Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: O-Ring Standards
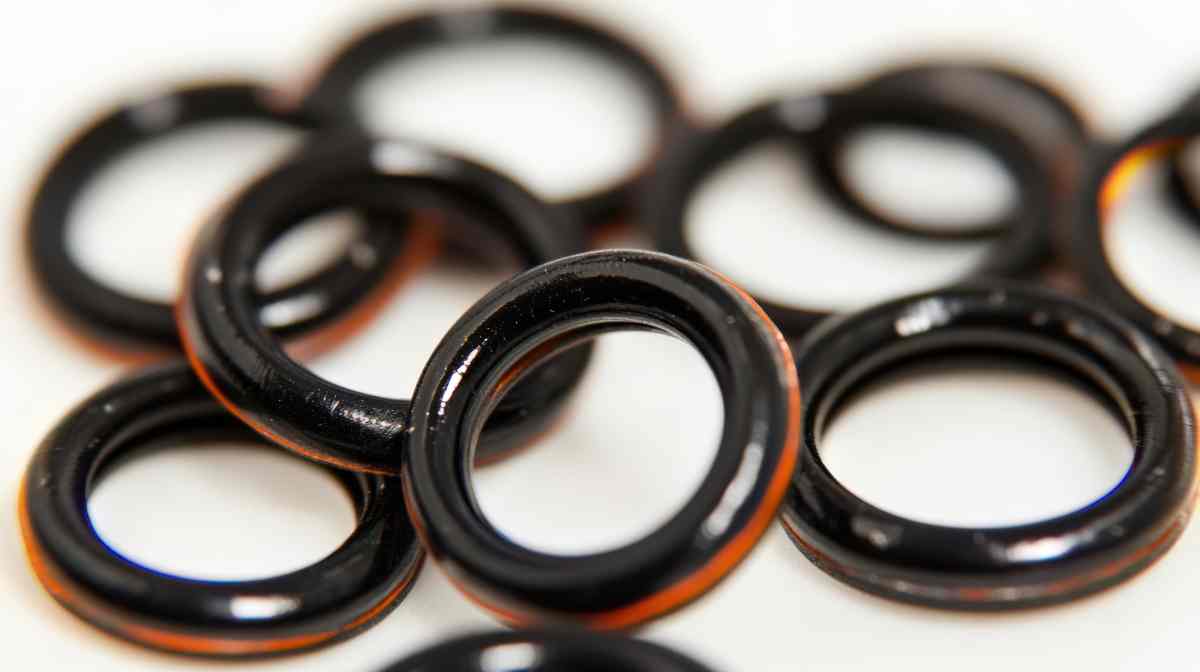

Engineering Insight Material Selection in O-Ring Standards
O-ring failure in critical applications rarely stems from dimensional inaccuracies alone but from fundamental mismatches between material properties and operational demands. Off-the-shelf solutions, often sourced against generic standards like ISO 3601 or AS568A, prioritize dimensional interchangeability while neglecting chemical, thermal, and mechanical compatibility. This oversight leads to premature seal degradation—manifested as extrusion, cracking, or loss of sealing force—resulting in costly downtime, contamination, or safety hazards. Material selection must transcend catalog numbers; it requires decoding the application’s full environmental profile against polymer chemistry limits.
Standard elastomers like NBR (Buna-N) or EPDM dominate commodity markets due to low cost and broad availability. However, their performance boundaries are narrow. NBR swells catastrophically in phosphate ester hydraulic fluids, while EPDM degrades rapidly in hydrocarbon fuels. Even within ASTM D2000 classifications, a “standard” NBR compound (RMA Grade 1) may specify only 70 Shore A hardness and 15 MPa tensile strength, ignoring critical factors like compression set resistance at elevated temperatures or resistance to dynamic stress cracking. Generic suppliers rarely validate performance beyond baseline cure characteristics, leaving engineers to assume risk for untested fluid exposures or thermal cycling.
The true cost of misselection emerges in harsh environments. Consider aerospace fuel systems: an off-the-shelf FKM O-ring rated for 200°C may fail within weeks due to inadequate resistance to aromatic additives in modern jet fuels, causing seal hardening and leakage. Similarly, semiconductor manufacturing demands ultra-pure perfluoroelastomers (FFKM) to withstand plasma etching chemistries; substituting standard FKM introduces particle generation and yield loss. Compression set—the permanent loss of elastic recovery—is the silent killer in high-temperature static seals. A standard FKM compound might exhibit 40% compression set after 70 hours at 200°C, while specialty grades maintain under 15%, directly impacting service life.
Material validation requires rigorous cross-referencing of fluid compatibility charts, thermal aging data, and dynamic testing protocols beyond ASTM D2000 minimums. The table below illustrates critical performance gaps between standard and engineered compounds under identical stress conditions.
| Property | Standard NBR (RMA 1) | Specialty HNBR | Specialty FFKM | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (200°C/70h) | 45% | 25% | 12% | ASTM D395 |
| Volume Swell in Skydrol 500B | 35% | 8% | 2% | ASTM D471 |
| Tensile Retention (200°C/168h) | 40% | 75% | 95% | ASTM D573 |
| Dynamic Heat Buildup (100k cycles) | Fail | 18°C rise | 8°C rise | ISO 1817 |
These metrics prove that material selection is a precision engineering exercise, not a procurement checkbox. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. mandates collaborative material qualification with OEMs, mapping fluid exposure, temperature transients, and mechanical loads to compound-specific databases. We reject dimensional compliance as the sole success metric; instead, we engineer seals where the polymer formulation is validated against the application’s total lifecycle stressors. Generic O-rings commoditize critical interfaces. Precision seals demand chemistry-aware engineering—where material selection defines reliability, not cost avoidance.
Material Specifications
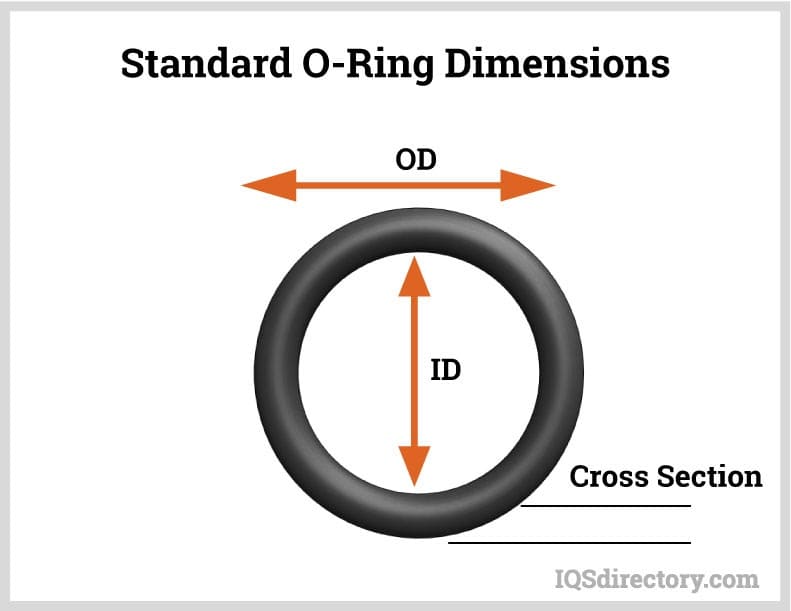
Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of precision rubber seals, particularly in demanding industrial environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-integrity O-rings engineered to meet exacting OEM and industrial standards. The most widely used elastomers in our product line—Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone—are selected based on their distinct chemical resistance, temperature stability, and mechanical properties. Understanding the material specifications of each enables optimal seal performance under specific operational conditions.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based elastomer (FKM), is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. It performs reliably in continuous service temperatures up to 200°C and short-term exposure up to 250°C. This makes Viton ideal for aerospace, automotive fuel systems, and chemical processing applications where exposure to hydrocarbons and elevated temperatures is common. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics further enhance its suitability for dynamic sealing environments.
Nitrile rubber, also known as Buna-N or NBR, is a cost-effective solution for applications involving petroleum-based oils and hydraulic fluids. It offers good abrasion resistance and tensile strength, with a typical operating temperature range of -40°C to +120°C. While not as chemically resistant as Viton, Nitrile provides excellent sealing performance in standard industrial machinery, automotive systems, and hydraulic equipment. Its versatility and resilience under mechanical stress make it one of the most widely used O-ring materials in general-purpose applications.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature environments, maintaining flexibility from -60°C to +200°C. It demonstrates high resistance to ozone and UV radiation, making it ideal for outdoor and medical applications. However, silicone has relatively low tensile strength and poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids, limiting its use in high-pressure hydraulic systems. It is frequently selected for food-grade, pharmaceutical, and electronic sealing applications due to its inert nature and compliance with stringent hygiene standards.
The following table provides a comparative overview of key physical and chemical properties for these materials:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +200 (up to 250 short-term) | -40 to +120 | -60 to +200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 6–10 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Fluid Compatibility | Hydrocarbons, acids, fuels | Aliphatic hydrocarbons, water, hydraulic fluids | Water, alcohols, silicone oils (not oils/fuels) |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, chemical processing, fuel systems | Automotive, hydraulics, industrial machinery | Medical devices, food processing, electronics |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer requires a comprehensive understanding of the operating environment, including media exposure, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we support OEMs with material certification, custom compounding, and full traceability to ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM D2000, ISO 3601, and FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 where applicable.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Seal Development at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise to deliver precision O-rings meeting the most stringent global standards. Our core strength resides in a dedicated engineering team comprising five specialized Mold Design Engineers and two advanced Rubber Formulation Engineers. This integrated structure ensures seamless transition from material science to precision manufacturing, critical for achieving consistent conformance to ASTM D2000, ISO 3601, SAE AS568, and custom OEM specifications. Our Formulation Engineers develop and validate proprietary rubber compounds across NBR, FKM, EPDM, Silicone, and specialty polymers, optimizing for specific fluid resistance, temperature extremes, compression set, and dynamic performance requirements defined by the application. Concurrently, our Mold Engineers utilize advanced CAD/CAM systems and scientific molding principles to design and validate cavity tooling that guarantees dimensional accuracy, minimal flash, and repeatability down to ±0.05mm tolerances, directly impacting seal reliability and service life.
This dual-engineering capability forms the foundation of our robust OEM partnership model. We excel in collaborative development, translating complex client drawings and performance criteria into manufacturable, high-yield solutions. Our process includes rigorous material selection based on fluid compatibility charts and accelerated aging tests, precise mold flow analysis to eliminate defects, and comprehensive First Article Inspection Reports (FAIR) per AS9102 standards. Crucially, we support full reverse engineering of legacy or competitor seals, enabling rapid qualification and seamless supply chain integration for our manufacturing partners. Suzhou Baoshida maintains an extensive library of 50+ validated material formulations and 200+ active mold sets, facilitating rapid prototyping and low-volume production for critical applications in automotive, aerospace, hydraulics, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Material performance is non-negotiable in critical sealing environments. Our engineers rigorously characterize key properties to ensure standards compliance and application success. The table below summarizes typical performance ranges for our most frequently specified compounds:
| Material Type | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Standard Temp Range (°C) | Key Fluid Resistance | Typical ASTM D2000 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrile (NBR) | 50 – 90 | -30 to +120 | Oils, Fuels, Hydraulic Fluids | BK 744 A14 B14 D10 F11 F21 |
| Fluorocarbon (FKM) | 60 – 90 | -20 to +230 | Aggressive Chemicals, High-Temp Oils | GF 735 A35 B35 E04 F15 F25 |
| EPDM | 50 – 80 | -50 to +150 | Water, Steam, Brake Fluid, Polar Solvents | EG 643 A10 B14 E04 F11 F21 |
| Silicone (VMQ) | 40 – 80 | -60 to +200 | Ozone, Weathering, Moderate Chemicals | AE 643 A10 B14 E04 F11 F21 |
Suzhou Baoshida’s commitment to engineering precision ensures every O-ring is not merely dimensionally correct, but functionally optimized for its operational environment. Our integrated team approach eliminates silos between material science and manufacturing, providing OEMs with a single-point technical resource for solving complex sealing challenges and achieving zero-defect production. This capability translates directly into reduced risk, extended component life, and minimized total cost of ownership for our industrial partners.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis: The Foundation of Precision Sealing Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., every custom O-ring development begins with a meticulous drawing analysis. This critical first step ensures dimensional accuracy, material compatibility, and functional performance under real-world operating conditions. Our engineering team evaluates client-submitted technical drawings or assists in generating precise CAD-based schematics when only conceptual input is available. We verify critical dimensions including inner diameter (ID), cross-section (CS), tolerance grades per ISO 3601, AS568, or JIS B 2401, and any special features such as beveled edges or multi-lobed profiles. Surface finish requirements, groove design, and mating component clearances are also assessed to prevent extrusion, compression set, or premature failure. This phase includes a Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review to identify potential production challenges early, reducing lead time and minimizing rework.
Rubber Formulation: Tailoring Material Performance
Once dimensional parameters are confirmed, our rubber formula engineers develop a compound specifically engineered for the application’s environmental demands. We analyze exposure to temperature extremes, fluid media (e.g., hydraulic oil, fuel, acids, steam), pressure cycles, and dynamic movement to select the optimal base polymer. Common elastomers include Nitrile (NBR), Fluorocarbon (FKM), Ethylene Propylene (EPDM), Silicone (VMQ), and specialty materials like Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) or Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR). Additives are precisely balanced to enhance abrasion resistance, compression set recovery, low-temperature flexibility, or flame retardancy. All formulations are documented and batch-traceable, meeting ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 standards. Material data sheets (MDS) and compatibility charts are provided for client validation prior to prototyping.
Prototyping: Validating Design and Material
Prototypes are produced using the same molding techniques intended for mass production—typically compression, transfer, or injection molding—to ensure process fidelity. Sample quantities range from 5 to 100 pieces, depending on testing requirements. Each prototype undergoes dimensional inspection via optical comparators and coordinate measuring machines (CMM), followed by functional testing such as leak rate evaluation, compression stress relaxation (CSR), and exposure to simulated service environments. Feedback from this stage informs final adjustments to tooling, compound, or tolerances.
Mass Production: Consistency at Scale
With client approval, we transition to full-scale manufacturing. Our production lines operate under strict process control, with in-line monitoring of cure time, temperature, and pressure. Every batch is subjected to first-article inspection and periodic quality audits. Final products are packaged per customer specifications, with full traceability from raw material lot to finished goods.
The following table outlines key specifications managed during the customization process:
| Parameter | Standard Reference | Typical Tolerance Range | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Diameter (ID) | ISO 3601, AS568 | ±0.05 mm to ±0.3 mm | Optical Comparator |
| Cross-Section (CS) | ISO 3601 | ±0.03 mm to ±0.1 mm | Micrometer, CMM |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | ±5 points | Durometer |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 8–25 MPa (varies by compound) | Universal Testing Machine |
| Compression Set | ASTM D395 | <20% (70 hrs @ 100°C typical) | Heat Aging Oven + Gauge |
| Fluid Resistance | ASTM D471 | Volume swell <15% | Immersion Test + Weighing |
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision O-Ring Solutions
Selecting the correct O-ring specification is a critical engineering decision impacting system integrity, longevity, and operational safety. Generic solutions often fail under demanding industrial conditions, leading to costly downtime and safety hazards. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision-engineered rubber seals where material science meets exacting application requirements. Our technical team does not merely supply components; we collaborate to solve sealing challenges through rigorous material formulation, dimensional tolerancing, and validation testing aligned with international standards.
Understanding the specific parameters of your application—fluid media, temperature extremes, pressure cycles, and dynamic/static conditions—is non-negotiable for optimal seal performance. We require detailed technical input to recommend or develop the precise elastomer compound and dimensional profile meeting ASTM D374, ISO 3601, AS568, or custom OEM specifications. Below is a representative overview of standard material capabilities for immediate reference:
| Material Grade | Durometer Range (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Fluid Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile) | 50–90 | -30 to +120 | Oils, fuels, water |
| FKM (Viton®) | 60–80 | -20 to +230 | Aggressive chemicals, high-temp oils |
| EPDM | 50–80 | -50 to +150 | Steam, water, brake fluids |
| Silicone | 40–80 | -60 to +200 | Ozone, weathering, biocompatible fluids |
Initiate a technical dialogue by contacting Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Engineering Liaison. Mr. Boyce possesses 14 years of hands-on experience in rubber compounding and sealing system validation across automotive, aerospace, and semiconductor manufacturing sectors. He will guide you through our collaborative engineering process, beginning with a detailed application review and culminating in certified production batches meeting your exact material and dimensional blueprints. Provide your fluid compatibility charts, pressure-temperature profiles, and failure mode analysis for accelerated solution development.
Do not submit generic inquiries requesting catalogs or price lists without technical context. Our engineering team prioritizes actionable data: specify your required ASTM D2000 line callout, ISO 3601 groove dimensions, or custom drawing references. Include critical performance thresholds such as maximum extrusion gap, dynamic stroke rate, or chemical exposure duration. This technical rigor ensures we eliminate guesswork and deliver seals performing reliably within your system’s operational envelope.
Email Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] with the subject line: “OEM O-Ring Technical Inquiry – [Your Company Name]”. Attach all relevant specifications, application schematics, and historical failure data. Our standard engineering response time is 24 business hours for complete technical submissions. For urgent validation support requiring material certification or rapid prototyping, clearly state “Priority: [Project Code] Validation” in the email body.
Suzhou Baoshida operates under IATF 16949 and ISO 9001 certified processes, with in-house rubber compounding, precision molding, and metrology labs. We transform complex sealing requirements into failure-resistant components through scientific material selection and process control. Partner with us where precision engineering supersedes transactional supply. Your next-generation sealing solution begins with a technically grounded inquiry to Mr. Boyce.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
