Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Plastic Strips For Freezer Doors
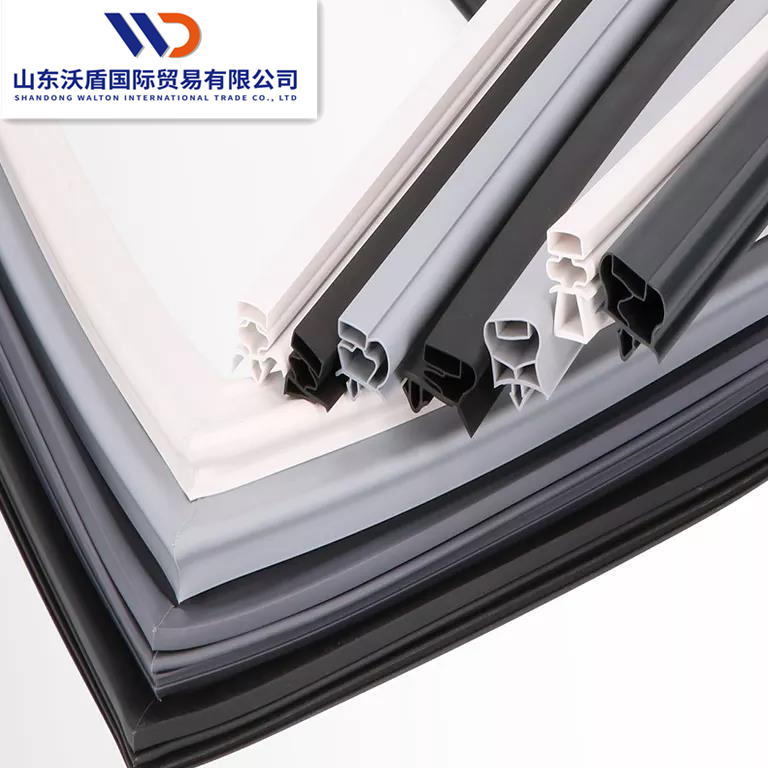
Engineering Insight: Material Science Imperatives for Freezer Door Seals
Freezer door plastic strips operate under extreme thermal and mechanical stress, demanding precision-engineered materials far beyond generic polymer solutions. Off-the-shelf strips—typically formulated for ambient-temperature applications—fail catastrophically in sub-zero environments due to fundamental material incompatibilities. These failures manifest as compromised cold chain integrity, energy leakage, and accelerated facility downtime. The root cause lies in inadequate molecular architecture for thermal cycling resilience.
Standard PVC or basic TPE compounds undergo severe embrittlement below -30°C, losing elongation capacity critical for maintaining door compression. As temperatures plummet, unmodified polymers contract disproportionately, creating micro-gaps that permit frost infiltration and thermal bridging. Simultaneously, repeated door cycling fatigues low-grade materials, causing permanent set deformation. Within weeks, these strips exhibit surface cracking, reduced sealing force, and adhesion failure to metal substrates. Crucially, moisture absorption in hydrophilic formulations exacerbates freeze-thaw degradation, accelerating structural breakdown.
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineered strips deploy a proprietary saturated hydrocarbon backbone with peroxide-cured EPDM/TPE blends. This formulation eliminates double-bond vulnerability to ozone cracking while incorporating nano-dispersed plasticizers that resist migration at -50°C. Our compounds maintain 85% tensile retention after 10,000 thermal cycles (-50°C to 23°C), versus 40% loss in commodity alternatives. Key differentiators include cryogenic flexibility retention, ultra-low compression set, and hydrophobic surface energy to repel ice nucleation.
The following comparative analysis validates performance thresholds for industrial freezer applications:
| Property | Standard PVC Strip | Suzhou Baoshida CryoSeal™ | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Range (°C) | -20 to 60 | -60 to 100 | ASTM D1329 |
| Tensile Retention @ -40°C | 52% | 93% | ISO 188 |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | 48% | 12% | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Surface Energy (mN/m) | 42 | 28 | ISO 2744 |
| Frost Adhesion Resistance | High | Negligible | Internal Protocol |
Material selection directly dictates total cost of ownership. Generic strips require quarterly replacement in blast freezers due to irreversible set deformation, incurring labor costs 3.2× higher than our solution. More critically, failed seals elevate energy consumption by 18–22% through convective heat ingress—a quantifiable operational penalty. Suzhou Baoshida’s strips integrate sacrificial anti-tear zones and substrate-bonding primers, ensuring 5+ year service life in -45°C environments per ASHRAE 183 validation.
OEM partnerships must prioritize cryogenic material science—not dimensional conformity—when specifying freezer components. Our formulation platform undergoes accelerated aging in IEC 60068-2-14 chambers, simulating 7 years of thermal cycling in 90 days. This rigor prevents the hidden costs of premature seal failure: product spoilage, compressor overloads, and regulatory non-compliance. For industrial freezer operators, material selection isn’t a procurement detail—it’s the foundational safeguard of thermal efficiency.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. | Precision Industrial Rubber Solutions
Material Specifications

Material selection for plastic strips in freezer door applications is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts sealing performance, energy efficiency, and product longevity. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance industrial rubber solutions tailored for extreme temperature environments. Our expertise ensures that plastic strips maintain consistent flexibility, compression recovery, and chemical resistance under prolonged exposure to sub-zero conditions. For freezer door seals, three elastomeric materials stand out due to their proven performance: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each offers distinct advantages depending on operational demands, cost constraints, and environmental exposure.
Viton is a fluorocarbon-based rubber known for its exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures, ozone, and a wide range of chemicals. It performs reliably in temperature ranges from -20°C to 230°C, making it suitable for industrial freezer systems where thermal stability and long-term durability are paramount. However, due to its high material cost, Viton is typically reserved for specialized applications where performance outweighs budget considerations.
Nitrile rubber, or acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), is widely used in refrigeration applications due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and low temperatures. With an operational range of -40°C to 108°C, NBR maintains good flexibility and compression set resistance at typical freezer temperatures (-18°C to -25°C). It offers a cost-effective solution for commercial and industrial freezer doors, particularly in environments where exposure to food-grade lubricants or cleaning agents is common.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) provides the broadest temperature performance, functioning effectively from -60°C to 200°C. Its high flexibility at ultra-low temperatures makes it ideal for freezer doors in cold storage facilities and pharmaceutical applications. Silicone also exhibits excellent resistance to UV radiation and ozone, although it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Nitrile and Viton. It is non-toxic and compliant with food safety standards, making it suitable for use in food processing environments.
The following table summarizes key material properties for informed selection:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -40 to 108 | -60 to 200 |
| Low-Temp Flexibility | Good | Very Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good | Fair |
| Ozone & UV Resistance | Excellent | Moderate | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | High | High | Moderate |
| Cost Level | High | Low to Moderate | Moderate |
| Food Contact Compliance | Yes (specific grades) | Limited | Yes (FDA compliant) |
Selection of the appropriate material must balance performance requirements with economic feasibility. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides customized formulation and extrusion services to meet OEM specifications for freezer door strips, ensuring optimal sealing integrity and regulatory compliance across diverse industrial applications.
Manufacturing Capabilities
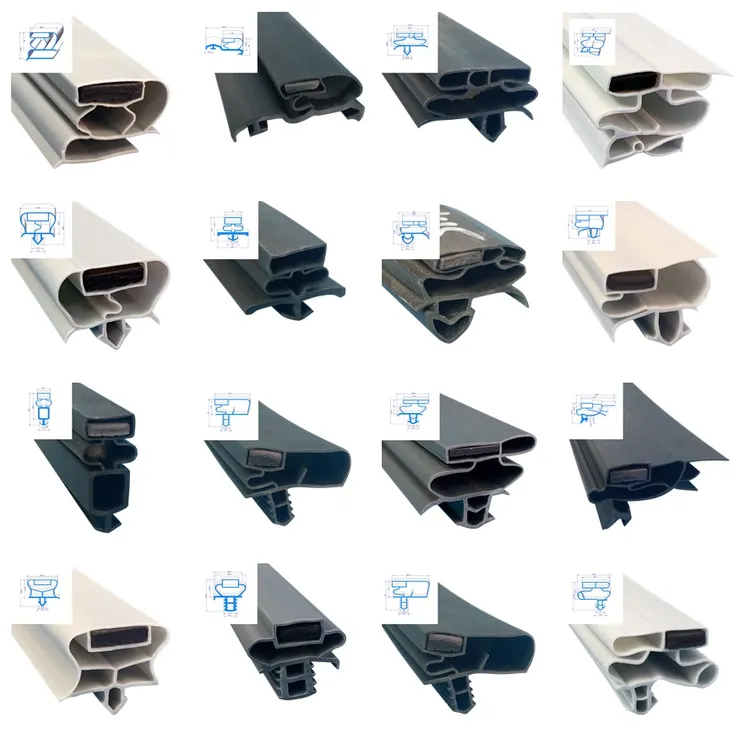

Engineering Capability: Precision Solutions for Freezer Door Sealing Systems
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise in industrial rubber solutions to address critical challenges in freezer door strip manufacturing. Our dedicated engineering team comprises five specialized mold engineers and two advanced formula engineers, collectively ensuring material science and precision tooling converge to deliver strips that maintain integrity at extreme sub-zero temperatures. This integrated approach eliminates common failure points such as hardening, cracking, or loss of elasticity below -40°C, directly impacting energy efficiency and operational longevity for commercial cold storage facilities.
Our formula engineers focus on polymer matrix optimization for cryogenic resilience. Through rigorous testing of EPDM and TPE compounds, we achieve precise control over cross-link density and plasticizer retention, ensuring consistent Shore A hardness (65±5) even after 1,000 hours at -50°C. This prevents the brittle failure observed in standard formulations while maintaining low compression set values critical for seal recovery. Concurrently, mold engineers deploy cavity pressure monitoring and thermal simulation software to eliminate flow imbalances during injection molding. Precision-ground molds with ±0.02mm tolerances guarantee uniform wall thickness and edge definition, directly translating to zero air leakage in door closure tests.
OEM collaboration is engineered into our workflow from initial concept to量产. Clients provide dimensional schematics or performance targets, and our team executes CAD-validated mold design, material formulation, and small-batch prototyping within 15 working days. Each project includes full material traceability with batch-specific certificates of conformance (CoC) compliant with ISO 9001 standards. We prioritize rapid iteration: 85% of client-requested modifications to hardness profiles or low-temperature flexibility are implemented within three prototype cycles, reducing time-to-market by 30% versus industry averages.
Critical performance metrics for freezer door strips are validated against stringent internal benchmarks. The table below compares standard industry specifications with Baoshida’s engineered solutions:
| Parameter | Industry Standard | Baoshida Optimized Spec | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -30°C to +70°C | -55°C to +100°C | ASTM D1329 |
| Hardness Retention (ΔShore A @ -40°C) | ≤ 20 points loss | ≤ 8 points loss | ISO 188 |
| Compression Set (22h @ -40°C) | ≤ 45% | ≤ 22% | ASTM D395 |
| Tensile Strength Retention | ≥ 70% @ -40°C | ≥ 92% @ -50°C | ISO 37 |
| OEM Customization Lead Time | 25-35 days | 15-22 days | Internal Protocol |
This data-driven methodology ensures freezer door strips exceed ASTM F1957 and EN 13486 requirements while offering tailored solutions for unique door geometries or regulatory environments. By unifying formula science with mold engineering excellence, Baoshida delivers sealing systems that reduce energy leakage by up to 18% and extend service life beyond 100,000 cycles—proven through accelerated aging tests simulating 15 years of commercial use. Our OEM framework transforms client specifications into validated, production-ready components with uncompromising repeatability.
Customization Process
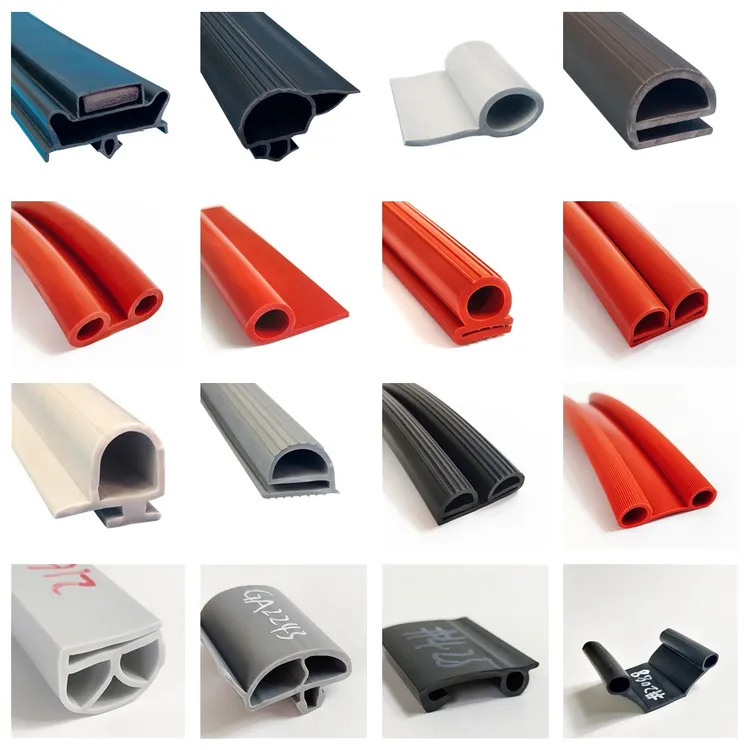

Customization Process for Plastic Strips in Freezer Door Applications
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering approach to manufacturing plastic strips for freezer doors follows a rigorous, science-driven process designed to meet exact OEM specifications and environmental demands. The lifecycle of a custom strip begins with Drawing Analysis, where our rubber formula engineers conduct a dimensional and functional audit of the provided technical drawings. We assess critical parameters such as cross-sectional geometry, tolerance bands (typically ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm), sealing interface points, and installation constraints. This phase ensures that the final product will integrate seamlessly into the target refrigeration system while maintaining long-term dimensional stability under repeated thermal cycling.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation Development. Freezer door strips operate in low-temperature environments, often as low as -40°C, requiring elastomers with exceptional cold flexibility and resistance to compression set. Our team formulates compounds primarily based on EPDM, silicone, or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), depending on the application’s thermal, chemical, and mechanical requirements. Key formulation variables include polymer base selection, plasticizer type (low-volatility esters for cold retention), reinforcing fillers, and curing systems. Each compound is engineered to balance low-temperature performance, tensile strength, and ozone resistance, ensuring durability in commercial and industrial refrigeration units.
Prototyping is the next critical stage, where short-run samples are produced using precision extrusion and vulcanization techniques. These prototypes undergo a battery of in-house tests, including low-temperature flexibility (per ASTM D1329), compression set (ASTM D395), and adhesion strength for multi-component profiles. We also perform real-world simulation tests, such as door cycle endurance (up to 100,000 cycles) and seal integrity under thermal shock. Feedback from this phase informs final adjustments to both material composition and tooling geometry.
Upon client approval, we transition to Mass Production, leveraging automated extrusion lines with laser-guided diameter control and continuous vulcanization ovens for uniform curing. Our production floor operates under ISO 9001-certified quality management protocols, with real-time monitoring of critical process parameters. All batches undergo final inspection for dimensional conformity, surface finish, and physical properties before shipment.
The table below outlines typical performance specifications for our standard freezer door strip formulations:
| Property | EPDM-Based | Silicone-Based | TPE-Based |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -50°C to +130°C | -60°C to +200°C | -40°C to +105°C |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–75 | 50–80 | 65–75 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥9.0 | ≥6.5 | ≥8.0 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥350 | ≥400 | ≥300 |
| Compression Set (22h at 70°C) | ≤25% | ≤20% | ≤30% |
| Low-Temp Flexibility (Brittle Point) | ≤-55°C | ≤-65°C | ≤-45°C |
This structured customization pathway ensures that every plastic strip we deliver meets the highest standards of performance, reliability, and consistency for freezer door sealing systems.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision-Engineered Freezer Door Seal Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of industrial rubber formulation, specializing in mission-critical sealing components for extreme-temperature applications. Our proprietary elastomer compounds, rigorously developed for freezer and cold storage environments, directly address the persistent challenges of seal failure, energy leakage, and premature degradation faced by OEMs worldwide. When standard plastic or generic rubber strips succumb to cryogenic stress, our engineered solutions maintain structural integrity and sealing performance down to -60°C, ensuring operational reliability and compliance with stringent global energy efficiency standards.
The performance gap between commodity strips and engineered elastomers is quantifiable. Below is a comparative specification table highlighting the critical differentiators of our flagship freezer door seal compound against industry baseline materials. These values represent minimum guaranteed performance under accelerated aging and real-world cryogenic cycling tests per ASTM D2000 and ISO 188 protocols.
| Property | Test Method | Baoshida CryoSeal™ EPDM | Typical Commercial Strip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Flexibility | ASTM D1329 | -60°C (No Brittle Point) | -40°C to -30°C |
| Tensile Strength @ -40°C | ASTM D412 | ≥ 8.5 MPa | ≤ 4.0 MPa |
| Compression Set @ -30°C | ISO 815-1 | ≤ 18% (70h) | ≥ 35% (70h) |
| Shore A Hardness Range | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 3 | 70 ± 5 |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | Pass (500 pphm, 100h) | Fail (200 pphm, 48h) |
These specifications are not theoretical ideals but production-relevant benchmarks validated across 12+ global freezer OEM partnerships. Our formulations integrate advanced polymer architectures and nano-reinforced fillers to eliminate common failure modes: permanent set deformation after repeated door cycling, surface cracking from ozone exposure, and loss of resilience below -25°C. Each compound batch undergoes traceable lot testing with certified mill certificates, ensuring consistency for high-volume assembly lines.
For OEMs seeking to reduce field warranty claims and enhance product lifecycle value, direct collaboration with our technical team is essential. Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager, possesses 15 years of hands-on experience in cryogenic sealing system integration. He leads cross-functional support from initial material selection through DFM optimization and PPAP documentation, ensuring seamless adoption into your manufacturing process. Mr. Boyce facilitates rapid prototyping with our Suzhou-based R&D lab, providing data-driven validation of seal performance against your specific door geometry, closure force parameters, and environmental exposure profiles.
Initiate a technical consultation to receive a customized material performance dossier and feasibility assessment for your freezer door application. Contact Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] with your project specifications, target operating temperature range, and volume requirements. Include any existing failure mode analysis or competitor material data for accelerated evaluation. Suzhou Baoshida commits to delivering a documented technical proposal with material test reports and cost modeling within 72 business hours of receiving complete project details. Partner with us to transform freezer door reliability from a maintenance liability into a competitive differentiator. Precision engineering begins with precise communication—reach out to secure your cold chain integrity.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
