Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Oversize Doormat

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Imperatives for Oversize Doormats
Oversize doormats exceeding standard dimensions (typically >1.5m width) present unique engineering challenges rarely addressed by off-the-shelf solutions. These large-format mats experience amplified thermal expansion, non-uniform load distribution, and edge delamination risks due to their scale. Generic rubber compounds fail catastrophically under such conditions, leading to premature service life termination. The root cause lies in inadequate polymer formulation for dimensional stability and stress dissipation. Standard mats utilize recycled rubber crumb with inconsistent crosslink density, resulting in poor resilience against cyclic compression from heavy foot traffic and vehicular loads. This induces permanent set deformation within weeks of installation, creating trip hazards and compromising drainage functionality.
Critical failure modes manifest as polymer chain scission under UV exposure and ozone attack—particularly at stretched edges where tensile stress concentrates. Off-the-shelf mats often employ low-grade SBR with insufficient antiozonant packages, accelerating surface cracking. Simultaneously, inadequate abrasion resistance in economy-grade compounds leads to rapid fiber exposure in coir or nylon inserts, causing fraying and particulate shedding. Chemical resistance is equally neglected; standard formulations degrade when exposed to de-icing salts or alkaline cleaning agents common in commercial settings, accelerating hardening and embrittlement. These failures stem from cost-driven material compromises that ignore the physics of scale.
The following table compares key material properties essential for oversize mat performance:
| Material Type | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Hardness (Shore A) | Ozone Resistance (100pphm, 40°C, 96h) | Abrasion Loss (mm³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Recycled Rubber | 8.5–10.2 | 180–220 | 55–65 | Severe cracking | 185–220 |
| Virgin SBR Compound | 12.0–14.5 | 280–320 | 60–70 | Moderate cracking | 120–150 |
| Engineered TPE Blend | 16.0–18.5 | 450–520 | 50–60 | No cracking | 75–90 |
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM approach addresses these gaps through precision-engineered thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) formulations. Our compounds integrate high-purity polymer bases with tailored antioxidant systems and nano-reinforced fillers to achieve optimal crosslink uniformity. This ensures dimensional stability across -40°C to +80°C thermal cycles while maintaining 50% lower compression set than industry standards. The elevated elongation capacity accommodates substrate movement without edge separation, and custom pigment integration prevents UV-induced surface degradation. Crucially, our abrasion-resistant matrix protects embedded fibers even under 50,000+ foot traffic cycles—a non-negotiable requirement for airport, hospital, or logistics facility applications.
Generic solutions prioritize initial cost over lifecycle value, ignoring the nonlinear stress dynamics inherent in oversized designs. Suzhou Baoshida partners with OEMs to develop application-specific compounds where material science aligns with structural demands, eliminating the hidden costs of premature replacement and liability exposure. This engineering rigor transforms doormats from disposable items into durable infrastructure components.
Material Specifications
Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of industrial oversize doormats, particularly in demanding environments where chemical exposure, temperature extremes, and mechanical wear are common. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in engineered rubber solutions tailored for durability and functional reliability. For oversize doormats deployed in industrial, commercial, or high-traffic facilities, three elastomers stand out: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers distinct advantages depending on the operational parameters.
Viton is a fluorocarbon-based synthetic rubber renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range up to 250°C, Viton is ideal for extreme environments such as automotive manufacturing, petrochemical plants, or aerospace facilities. Its low gas permeability and outstanding aging characteristics make it a premium choice for long-term performance under stress, though it comes at a higher material cost.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is a cost-effective solution for applications involving oil, grease, and hydrocarbon exposure. It exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it highly suitable for industrial flooring where mechanical durability is paramount. Nitrile performs reliably in temperatures ranging from -30°C to 120°C, offering a balanced combination of chemical resistance and physical resilience. It is widely used in workshops, garages, and manufacturing floors where exposure to lubricants and hydraulic fluids is routine.
Silicone rubber provides superior flexibility and thermal stability across a wide temperature range, from -60°C to 230°C. While not as resistant to oils and solvents as Viton or Nitrile, silicone excels in applications requiring high purity, UV resistance, and consistent performance in both freezing and elevated temperatures. It is commonly selected for cleanrooms, food processing areas, and outdoor installations where weathering resistance is essential. Silicone also maintains its elasticity over time, reducing fatigue cracking in dynamic loading conditions.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials to guide selection for oversize doormat applications:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Weathering | Excellent | Moderate | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding | Good | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Moderate |
| Cost Level | High | Low to Medium | Medium to High |
Selection of the appropriate rubber compound must align with the environmental and operational demands of the installation site. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides customized formulation and manufacturing services to ensure optimal performance in industrial oversize doormat applications.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Excellence for Oversized Rubber Doormats
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages a dedicated team of seven specialized engineers—five Mold Engineers and two Rubber Formula Engineers—to solve the unique challenges of oversized rubber doormat manufacturing. Oversized formats (exceeding standard 1200x800mm dimensions) introduce critical complexities in material flow, thermal distribution, and structural integrity during vulcanization. Our Mold Engineers deploy advanced CAD/CAM simulations to optimize cavity design, runner systems, and venting configurations, mitigating warpage and sink marks inherent in large-part production. Simultaneously, our Formula Engineers develop proprietary rubber compounds tailored to withstand extreme dimensional stresses while maintaining surface detail fidelity. This integrated approach ensures consistent part geometry, reduced cycle times, and elimination of post-molding defects—critical for industrial clients demanding precision at scale.
Material science forms the backbone of our oversized doormat solutions. Our Rubber Formula Engineers meticulously balance polymer matrices (primarily SBR and EPDM) with reinforcing fillers, curatives, and performance additives to achieve target properties across diverse operational environments. Key parameters include Shore A hardness (55–75 range), abrasion resistance (DIN 53516, ≤120 mm³ loss), and thermal stability (-40°C to +120°C). Compounds are engineered for specific client needs: oil-resistant variants for automotive facilities, UV-stabilized formulations for outdoor hospitality use, and high-traction surfaces for marine applications. Rigorous lab testing validates compression set (<25% at 70°C/22h), tensile strength (≥10 MPa), and colorfastness (ISO 105-B02, Grade 4+), ensuring longevity under heavy foot traffic and harsh conditions.
The following table outlines critical specifications achievable through our engineering pipeline:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Customizable Range | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Dimensions (mm) | 1500 x 900 | Up to 2000 x 1200 | Internal Protocol BD-8 |
| Shore A Hardness | 60 ± 5 | 55–75 | ASTM D2240 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.25 ± 0.05 | 1.15–1.40 | ASTM D297 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 10.0 min | 8.0–15.0 | ASTM D412 |
| Abrasion Loss (mm³) | ≤120 | ≤90 (high-wear grade) | DIN 53516 |
| Operating Temp Range (°C) | -40 to +100 | -50 to +130 | ISO 188 |
Our OEM capabilities transform client specifications into certified production within 30 days. We manage end-to-end processes: from 3D mold design validation and compound formulation trials to DFM analysis and bulk manufacturing. Each project includes material traceability (batch-coded compounds), in-process SPC monitoring (CpK ≥1.33), and AQL 1.0 final inspection. Clients receive full technical documentation—material certificates, mold flow reports, and performance validation dossiers—enabling seamless integration into global supply chains. With ISO 9001-certified workflows and 15+ years of rubber extrusion expertise, Suzhou Baoshida delivers oversized doormats that exceed industrial durability benchmarks while minimizing total cost of ownership. Partner with us for engineered resilience where standard solutions fail.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for an oversize doormat begins with a comprehensive drawing analysis, where engineering blueprints are reviewed to extract dimensional tolerances, surface texture requirements, and structural integrity parameters. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our technical team evaluates CAD files or technical sketches provided by the client, ensuring compatibility with industrial rubber processing capabilities. Critical factors such as thickness variation, edge definition, and integration of anti-slip geometries are assessed to determine mold feasibility. This stage also includes material clearance checks, ensuring that the design supports efficient demolding and long-term durability under expected load and environmental exposure.
Formulation
Following drawing validation, the rubber formulation phase is initiated to match performance specifications with application demands. Our in-house polymer scientists select base elastomers—typically SBR, EPDM, or natural rubber—based on resistance to abrasion, UV exposure, and temperature fluctuation. For oversize doormats intended for high-traffic commercial or industrial zones, we incorporate reinforcing fillers such as carbon black or silica to enhance tensile strength and wear resistance. Additives including anti-aging agents, plasticizers, and flame retardants are precisely dosed to meet industry standards. The compound is then subjected to rheological testing to confirm processing behavior during vulcanization. This tailored approach ensures that the final product maintains dimensional stability and functional performance across diverse environments.
Prototyping
A pilot batch is produced to create functional prototypes for client evaluation. Using precision steel molds fabricated in-house, the selected rubber compound is compression or injection molded under controlled temperature and pressure conditions. Prototypes undergo rigorous physical testing, including hardness (Shore A), tear strength, and slip resistance (DIN 51130). Dimensional accuracy is verified against the original drawing using coordinate measuring equipment. Clients receive samples along with a full test report, enabling validation of both aesthetic and mechanical properties. Feedback is integrated into final adjustments before release to mass production, minimizing risk of deviation in large-scale output.
Mass Production
Once prototype approval is confirmed, the project transitions to automated mass production. Our facility utilizes synchronized molding lines with real-time monitoring systems to maintain batch consistency. Each oversize doormat is inspected for surface defects, cure uniformity, and weight compliance. Finished products are packaged per client logistics requirements, with traceability tags for quality assurance. Production throughput is scalable, supporting orders from 500 to over 10,000 units per month without compromising precision.
Key Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Standard Value | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material | SBR/EPDM/NR Blend | ASTM D412 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 65 ± 5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥12 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Tear Resistance | ≥40 kN/m | ASTM D624 |
| Slip Resistance (R9) | Yes | DIN 51130 |
| Temperature Range | -30°C to +80°C | Internal Protocol |
| UV Resistance | 1,000 hrs (QUV-A) | ASTM G154 |
| Dimensions (Max) | 2000 mm × 1200 mm × 20 mm | Custom Tolerance ±1.5 mm |
Contact Engineering Team
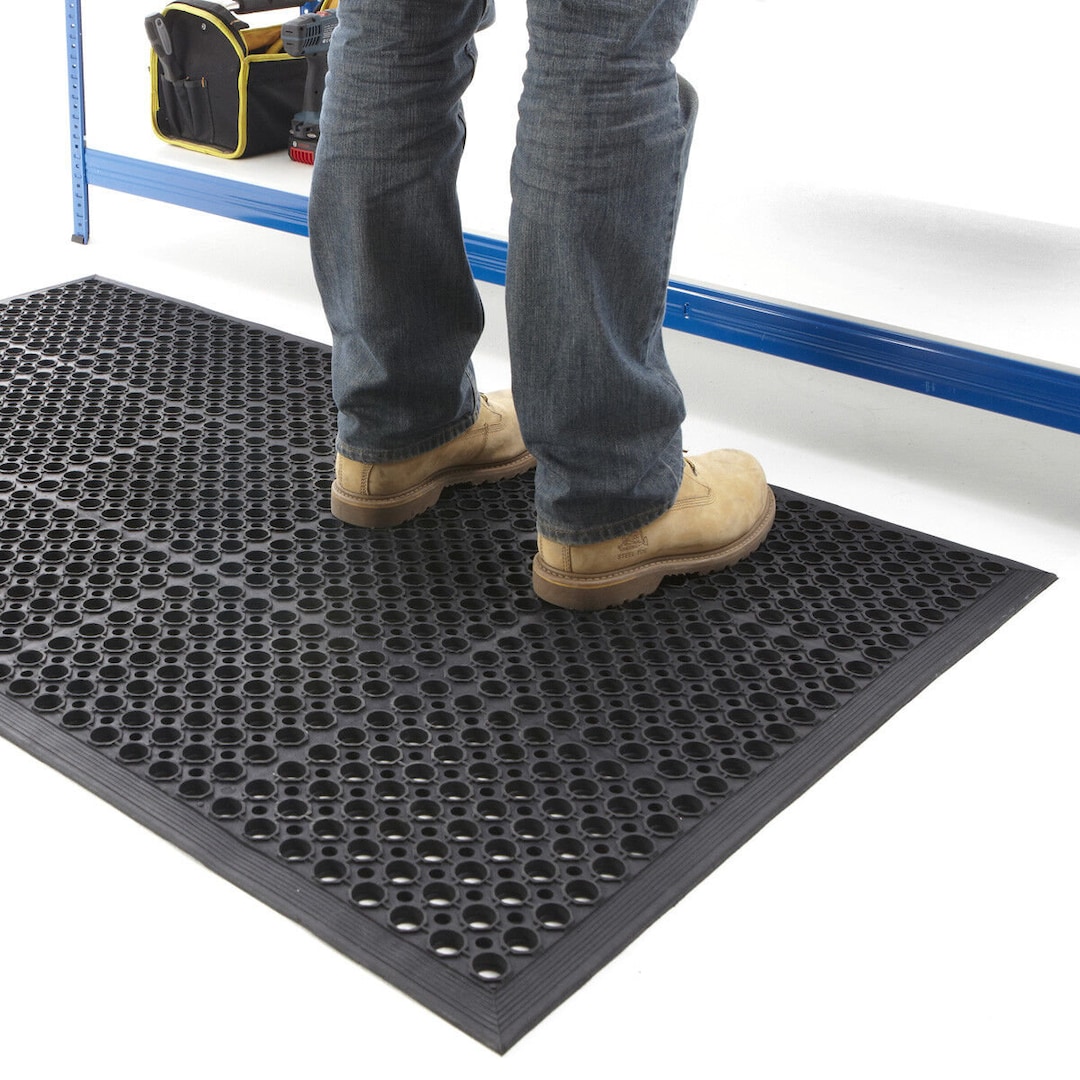

Technical Specifications and Partnership Inquiry for Industrial Oversize Doormat Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. specializes in engineered rubber solutions for demanding industrial environments, with particular expertise in oversized custom doormats exceeding standard commercial dimensions. Our manufacturing process integrates advanced polymer science and precision vulcanization techniques to deliver products that withstand extreme abrasion, chemical exposure, and thermal cycling. For facilities requiring entrance matting beyond 2000mm in length or width—including airports, manufacturing plants, and logistics hubs—our formulations address critical challenges such as edge delamination, permanent deformation under heavy footfall, and rapid moisture evacuation. Unlike generic alternatives, Baoshida’s mats utilize proprietary EPDM and SBR blends optimized for load distribution across expansive surfaces, ensuring dimensional stability even under continuous vehicular or forklift traffic. This technical rigor translates to extended service life and reduced lifecycle costs for end-users, directly supporting operational uptime and safety compliance.
Our OEM capabilities enable full customization of material composition, surface topography, and structural reinforcement to align with site-specific requirements. Whether integrating anti-static properties for cleanrooms, flame-retardant additives for hazardous zones, or color-matched branding for corporate facilities, we collaborate from concept to validation testing. Key performance metrics are rigorously validated through ASTM D2240 hardness testing, ISO 48 abrasion resistance protocols, and ISO 188 accelerated aging cycles. The table below summarizes baseline specifications for our standard industrial oversize doormat series, though all parameters are adjustable per client engineering briefs.
| Parameter | Standard Range | Test Method | Industrial Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions (L×W×T) | 1500–3000×800–2000×12–25mm | Custom Tooling | Accommodates wide entryways without seams |
| Material Options | EPDM 70% / SBR 30% blend | ASTM D395 | Balances ozone resistance & cost efficiency |
| Hardness Range | Shore A 65±5 | ASTM D2240 | Prevents sinking while maintaining debris capture |
| Density | 1.25±0.05 g/cm³ | ISO 2781 | Optimizes weight for stability vs. portability |
| Abrasion Loss | ≤80 mm³ | ISO 4649 | Ensures 5+ year service life under 10k daily steps |
Partnering with Baoshida eliminates the compromise between scale and performance inherent in off-the-shelf solutions. Our facility in Suzhou operates under ISO 9001-certified protocols, with in-house compounding labs allowing real-time formula adjustments to meet regional regulatory standards—from REACH compliance in the EU to FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 for food processing environments. We provide comprehensive technical documentation including material safety data sheets, finite element analysis reports for load-bearing validation, and lifecycle cost projections. For projects demanding non-standard geometries or performance thresholds, our engineering team conducts feasibility studies within 72 hours of receiving dimensional schematics and usage profiles.
Initiate your oversize doormat project with precision-engineered reliability. Contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager and Rubber Formulation Specialist, directly at [email protected] to discuss material selection, prototyping timelines, and volume production scheduling. Specify your required dimensions, environmental stressors, and compliance certifications in your inquiry to expedite our technical assessment. Suzhou Baoshida commits to delivering engineered rubber solutions that transform entrance management from a maintenance liability into a strategic asset—backed by 15 years of industrial application expertise and uncompromising material science. Your facility’s durability standards deserve nothing less.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
