Technical Contents
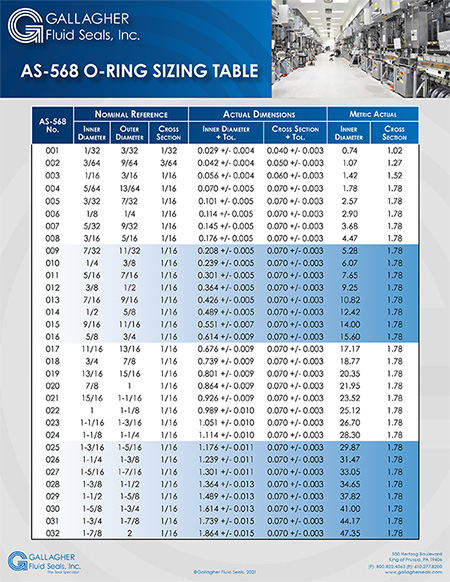
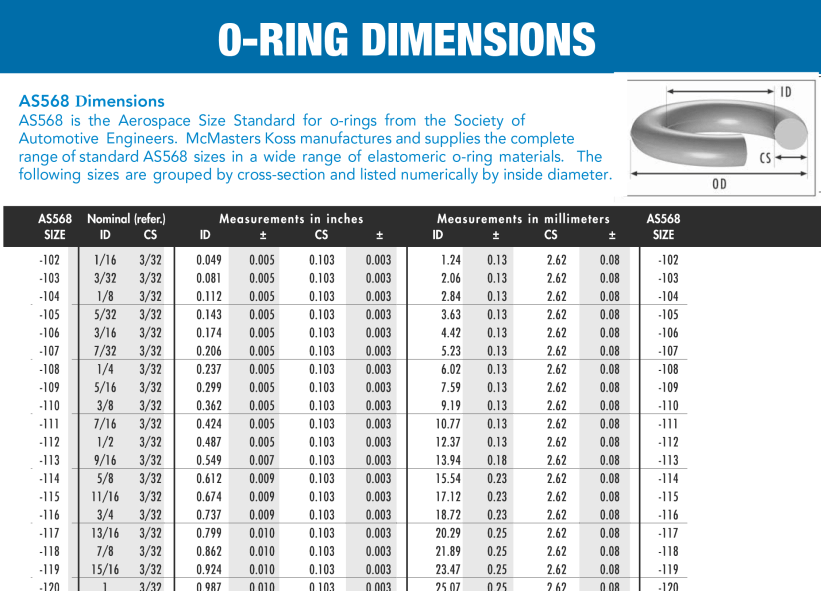
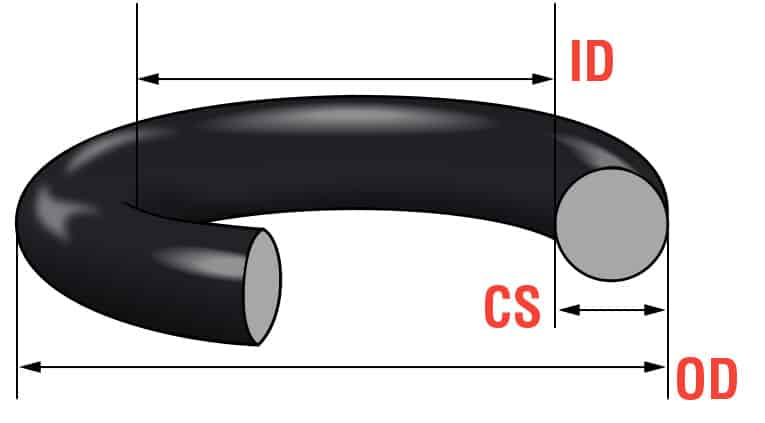
Engineering Guide: O-Rings Metric Size Chart
Engineering Insight: Material Selection Beyond Metric O-Ring Dimensions
Precision in O-ring application extends far beyond selecting the correct metric cross-section and internal diameter from a standard size chart. While dimensional accuracy is foundational, the catastrophic failure of off-the-shelf seals in demanding industrial environments overwhelmingly stems from inappropriate elastomer material selection. Generic O-rings, chosen solely based on size compatibility and lowest cost, lack the tailored polymer chemistry required to withstand the specific thermomechanical and chemical stresses encountered in real-world OEM systems. This mismatch leads to premature seal degradation, unplanned downtime, and significant warranty liabilities – costs that dwarf the initial savings of a standard part.
The inherent limitation of off-the-shelf solutions lies in their one-size-fits-all material formulation. Standard NBR or FKM compounds offered in catalogues possess baseline properties suitable only for benign conditions. When exposed to aggressive media like biofuels, phosphate ester hydraulic fluids, or high-concentration ozone, the polymer backbone undergoes rapid chemical attack. Similarly, standard compounds often fail under sustained high temperature due to inadequate thermal stability, leading to excessive compression set. A seal exhibiting 30% compression set at 150°C after 70 hours (typical of generic FKM) will lose sealing force long before a custom-formulated FKM variant achieving under 15% set under identical conditions. This thermomechanical degradation is the primary cause of leakage in systems operating near the nominal limits of standard materials.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses this critical gap through engineered elastomer solutions. Our role transcends mere distribution; we leverage deep rubber compounding expertise to modify base polymers at the molecular level. By adjusting filler systems, optimizing cure chemistry, and incorporating specialized additives, we develop bespoke compounds that precisely match the operational envelope defined by the OEM’s fluid, temperature, pressure, and dynamic requirements. This targeted formulation approach ensures polymer integrity under stress, directly translating to extended service life and system reliability unattainable with commoditized seals.
The following table highlights critical material properties where standard off-the-shelf compounds often fall short compared to engineered solutions for common industrial challenges:
| Elastomer Type | Standard Off-the-Shelf Limitation | Engineered Solution Target (Suzhou Baoshida) | Critical Failure Mode Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | Poor resistance to modern biofuels & ozone; Compression set >40% @ 100°C/70h | Enhanced saturation resistance; Compression set <25% @ 100°C/70h (ASTM D2000) | Swelling, extrusion, loss of sealing force |
| FKM | Limited low-temperature flexibility (< -20°C); High compression set in sour gas | Extended low-temp grade (-35°C); Compression set <18% @ 150°C/70h in H₂S | Seal fracture, leakage at cold start, H₂S degradation |
| EPDM | Inadequate resistance to petroleum oils; Compression set >35% @ 125°C/70h | Formulated for specific glycol ethers; Compression set <22% @ 125°C/70h | Swelling in brake fluids, loss of sealing in hot water systems |
| VMQ | Poor tear strength in dynamic apps; Compression set >25% @ 200°C/22h | Reinforced for reciprocating motion; Compression set <15% @ 200°C/22h | Nibbling, chunking in high-cycle applications |
Material selection is not a secondary consideration but the cornerstone of O-ring functionality. Relying on standard metric size charts without concurrent, application-specific elastomer engineering invites failure. Suzhou Baoshida partners with OEMs to transform seal specification from a dimensional exercise into a robust materials science solution, ensuring dimensional precision is matched by molecular resilience under actual operating conditions. This integrated approach is non-negotiable for mission-critical sealing performance.
Material Specifications
Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of metric O-rings under diverse industrial conditions. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision rubber seals engineered to meet exacting international standards. Our core materials—Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone—are selected for their distinct chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and mechanical properties. Understanding these characteristics ensures optimal sealing performance across automotive, aerospace, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based elastomer (FKM), offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals. It maintains seal integrity in continuous operating environments up to 200°C, with short-term exposure tolerance reaching 250°C. This makes Viton ideal for aggressive media such as mineral oils, hydraulic fluids, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics further enhance reliability in demanding systems. However, Viton exhibits lower flexibility at sub-zero temperatures and is generally more expensive than standard elastomers.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is one of the most widely used materials in dynamic and static sealing due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. With a standard operating range from -30°C to 120°C, Nitrile provides a balanced performance profile for general-purpose applications. It demonstrates good abrasion resistance and compressive strength, making it suitable for hydraulic systems, fuel delivery components, and pneumatic equipment. While cost-effective and widely available, Nitrile is not recommended for exposure to ozone, UV radiation, or polar solvents such as ketones and esters.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature applications, functioning reliably from -60°C to 200°C. It offers outstanding resistance to ozone, UV light, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor and high-purity environments such as medical devices and food processing equipment. Silicone is inherently biocompatible and meets numerous FDA and USP Class VI requirements. However, it has relatively low tensile and tear strength compared to Viton and Nitrile, limiting its use in high-pressure or dynamic mechanical applications. Additionally, silicone is not recommended for use with petroleum-based fluids.
The following table summarizes the key physical and chemical properties of these materials to assist in material selection for metric O-rings.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 200 (up to 250 short-term) | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–20 | 5–8 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Fluid Compatibility | Mineral oils, fuels, acids, solvents | Petroleum oils, water, alcohols | Water, alcohols, silicone fluids |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, chemical processing, automotive fuel systems | Hydraulics, pumps, seals, gaskets | Medical devices, food processing, electrical insulation |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer ensures seal reliability, reduces maintenance cycles, and enhances system safety. At Suzhou Baoshida, we support OEMs with material testing, custom formulations, and full traceability to meet ISO 3601 and AS568 standards.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Capability: Precision Integration for Metric O-Ring Excellence
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our Engineering Capability pillar integrates advanced mould design, proprietary rubber formulation, and rigorous OEM process control to deliver metric o-rings meeting the strictest global industrial standards. This synergy between our dedicated technical teams ensures dimensional accuracy, material resilience, and application-specific performance for critical sealing applications.
Our team of five specialized Mould Engineers employs 3D CAD/CAM simulation and cavity pressure mapping to optimize tool geometry for metric o-ring production. Each mould undergoes finite element analysis (FEA) to predict flow behavior, minimize flash, and maintain tolerances within ISO 3601-3:2010 Class M2 limits. This precision engineering reduces part-to-part variation to ≤±0.05 mm on critical dimensions, even for complex multi-cavity tools producing sizes from 1.5 mm to 500 mm inner diameter. Real-time process validation during tool trials ensures consistent replication of groove-filling dynamics under varying cure temperatures.
Complementing this, our two Rubber Formula Engineers develop and validate custom elastomer compounds for demanding environments. Leveraging polymer chemistry expertise, we optimize crosslink density, filler dispersion, and additive packages to achieve target properties such as compression set resistance (<20% at 70°C per ASTM D395), fluid compatibility, and low-temperature flexibility (down to -55°C for FKM). Every formulation undergoes accelerated aging testing against ASTM D2000 standards, with Shore A hardness stability maintained within ±3 points across 1,000-hour exposures. This material science rigor directly translates to extended service life in hydraulic, pneumatic, and chemical processing systems.
Our OEM capability transforms engineering precision into seamless client integration. We manage end-to-end production from raw material sourcing (certified to ISO 9001) through automated vision inspection of finished o-rings. Clients receive full traceability via lot-specific certificates of conformance, including hardness, tensile strength, and dimensional reports. For custom applications, we co-engineer solutions—such as modifying NBR for ozone resistance or tailoring FVMQ for aerospace fuel exposure—while maintaining compliance with ISO 3601 metric size specifications.
The following table details critical metric o-ring parameters we consistently achieve, reflecting our engineering control:
| Inner Diameter (mm) | Cross-Section (mm) | Tolerance (ISO 3601-3:2010 Class M2) | Critical Engineering Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0 | 1.5 | ±0.05 mm | Optimized for low-friction pneumatic systems; NBR compound with 70±5 Shore A hardness |
| 25.4 | 2.65 | ±0.08 mm | FKM formulation for -20°C to +200°C range; passes ASTM D2000 R2AA707 B14 |
| 50.0 | 3.53 | ±0.09 mm | EPDM variant with 15% compression set at 100°C; NSF 51 certified |
| 100.0 | 5.30 | ±0.12 mm | Custom HNBR for oilfield exposure; tensile strength ≥20 MPa per ISO 37 |
This engineering framework—combining mould precision, material science, and OEM agility—positions Suzhou Baoshida as a strategic partner for industries where seal failure is not an option. We deliver not just o-rings, but validated engineering solutions calibrated to your operational demands.
Customization Process
Drawing Analysis
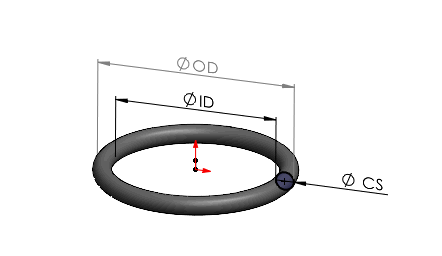
The customization process for metric O-rings begins with rigorous drawing analysis, a critical step to ensure dimensional accuracy and functional compatibility. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team evaluates customer-provided technical drawings or CAD models to verify compliance with ISO 3601, AS568, or custom specifications. Key parameters assessed include inner diameter (ID), cross-section (CS), tolerance class, and surface finish requirements. We also confirm groove design compatibility and identify potential sealing challenges related to pressure, temperature, or media exposure. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities are communicated directly to the client for approval prior to progression.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, the rubber compound is precisely engineered to meet the operational demands of the application. Our formulation process leverages advanced polymer science to select base elastomers such as NBR, EPDM, FKM, or silicone, depending on chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical performance requirements. Additives including reinforcing fillers, antioxidants, and processing aids are calibrated to achieve target hardness (Shore A), compression set resistance, and tensile strength. Each formulation is documented under strict quality control protocols, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency and traceability. Regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, ROHS, REACH) is integrated as needed for industry-specific applications.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the compound is finalized, prototype O-rings are manufactured using precision molding techniques. These samples are produced in controlled environments to mirror mass production conditions, ensuring accurate evaluation of form, fit, and function. Prototypes undergo a series of validation tests, including dimensional inspection via optical comparators, hardness measurement, and simulated application testing under dynamic or static load conditions. Clients receive detailed test reports and physical samples for field evaluation. Feedback is incorporated into final design or material adjustments, ensuring optimal performance prior to scale-up.
Mass Production
After client approval of prototypes, the project transitions to mass production. Our automated molding lines, supported by statistical process control (SPC), ensure high repeatability and adherence to tight tolerances. Each production batch is subjected to in-process and final quality inspections, including visual checks, dimensional sampling, and material property verification. All metric O-rings are packaged per customer specifications, with full documentation including certificates of conformance and material test reports.
The following table outlines standard metric O-ring specifications commonly processed through this workflow:
| Inner Diameter (mm) | Cross Section (mm) | Tolerance (ISO 3601 Class M) | Common Material | Application Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0 | 1.5 | ±0.09 | NBR | Hydraulic Systems |
| 25.0 | 2.0 | ±0.10 | FKM | High-Temperature Seals |
| 50.0 | 3.0 | ±0.12 | EPDM | Water and Steam Systems |
| 100.0 | 2.5 | ±0.11 | Silicone | Food & Pharmaceutical |
This structured approach ensures every custom metric O-ring meets the highest standards of precision, reliability, and performance.
Contact Engineering Team
Technical Consultation for Precision Metric O-Ring Sourcing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial sealing solutions, delivering metric O-rings engineered for critical applications across aerospace, automotive, and semiconductor manufacturing. Our ISO 9001-certified production facilities utilize proprietary rubber formulations—silicone, FKM, EPDM, and HNBR—optimized for extreme temperature resilience, chemical resistance, and minimal compression set. When standard metric size charts fail to address your sealing challenges, our engineering team collaborates directly with OEMs to refine material selection, dimensional tolerances, and performance validation. We do not merely supply components; we solve sealing integrity failures at their molecular origin.
The following table outlines our core metric O-ring specifications per ISO 3601-1:2012, demonstrating our adherence to global precision standards. All dimensions reflect achievable tolerances under controlled vulcanization processes, with cross-section (CS) deviations maintained at ±0.04 mm for critical sealing zones.
| Inner Diameter (mm) | Cross-Section (mm) | Tolerance (ID ± mm) | Tolerance (CS ± mm) | Common Material Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.8 | 1.5 | 0.08 | 0.04 | Fuel systems, hydraulic actuators |
| 5.3 | 2.4 | 0.10 | 0.05 | Semiconductor wafer handling |
| 12.0 | 3.0 | 0.12 | 0.06 | Aerospace fluid conduits |
| 22.4 | 3.5 | 0.15 | 0.07 | High-pressure industrial valves |
| 40.0 | 5.3 | 0.20 | 0.09 | Offshore hydraulic equipment |
This precision stems from our dual focus: rigorous material formulation protocols and real-time process analytics during molding. Each batch undergoes ASTM D2000-compliant testing for tensile strength, elongation, and volume swell—data sheets are provided with every shipment. For applications demanding non-standard geometries or exotic compounds (e.g., peroxide-cured FFKM for 300°C+ environments), our R&D division develops custom solutions validated through accelerated life-cycle testing. We eliminate guesswork in seal selection by correlating your operational parameters—pressure differentials, media exposure, and dynamic movement—with empirical performance curves.
OEMs partner with Suzhou Baoshida to mitigate field failure risks inherent in off-the-shelf sealing components. Our engineering team conducts failure mode analysis on returned samples, identifying root causes from material degradation to improper gland design. This forensic approach informs iterative design improvements, reducing your warranty claims and downtime. With in-house tooling capabilities and a 15-day rapid prototyping cycle, we transform technical specifications into validated production-ready seals faster than conventional suppliers.
Initiate a technical consultation with Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer, to resolve your most complex sealing challenges. Mr. Boyce possesses 12 years of experience formulating compounds for extreme environments and will review your application requirements, material compatibility data, and dimensional constraints without obligation. Contact him directly at [email protected] to submit technical drawings, request ASTM test reports, or schedule a virtual engineering review. Suzhou Baoshida responds to all technical inquiries within 4 business hours, providing actionable data—not generic quotations—to advance your project timeline. For mission-critical applications where sealing integrity dictates system reliability, precision begins with an engineered dialogue.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
