Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Plastic Window Molding
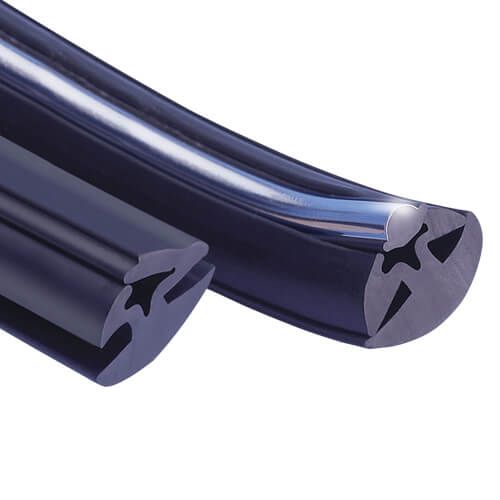

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Plastic Window Molding
Material selection is the cornerstone of functional plastic window molding performance, directly dictating service life, sealing integrity, and compliance with OEM specifications. Off-the-shelf rubber compounds frequently fail in demanding automotive and architectural applications due to inherent compromises in standardized formulations. These generic solutions prioritize broad market compatibility over the precise environmental and mechanical stresses encountered in real-world window systems. Consequently, premature degradation—manifested as cracking, hardening, compression set, or fluid intrusion—compromises weatherproofing and accelerates system failure.
The root cause lies in unaddressed application-specific variables. Standard EPDM or TPE compounds often lack tailored resistance to localized conditions: prolonged UV exposure in sunbelt regions, extreme cold cycling in northern climates, or exposure to modern automotive fluids like ethanol-blended fuels and ozone-rich urban atmospheres. Off-the-shelf materials typically exhibit narrow operational windows, failing to balance critical properties such as low-temperature flexibility (-40°C) with high-temperature stability (130°C+). Furthermore, they rarely incorporate specialized additives for hydrolytic stability against acid rain or chemical resistance to window cleaning agents, leading to surface degradation and loss of elasticity. This one-size-fits-all approach ignores the nuanced interplay between material chemistry and dynamic sealing requirements, where even minor property deviations cause cascading failures in window mechanism operation and occupant comfort.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses these gaps through application-driven compound engineering. We formulate custom rubber solutions by rigorously analyzing OEM environmental profiles, mechanical loads, and regulatory mandates (e.g., ISO 1817, ASTM D2000). Our process begins with substrate adhesion testing to ensure bonding integrity with PVC or aluminum window frames, followed by accelerated aging protocols simulating 10+ years of exposure. Critical additives—including定制ized antioxidant packages, nano-reinforced fillers, and proprietary plasticizers—are precisely dosed to achieve target Shore A hardness (65–75), elongation (>300%), and compression set (<25% per ASTM D395). This eliminates the trade-offs inherent in commodity materials, where improving one property (e.g., ozone resistance) often degrades another (e.g., low-temperature flexibility).
The performance delta between generic and engineered compounds is quantifiable. Consider the comparative specifications below:
| Property | Off-the-Shelf EPDM | Baoshida Custom Compound | Critical Impact of Deficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | 35–45% | ≤22% | Permanent deformation → air/water ingress |
| Low-Temperature Flexibility | -30°C (brittle point) | -50°C (brittle point) | Seal fracture during cold cycling |
| Fluid Resistance (SAE 2) | Severe swelling (>25%) | Swelling <8% | Loss of sealing force → fogging |
| Ozone Resistance (50pphm) | Cracking at 25% strain | No cracks at 50% strain | Surface degradation → accelerated aging |
OEMs must recognize that window molding is not a commodity component but a precision-engineered system interface. Partnering with a compound specialist during the design phase—rather than retrofitting failures—ensures material properties align with dynamic sealing physics and lifetime cost targets. At Suzhou Baoshida, we transform material science into operational reliability, eliminating the hidden costs of premature field failures through chemistry calibrated to your exact requirements.
Material Specifications
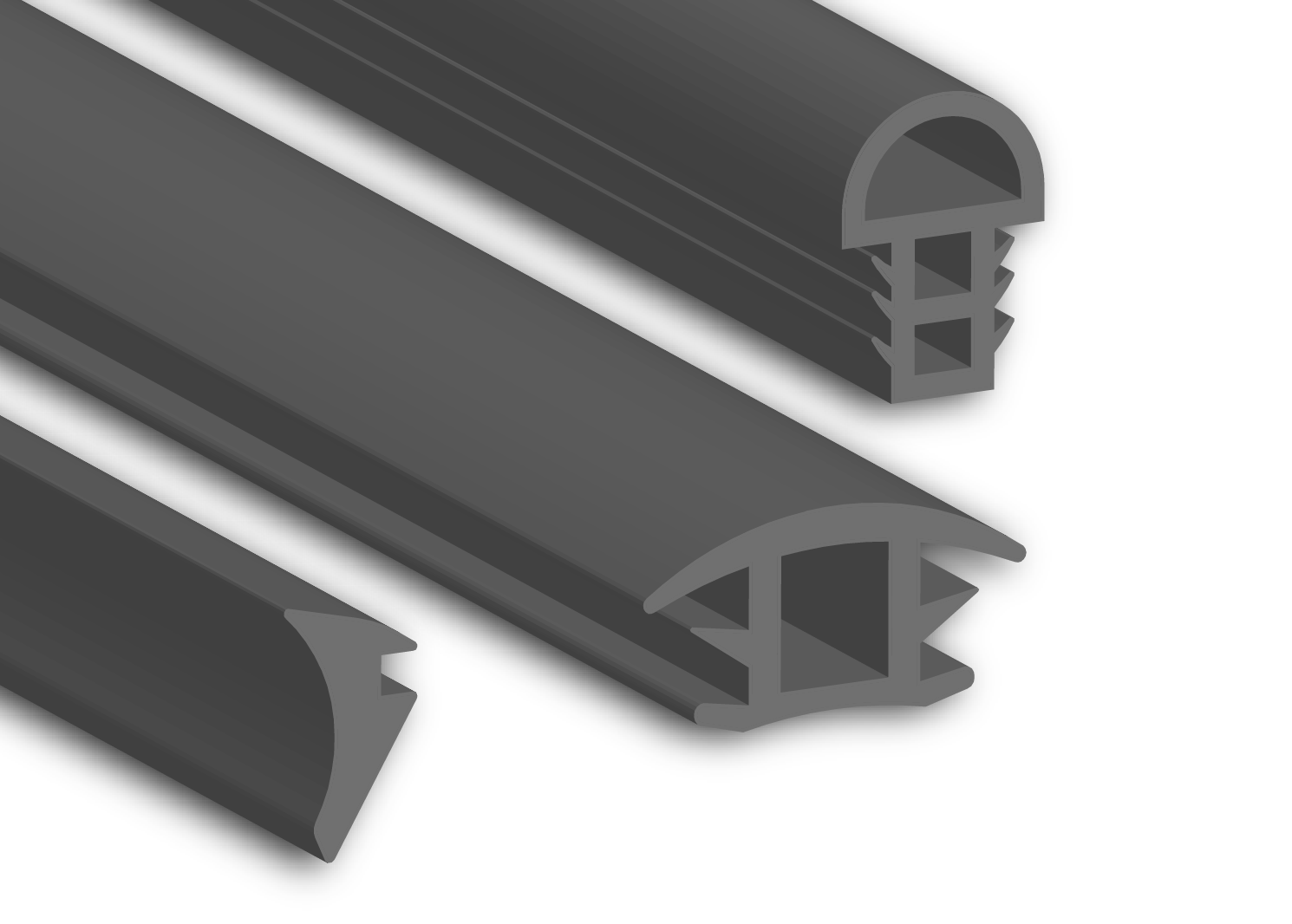
Material selection is a critical factor in the performance, durability, and cost-efficiency of custom molded rubber parts, particularly in demanding applications such as plastic window molding. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision-engineered rubber components tailored to meet OEM specifications and environmental challenges. For plastic window molding, the three most widely used elastomers are Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers distinct advantages depending on temperature range, chemical exposure, mechanical stress, and sealing requirements.
Viton is a fluorocarbon-based rubber renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. With continuous service capabilities up to 230°C and intermittent exposure tolerance beyond that, Viton is ideal for automotive and industrial applications where extreme thermal stability and chemical inertness are required. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it a preferred choice for long-life seals in harsh environments. However, Viton has higher material costs and lower flexibility at low temperatures compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is a cost-effective solution for applications involving exposure to petroleum-based oils, greases, and hydraulic fluids. It offers good abrasion resistance and tensile strength, with operational temperatures typically ranging from -30°C to 100°C, extendable to 120°C for limited durations. Nitrile is widely used in automotive and general industrial sealing due to its reliable performance and economic efficiency. While it performs poorly in ozone and UV environments and has limited high-temperature capability, its compatibility with common fluids makes it a staple in window molding for vehicles and machinery.
Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature applications, with a service range from -60°C to 200°C, and short-term resilience up to 250°C. It offers excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for exterior-facing window seals exposed to sunlight and climatic variation. Silicone also maintains flexibility at low temperatures and demonstrates good electrical insulation properties. However, it has lower mechanical strength and abrasion resistance compared to Nitrile and Viton, and it is less resistant to petroleum-based fluids.
Understanding these material properties enables optimal selection based on operational demands and lifecycle expectations.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Fluid Resistance | Excellent (oils, fuels, acids) | Good (oils, greases) | Poor (oils, fuels) |
| Ozone/UV Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Low | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Typical Applications | Automotive engine seals, aerospace | Fuel systems, gaskets, O-rings | Exterior seals, medical, electrical |
Material selection directly impacts product longevity and system integrity. Our engineering team at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports clients in matching material properties with real-world operating conditions to ensure optimal performance in plastic window molding and other custom rubber applications.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capabilities for Precision Plastic Window Molding
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber solutions for plastic window molding through integrated material science and precision manufacturing. Our technical foundation rests on a dedicated team of five Mold Design Engineers and two Rubber Formula Engineers, operating within a unified OEM framework. This structure ensures seamless translation of client specifications into high-performance, production-ready components. Unlike commodity suppliers, we prioritize material-property optimization and mold-flow dynamics at the design phase, directly addressing industry pain points such as thermal expansion mismatches, compression set in dynamic seals, and adhesion failures at plastic-rubber interfaces.
Our Formula Engineers specialize in custom elastomer development for window gasket applications, focusing on Shore A hardness stability (60–80 durometer range), UV/ozone resistance per ASTM D1149, and low-temperature flexibility down to -40°C. Each compound formulation undergoes rigorous crosslink density analysis and dynamic mechanical testing to ensure dimensional stability across temperature cycles. Concurrently, Mold Engineers deploy advanced CAD/CAM tools (SolidWorks, Moldflow) to optimize cavity geometry, runner systems, and venting for zero-flashing production. Critical attention is given to parting line placement and gate design to eliminate weld lines in high-stress sealing zones, directly enhancing product longevity.
As an OEM partner, we implement a closed-loop engineering process from initial RFQ to量产. Clients receive detailed Design for Manufacturability (DFM) reports within 72 hours of concept submission, including mold-flow simulation data and material suitability assessments. Prototyping utilizes rapid steel molds with 3D-printed inserts for accelerated validation, reducing time-to-market by 30%. Full production leverages automated presses with real-time pressure-temperature monitoring, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency essential for automotive and architectural glazing systems.
Key engineering specifications are maintained across all projects as follows:
| Capability | Specification | Industrial Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Material Formulation | Custom EPDM/Silicone/TPV compounds | Eliminates seal degradation in coastal/high-UV environments |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.05 mm (critical sealing surfaces) | Ensures leak-proof window assembly |
| Mold Design Complexity | Up to 16-cavity hot-runner systems | Supports high-volume OEM demands (>500k units/year) |
| Testing Validation | 10,000+ compression set cycles (ASTM D395) | Guarantees 10+ year service life in operando |
| Process Control | SPC with CpK ≥1.67 on key dimensions | Reduces scrap rates to <0.15% |
This engineering rigor extends to regulatory compliance, with all materials meeting REACH, RoHS, and ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards where required. Suzhou Baoshida’s value lies in preempting field failures through science-led design—transforming window molding from a passive component into a reliability-critical system. Clients gain not just a supplier, but an extension of their R&D team, with full traceability from raw polymer batches to finished part certification. For plastic window systems demanding zero-defect performance, our integrated engineering approach delivers measurable risk reduction and lifecycle cost savings.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Plastic Window Molding at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., the customization of plastic window molding is executed through a rigorous, phase-gated engineering process designed to ensure dimensional accuracy, material compatibility, and long-term performance under real-world conditions. Our methodology integrates technical drawing analysis, precision rubber formulation, iterative prototyping, and scalable mass production, all aligned with OEM specifications and international quality standards.
The first phase, Drawing Analysis, involves a detailed review of customer-provided CAD models or 2D technical drawings. Our engineering team evaluates critical dimensions, tolerances, surface finish requirements, and installation interfaces. Special attention is given to sealing profiles, compression set zones, and environmental exposure zones such as UV, temperature extremes, and chemical contact. Any discrepancies or potential manufacturability issues are flagged and discussed with the client for resolution prior to material selection.
Following drawing validation, the Formulation phase begins. Based on the application environment and performance demands, our rubber chemists develop a custom elastomer compound. For plastic window molding, this typically involves EPDM, TPE, or silicone, selected for their weather resistance, flexibility, and adhesion properties. The formulation is optimized for Shore A hardness, tensile strength, elongation at break, and compression set—key parameters that determine sealing efficacy and service life. Additives such as UV stabilizers, anti-oxidants, and flame retardants are incorporated as required.
Once the compound is finalized, we proceed to Prototyping. Using precision CNC-machined molds or 3D-printed tooling, short-run samples are produced for functional testing. These prototypes undergo dimensional inspection via coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and are subjected to simulated environmental aging, compression stress relaxation, and adhesion tests. Feedback from customer trials is integrated into final design or material adjustments, ensuring compliance with both mechanical and aesthetic specifications.
Upon prototype approval, the project transitions to Mass Production. High-speed extrusion or injection molding lines are deployed, with real-time process monitoring and statistical process control (SPC) to maintain consistency. Each production batch undergoes rigorous quality checks, including visual inspection, hardness testing, and dimensional sampling. All materials are traceable, and certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH) are provided as standard.
The table below summarizes typical technical specifications for custom plastic window molding:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material | EPDM, TPE, Silicone | ASTM D1418 |
| Shore A Hardness | 40–80 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥7 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +120°C (up to +200°C for silicone) | — |
| Color Options | Custom (Pantone or RAL matched) | Visual Comparison |
This structured approach ensures that every custom plastic window molding solution delivered by Suzhou Baoshida meets the highest standards of engineering precision and field reliability.
Contact Engineering Team

Initiate Precision Rubber Component Collaboration with Suzhou Baoshida
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial manufacturing rigor, specializing in custom molded rubber solutions for demanding applications like plastic window molding systems. Our engineering team possesses deep expertise in formulating compounds that meet exacting automotive, architectural, and industrial sealing requirements, where thermal stability, compression set resistance, and UV durability are non-negotiable. We understand that suboptimal material selection or dimensional variance directly impacts assembly efficiency, product lifespan, and end-user satisfaction. Our commitment extends beyond part production to becoming a technical extension of your engineering department, ensuring seamless integration of our components into your final assembly process.
Our proprietary rubber formulations undergo stringent molecular-level optimization for plastic window molding applications. We prioritize compounds exhibiting exceptional adhesion to polycarbonate, PVC, and acrylic substrates while maintaining flexibility across extreme temperature ranges (-50°C to +150°C). Each compound batch is validated through accelerated aging protocols, Shore A hardness consistency checks, and dynamic mechanical analysis to guarantee performance under real-world stress conditions. Critical dimensional tolerances are maintained through precision tooling and in-process statistical process control, ensuring repeatability essential for automated window line integration. Below details our core technical capabilities for plastic window molding components:
| Parameter | Standard Capability | High-Precision Option | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Grades | EPDM, TPE, Silicone | Custom fluorosilicone | ASTM D2000, ISO 3767 |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.15 mm | ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768-mK |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 40 – 90 | 30 – 95 | ASTM D2240 |
| Compression Set (70°C) | ≤25% (22h) | ≤15% (22h) | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Adhesion Strength | 50 N/cm² (min) | 80 N/cm² (min) | ISO 813 |
| Lead Time (Prototype) | 15-20 days | 10-12 days | – |
Collaboration with Suzhou Baoshida eliminates the guesswork in rubber component specification. We conduct comprehensive failure mode analysis during the design phase, leveraging finite element analysis (FEA) to predict seal behavior under compression load and environmental exposure. Our ISO 9001-certified facility implements real-time process monitoring with traceability to individual material lots, providing auditable quality data crucial for OEM compliance. Whether you require low-volume prototyping for new window system validation or high-volume production with JIT delivery, our scalable manufacturing infrastructure ensures consistent part integrity without compromising on-speed line requirements.
To resolve specific challenges in your plastic window molding application—be it material hysteresis affecting window glide performance, seal distortion during high-speed installation, or long-term weathering resistance—direct engagement with our technical leadership is imperative. Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager, possesses 12 years of experience in automotive sealing systems and will initiate a structured technical consultation upon contact. He will coordinate material datasheets, coordinate dimensional validation protocols, and establish a project-specific communication channel within 24 hours of your inquiry. Do not proceed with generic rubber suppliers lacking application-specific formulation control. Contact Mr. Boyce immediately at [email protected] with your part drawings, performance requirements, and target volumes. Include reference code PWS-2024 in the subject line to prioritize engineering resource allocation. Suzhou Baoshida delivers not just molded rubber, but engineered sealing certainty.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
