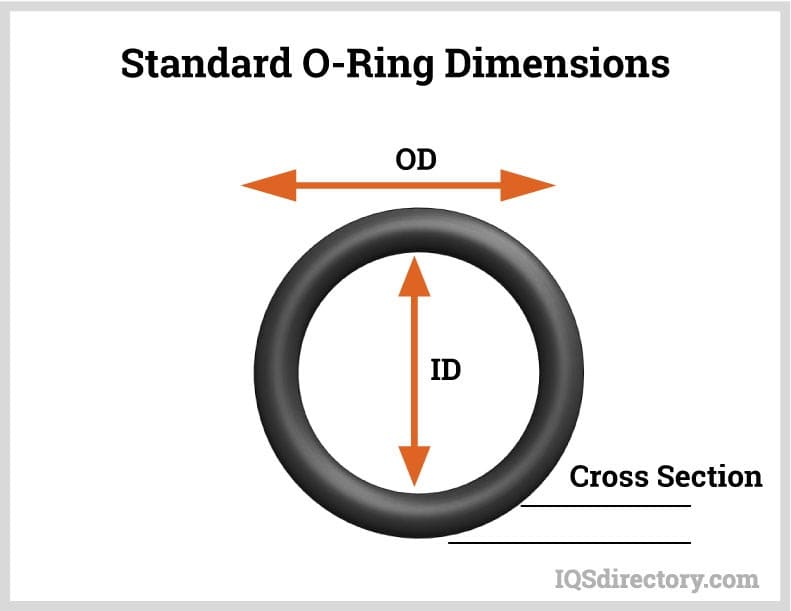
O-Ring Size Specification Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., precision in O-ring size specifications is non-negotiable for sealing integrity across automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Our OEM-driven customization process rigorously transforms client drawings into validated production-ready components. This begins with Drawing Analysis, where engineering teams dissect ASME Y14.5 or ISO 11211 technical schematics. Critical parameters scrutinized include inner diameter (ID), cross-section (CS), tolerance classes (e.g., ±0.05 mm for aerospace), and surface finish requirements (Ra ≤ 0.8 µm). We verify compatibility with international standards like AS568A or ISO 3601 and flag dimensional conflicts—such as undersized IDs causing excessive stretch or oversized CS leading to groove overfill. Client-supplied CAD models undergo GD&T validation to preempt assembly failures.
Formulation Development directly correlates material chemistry to dimensional stability. Rubber compounds are engineered to counteract compression set and fluid-induced swell within specified size limits. For instance, NBR formulations for fuel systems incorporate controlled acrylonitrile content to limit swell to ≤5% per ASTM D2000, preserving critical ID/CS ratios. EPDM blends for coolant applications use peroxide curing to minimize thermal expansion at 150°C. Each compound’s Shore A durometer (typically 60–90A) is calibrated to ensure elastic recovery within ±2% dimensional variance after 24-hour compression testing.
Prototyping validates both formulation and geometry. We produce 5–10 sample O-rings per ISO 3302-1 using precision molds with hardened steel cavities. Samples undergo:
Laser micrometry for ID/CS verification (accuracy ±0.01 mm)
ASTM D395 compression set testing at 70°C for 22 hours
Fluid immersion per SAE AS1241 to measure swell in target media
Microscopic flash inspection (max 0.05 mm protrusion)
Client feedback on prototype fit/function triggers iterative adjustments before tooling finalization.
Mass Production executes with zero deviation tolerance. CNC-machined molds feature thermal uniformity control (±1°C) to prevent cure-induced shrinkage variances. Every production batch undergoes 100% automated vision inspection against the approved drawing, with statistical process control (SPC) tracking CS variance in real time. Traceability documentation—including material batch codes, cure profiles, and dimensional certificates—is provided per PPAP Level 3 requirements. Final shipment includes ISO 1817 test reports confirming dimensional retention after 72-hour fluid exposure.
Critical O-Ring Size Specifications Reference
| Standard | ID Range (mm) | CS Tolerance (mm) | Material Durometer Range | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS568A | 1.78–279.40 | ±0.08 to ±0.13 | 50–90 Shore A | Aerospace hydraulic systems |
| ISO 3601-1 | 3.53–1,245.00 | ±0.05 to ±0.25 | 60–80 Shore A | Industrial pneumatic seals |
| JIS B 2401 | 2.50–500.00 | ±0.05 to ±0.20 | 50–90 Shore A | Automotive fuel systems |
This end-to-end workflow ensures Suzhou Baoshida delivers O-rings that meet exact size specifications under operational stress, eliminating leakage risks while adhering to global OEM quality protocols. All processes are certified to IATF 16949:2016 with full documentation traceability.
Contact Engineering Team
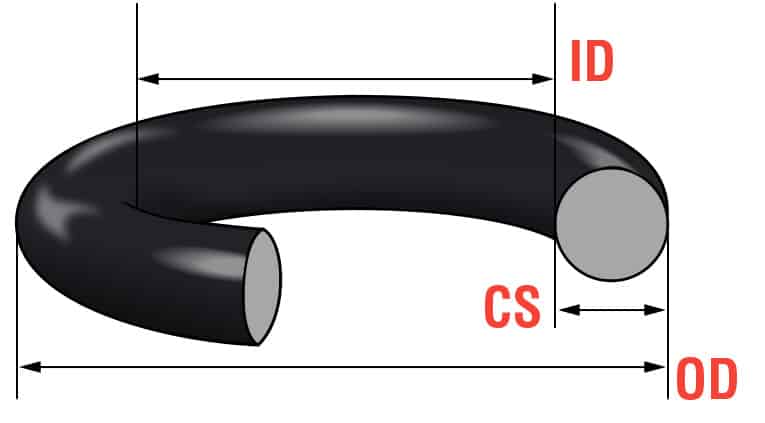
For precision rubber seals, accurate sizing is critical to ensuring reliable performance across industrial applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in the engineering and supply of high-performance O-rings tailored to meet exacting international standards. Our expertise in rubber formulation and dimensional control ensures that every O-ring we deliver provides optimal sealing efficiency, longevity, and resistance to environmental stressors such as temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure.
We understand that selecting the correct O-ring size is not merely a matter of convenience—it is a fundamental requirement for system integrity. Whether your application involves hydraulic systems, pneumatic equipment, automotive components, or high-vacuum environments, adherence to standardized dimensions is essential. Our team supports clients in identifying the appropriate O-ring size based on application parameters, including groove dimensions, compression requirements, and media compatibility.
To assist in selection, the following table outlines standard O-ring size specifications under the AS568 and ISO 3601 international standards, which are widely adopted across the global manufacturing sector. These standards define inside diameter (ID), cross-section (CS), and outside diameter (OD) with high precision to ensure interchangeability and sealing consistency.
| AS568 Dash Number | Inside Diameter (in) | Cross Section (in) | Outside Diameter (in) | ISO 3601 Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 102 | 0.125 | 0.070 | 0.265 | 1.004 |
| 214 | 1.500 | 0.103 | 1.706 | 2.022 |
| 326 | 3.000 | 0.139 | 3.278 | 3.038 |
| 438 | 5.000 | 0.210 | 5.420 | 4.074 |
These dimensions represent just a sample of the comprehensive range available through Suzhou Baoshida. We maintain inventory across multiple elastomer materials—including NBR, EPDM, FKM (Viton), Silicone, and FFKM—each formulated for specific operational environments. Our in-house testing protocols validate physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation, compression set, and fluid resistance to ensure compliance with OEM specifications.
For custom applications requiring non-standard sizes or proprietary compounds, our engineering team collaborates directly with clients to develop tailored sealing solutions. We support prototyping, material validation, and full-scale production with rigorous quality control in accordance with ISO 9001 standards.
To ensure your sealing systems perform with maximum reliability and safety, consult with an expert. For technical inquiries, custom formulation requests, or volume procurement, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Account Manager at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. He is available to provide detailed product specifications, material compatibility assessments, and prompt quotation support. Reach Mr. Boyce directly via email at [email protected]. Our team responds to all inquiries within 24 hours during business days. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for precision-engineered rubber seals that meet the highest standards of industrial performance.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
