Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Options For Stair Treads
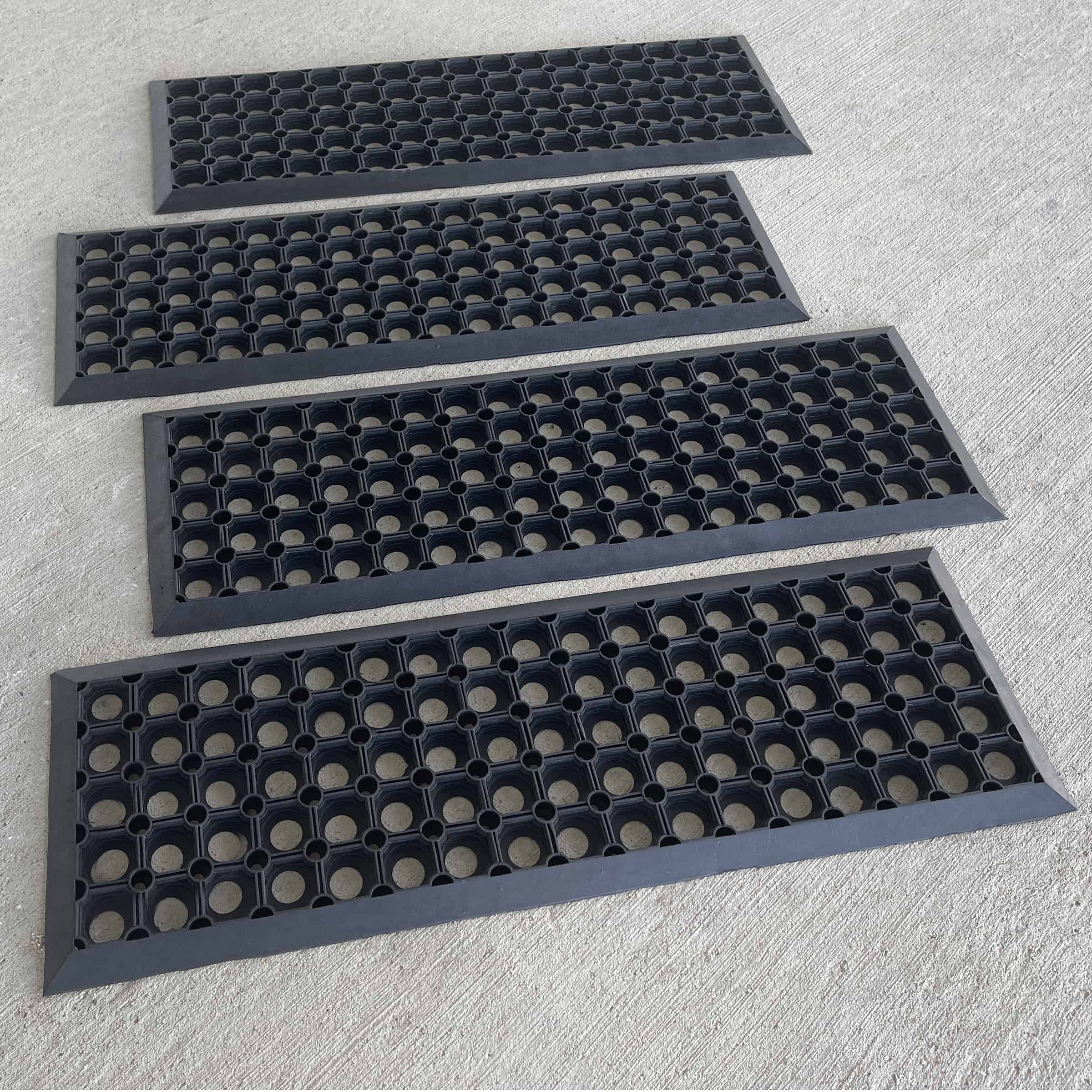

Engineering Insight: Critical Material Selection for Industrial Stair Treads
Generic rubber stair treads marketed for commercial use frequently fail in demanding industrial environments due to fundamental material inadequacies. Off-the-shelf solutions prioritize cost reduction over performance engineering, utilizing standardized compounds lacking resilience against specific operational hazards. This results in premature wear, safety hazards, and increased lifecycle costs from frequent replacements. Industrial facilities require stair treads engineered for extreme abrasion resistance, chemical exposure, temperature fluctuations, and consistent slip resistance under wet or contaminated conditions. Standard formulations often neglect these variables, leading to catastrophic degradation.
Unmodified EPDM compounds, common in budget treads, exhibit severe swelling and loss of mechanical integrity when exposed to industrial oils, solvents, or hydraulic fluids. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers better oil resistance but suffers from poor UV stability and ozone cracking in outdoor or ventilated settings, compromising structural integrity. Furthermore, many standard treads rely on surface texturing alone for slip resistance, which rapidly wears smooth under heavy foot traffic, negating safety features. The dynamic coefficient of friction (CoF) must remain stable across contaminants like water, grease, or metal shavings—a requirement generic treads cannot sustain.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses these failures through proprietary rubber compounding. Our engineered solutions integrate high-purity synthetic polymers, specialized fillers, and performance additives tailored to the client’s exact environmental stressors. This ensures dimensional stability, prolonged service life, and compliance with ISO 13287 safety standards for slip resistance under real-world conditions. Below is a comparative analysis of material performance under industrial stressors.
| Material Type | Abrasion Loss (mm³) ASTM D5963 | Oil Resistance (Volume Swell %) ASTM D471 | Static CoF (Wet Steel) | Max Continuous Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard EPDM Tread | 180-220 | 45-60% | 0.35-0.45 | 100 |
| Standard NBR Tread | 120-150 | 15-25% | 0.40-0.50 | 120 |
| Baoshida BD-8000 | 65-80 | <8% | 0.75-0.85 | 150 |
The BD-8000 formulation exemplifies our precision engineering approach. Reinforced with nano-silica and ozone-resistant modifiers, it maintains structural integrity after 500+ hours of ASTM D1149 ozone exposure. Its optimized filler dispersion reduces abrasion loss by 60% compared to standard EPDM while sustaining a minimum wet CoF of 0.75—exceeding OSHA and ANSI A1264.2 safety thresholds. Crucially, this performance is achieved without surface coatings that degrade, ensuring longevity in high-traffic zones like manufacturing floors, offshore platforms, or chemical processing plants.
Relying on off-the-shelf treads ignores the physics of industrial wear mechanisms. Material selection must begin with a forensic analysis of the operational environment: contaminant types, load cycles, and safety-critical friction requirements. Suzhou Baoshida partners with OEMs to co-develop stair tread solutions where compound chemistry directly correlates with site-specific durability and safety mandates. Contact our engineering team to initiate material stress testing for your application.
Material Specifications
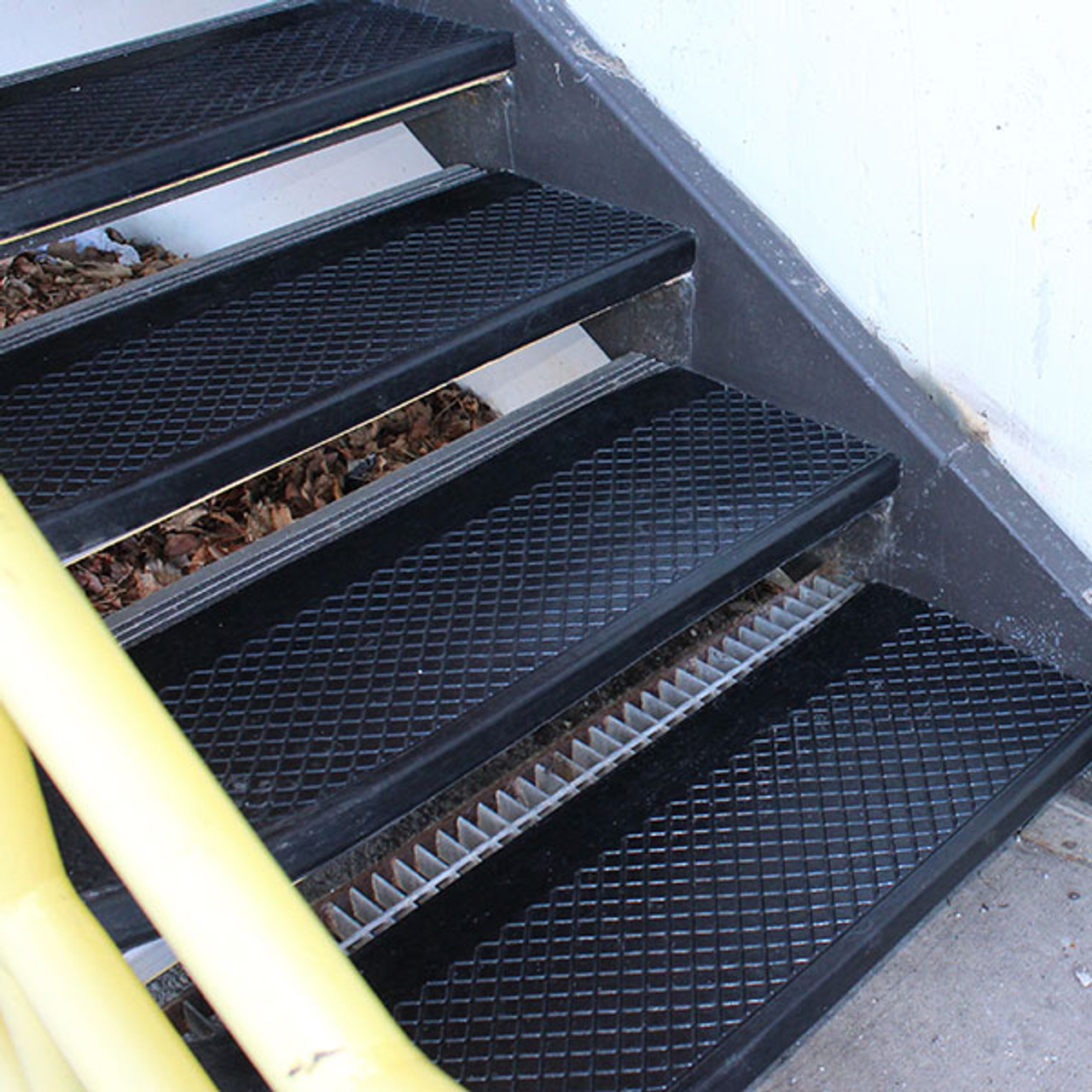

When selecting rubber compounds for stair tread applications in industrial and commercial environments, material performance under mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and temperature extremes becomes critical. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance rubber solutions engineered for durability, slip resistance, and long-term service life. For stair treads, three elastomers stand out due to their distinct property profiles: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers unique advantages depending on operational conditions, making precise material selection essential for optimal performance.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, delivers exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. Its thermal stability extends up to 250°C (482°F), making it ideal for high-temperature environments such as industrial ovens, chemical processing facilities, or offshore platforms. While Viton exhibits excellent aging and ozone resistance, its mechanical strength and abrasion resistance are moderate compared to other industrial rubbers. As such, it is best suited for specialized stair treads where chemical and thermal resistance outweigh the need for high physical durability.
Nitrile rubber, or NBR, is widely used in industrial applications due to its outstanding resistance to petroleum-based oils and greases. With a service temperature range of -30°C to 108°C (-22°F to 226°F), NBR provides reliable performance in typical factory, warehouse, and transportation environments. It offers high tensile strength, good abrasion resistance, and excellent compression set characteristics. These properties make Nitrile an optimal choice for stair treads in automotive plants, machinery platforms, and oil-handling facilities where slip resistance and oil resistance are paramount.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature applications, with a functional range from -60°C to 230°C (-76°F to 446°F). It maintains flexibility at low temperatures and resists hardening or cracking under thermal cycling. While silicone has lower mechanical strength and abrasion resistance than Nitrile or Viton, it offers superior resistance to UV radiation and ozone, making it suitable for outdoor stair treads exposed to weathering. Additionally, silicone is non-toxic and complies with food and pharmaceutical industry standards, allowing use in cleanroom access structures or sanitary facilities.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for informed selection in stair tread manufacturing.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 108 | -60 to 230 |
| Temperature Range (°F) | -4 to 482 | -22 to 226 | -76 to 446 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 15–30 | 6–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | Good to Excellent | Fair |
| Ozone/UV Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
Material selection must align with environmental exposure, load requirements, and safety standards. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides customized rubber formulations and technical support to ensure stair tread solutions meet exact industrial demands.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Stair Tread Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber stair tread solutions grounded in deep material science and advanced manufacturing expertise. Our core strength resides in the integrated capabilities of our dedicated engineering team: five specialized Mold Engineers and two senior Rubber Formula Engineers. This dual-discipline structure ensures seamless translation of performance requirements into robust, high-yield production, directly addressing the critical safety and durability demands inherent in stair tread applications. We do not merely supply rubber; we engineer polymer systems and tooling optimized for the specific mechanical stresses, environmental exposure, and stringent slip-resistance standards encountered in commercial and industrial staircases.
Our Rubber Formula Engineers possess mastery over elastomer chemistry, focusing exclusively on compounds where wear resistance, consistent coefficient of friction (CoF), and long-term resilience are non-negotiable. Through rigorous laboratory testing and iterative development, we formulate proprietary rubber blends utilizing natural rubber (NR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), and specialized additives. Key development parameters include optimizing the polymer matrix for abrasion resistance against foot traffic, ensuring stable CoF values exceeding ASTM F2508 standards under both dry and wet conditions, and achieving the precise Shore A hardness required for impact absorption without compromising structural integrity. We meticulously control curing kinetics to guarantee uniform cross-link density throughout the tread profile, eliminating weak points prone to premature wear or delamination. This scientific approach to compound design directly translates to extended service life and reduced lifecycle costs for end-users.
Complementing formula development, our five Mold Engineers execute precision tooling design and validation. They leverage advanced CAD/CAM systems and deep understanding of rubber flow dynamics, shrinkage characteristics, and ejection mechanics to create molds ensuring dimensional accuracy, sharp detail reproduction (critical for anti-slip patterns), and minimal flash. Their expertise minimizes production defects, maximizes part consistency across high-volume OEM runs, and significantly reduces time-to-market for custom tread profiles. This close collaboration between formula and mold engineering eliminates the common disconnect between material specification and manufacturability, a critical factor for complex geometries like nosings and integrated drainage channels.
Our OEM capabilities are engineered for reliability and scalability. We manage the entire process under strict ISO 9001 protocols: from initial material selection and prototype validation through tooling fabrication, process parameter optimization, and full-scale production. Clients benefit from complete material traceability, in-process quality control aligned with ASTM D2240 (hardness), DIN 53516 (abrasion), and internal CoF testing regimes, and dedicated production lines ensuring batch consistency. This integrated engineering and manufacturing ecosystem guarantees stair treads meeting exacting global safety and performance benchmarks.
The following table summarizes key performance characteristics achievable through our engineered rubber compounds for stair treads:
| Property | Typical Range/Value | Test Standard | Significance for Stair Treads |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 55 – 75 | ASTM D2240 | Optimal balance: Comfort underfoot, resistance to indentation, pattern retention |
| DIN Abrasion Loss | ≤ 120 mm³ | DIN 53516 | Superior resistance to wear from foot traffic, extending product lifespan |
| Static CoF (Wet Ceramic) | ≥ 0.60 | ASTM F2508 | Critical slip resistance on wet surfaces, meeting safety codes |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +100°C | Internal | Durability across diverse indoor/outdoor climates |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 15 MPa | ASTM D412 | Structural integrity under load and impact |
| Elongation at Break | ≥ 300% | ASTM D412 | Flexibility to absorb impact without cracking |
This engineering-led methodology, combining advanced material science with precision manufacturing oversight, positions Suzhou Baoshida as the strategic partner for OEMs demanding technically superior, code-compliant, and reliably produced rubber stair tread solutions.
Customization Process
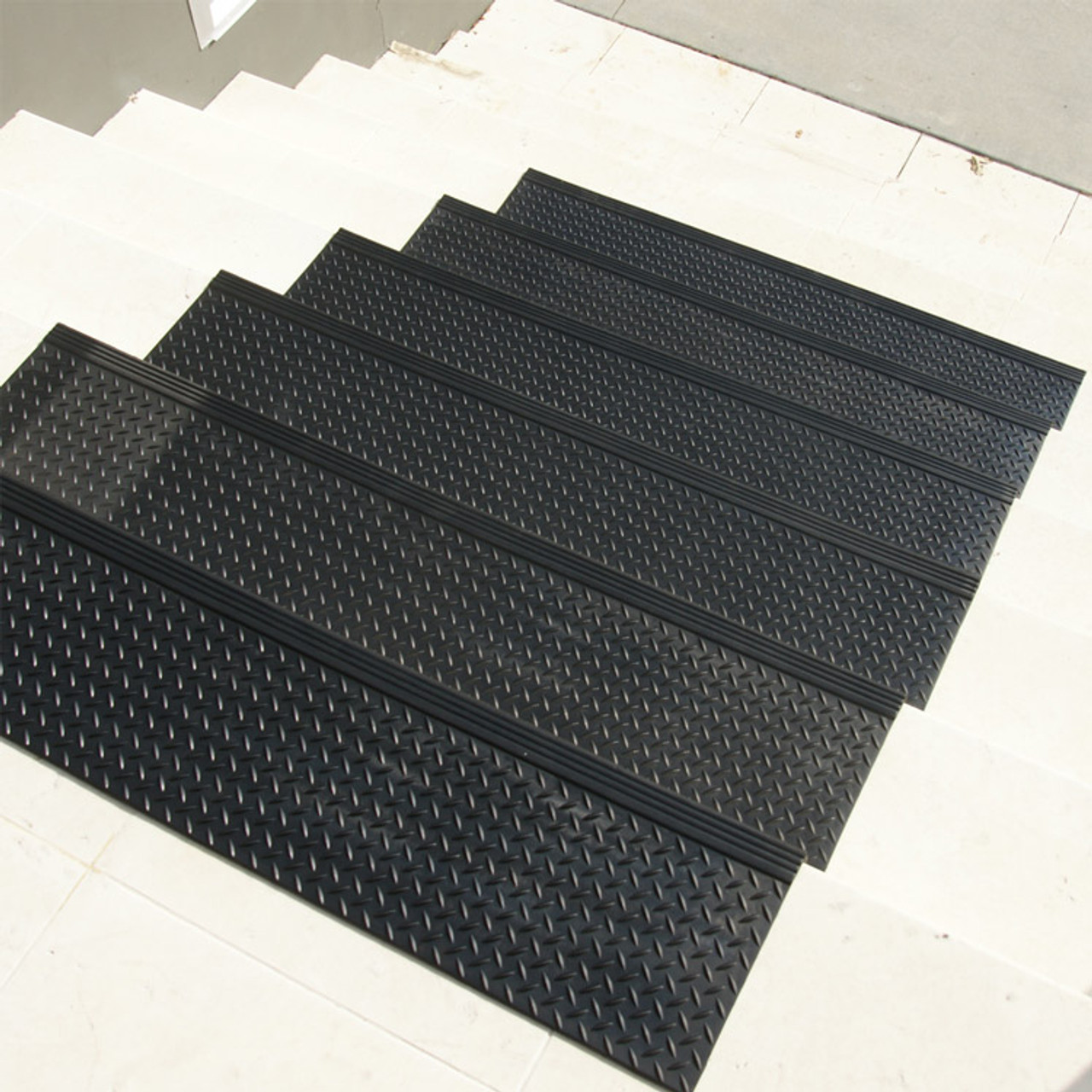

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for industrial rubber stair treads begins with a comprehensive drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we prioritize dimensional accuracy, load-bearing requirements, and installation environment specifications. Upon receiving customer-provided technical drawings or CAD models, our engineering team conducts a detailed review to verify critical parameters such as tread depth, riser height, anti-slip pattern geometry, edge radius, and mounting interface design. We assess compliance with international safety standards, including ISO 14122-3 for permanent means of access and ASTM F1637 for safe walking surfaces. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities—such as enhancing drainage channels or reinforcing high-wear zones—are flagged for collaborative refinement. This stage ensures that the design is not only manufacturable but also optimized for long-term durability under expected mechanical and environmental stress.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our rubber formula engineers initiate material formulation tailored to the operational demands of the stair tread application. The selection of base polymers—such as natural rubber (NR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), or nitrile rubber (NBR)—depends on required properties like abrasion resistance, UV stability, oil resistance, or low-temperature flexibility. Additives are precisely compounded to achieve Shore A hardness between 60–80, optimal friction coefficient (≥0.6 on dry/wet surfaces), and flame retardancy if needed. For outdoor or marine environments, we incorporate anti-aging agents and ozone-resistant formulations. Each compound is validated through accelerated aging, tensile testing, and slip resistance analysis using standardized ASTM D1894 and DIN 51130 Ramp Test protocols. The finalized formulation is documented and batch-traceable to ensure consistency across production cycles.
Prototyping and Validation
A functional prototype is manufactured using precision compression or injection molding, depending on complexity and volume expectations. Prototypes undergo rigorous performance testing, including impact resistance (per ASTM D5420), repeated load cycling, and adhesion strength for bonded metal substrates. Customers are provided with physical samples and test data reports for evaluation. Feedback is integrated into final design or material adjustments, ensuring full alignment with application requirements before release to mass production.
Mass Production and Quality Control
Once approved, the project transitions to automated mass production with strict in-process quality controls. Each batch is subjected to dimensional inspection, hardness testing, and visual defect screening. Final products are packaged per client specifications, with optional labeling and traceability coding.
| Parameter | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 60–80 | ASTM D2240 |
| Coefficient of Friction (wet) | ≥0.6 | ASTM D1894 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥10 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Abrasion Loss (DIN) | ≤120 mm³ | DIN 53516 |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +100°C | ISO 188 |
Contact Engineering Team
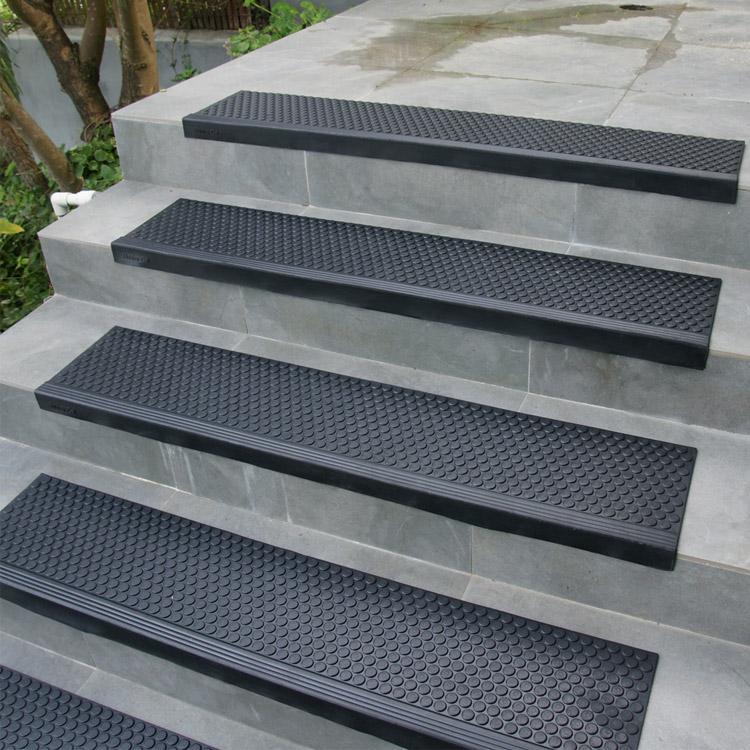

Optimized Stair Tread Solutions: Engineering Safety and Durability for Industrial Applications
Selecting the appropriate stair tread material is a critical engineering decision impacting workplace safety, operational continuity, and lifecycle costs. Generic solutions often fail under demanding industrial conditions, leading to premature wear, increased slip hazards, and costly downtime for replacement. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in advanced rubber compound formulations engineered specifically for high-traffic, high-risk stair applications. Our approach transcends standard off-the-shelf products through rigorous polymer matrix optimization, filler dispersion technology, and application-specific vulcanization protocols. This ensures treads deliver superior traction under wet, oily, or contaminated conditions while resisting abrasion, cutting, and environmental degradation over extended service life. We understand that your facility’s safety compliance and maintenance schedules depend on materials performing predictably under real-world stress.
Our core competency lies in tailoring rubber formulations to meet exacting OEM and end-user specifications. We utilize premium synthetic and natural rubber blends, incorporating specialized additives for enhanced properties without compromising processability. Key performance characteristics are meticulously balanced during development, including coefficient of friction (dry/wet), Shore A hardness profile, tear strength, and resistance to ozone, UV exposure, and common industrial chemicals. This scientific methodology guarantees consistent part-to-part quality and adherence to international safety standards such as ASTM F1637 and ISO 22196. Below details the performance parameters of our standard industrial stair tread compounds, demonstrating the precision achievable through our engineering process.
| Property | Standard Compound (BD-500) | Premium Compound (BD-700) | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 65 ± 3 | 72 ± 3 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 18.0 | ≥ 22.0 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥ 450 | ≥ 380 | ASTM D412 |
| Abrasion Resistance (mm³) | ≤ 120 | ≤ 85 | ASTM D5963 |
| Coefficient of Friction (Wet) | ≥ 0.65 | ≥ 0.75 | ASTM F2913 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -30°C to +80°C | -40°C to +100°C | Internal Protocol |
| Flame Resistance (UL94) | HB | V-0 | UL 94 |
Beyond standard formulations, Suzhou Baoshida excels in collaborative OEM development. We partner with manufacturers to create bespoke tread solutions addressing unique challenges such as extreme temperature cycling, exposure to aggressive solvents, or requirements for antimicrobial properties. Our in-house R&D laboratory conducts accelerated aging tests, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), and full-scale prototype validation to de-risk your product integration. This engineering partnership model minimizes your development timeline and ensures the final component meets all functional, regulatory, and aesthetic criteria before full-scale production.
Initiate the engineering dialogue to secure a stair tread solution engineered for uncompromised safety and longevity. Contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager and Rubber Formulation Specialist, directly at [email protected]. Provide your specific application requirements, performance targets, and volume expectations. Mr. Boyce will coordinate our technical team to deliver comprehensive material data sheets, feasibility assessments, and tailored compound recommendations within 48 business hours. Do not settle for generic rubber products that compromise safety margins; leverage Suzhou Baoshida’s precision engineering expertise to develop stair treads that actively enhance workplace safety and reduce total cost of ownership. Your next-generation stair safety solution begins with a single, decisive technical consultation. Reach out to Mr. Boyce today to schedule your engineering review.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
