Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Pneumatic Fender
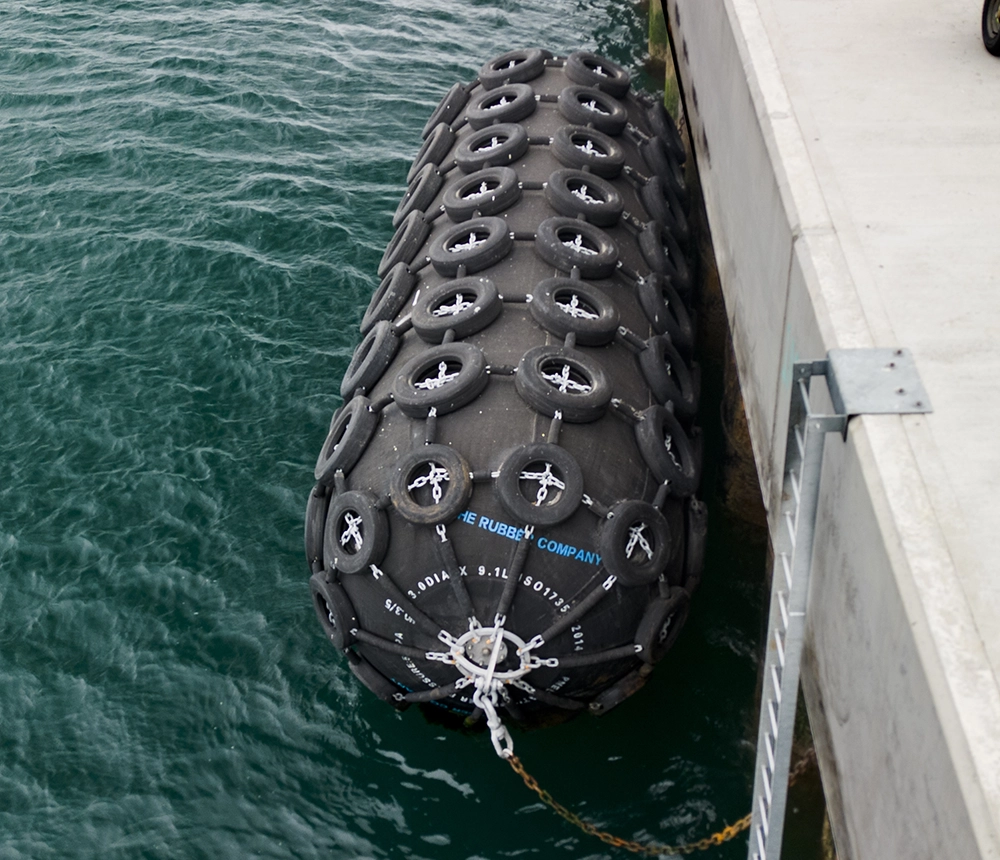

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality in Pneumatic Fender Performance
Pneumatic fenders serve as vital energy-absorbing interfaces in marine docking, offshore operations, and heavy machinery handling. Their failure directly compromises safety, increases downtime, and escalates operational costs. While off-the-shelf rubber solutions appear cost-effective initially, they consistently underperform in demanding industrial environments due to inadequate material science alignment with application-specific stressors. Generic compounds prioritize low production cost over engineered resilience, leading to premature degradation through three primary mechanisms: ozone-induced cracking, hydrocarbon fluid absorption, and irreversible compression set. These failures stem from unmodified polymer matrices lacking targeted stabilization against real-world exposure profiles.
Standard pneumatic fenders often utilize basic EPDM or SBR formulations with minimal additive packages. Such materials exhibit critical vulnerabilities when exposed to marine atmospheres rich in ozone, hydraulic oils, or prolonged compressive loads. Ozone attack initiates surface microcracks that propagate under cyclic stress, culminating in catastrophic structural failure. Similarly, unresistant elastomers swell excessively upon contact with petroleum-based fluids, reducing load-bearing capacity and dimensional stability. Most critically, poor rebound resilience in commodity rubbers causes permanent deformation after repeated compression cycles, eliminating the fender’s energy-absorbing function. These flaws are not manufacturing defects but inherent limitations of non-specialized formulations.
Suzhou Baoshida addresses these challenges through precision-tailored compound engineering. Our OEM-grade pneumatic fender materials leverage advanced polymer architectures—such as peroxide-cured HNBR or specialty EPDM blends—with rigorously optimized additive systems. Critical enhancements include: ozone-resistant polymer backbones, custom-synthesized antidegradants, and nano-reinforced fillers that maintain elasticity under sustained load. This approach ensures consistent performance across extreme variables: saltwater immersion, UV exposure, temperature fluctuations from -40°C to +120°C, and intermittent contact with hydraulic fluids.
The performance delta between generic and engineered compounds is quantifiable:
| Property | Standard EPDM Compound | Baoshida Engineered HNBR Blend | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ozone Resistance (50 pphm, 40°C, 96h) | Severe cracking | No visible cracks | ASTM D1149 |
| Oil Resistance (IRM 903, 70°C, 70h) | Volume swell >50% | Volume swell <15% | ASTM D471 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | 35% | 15% | ASTM D395 |
| Hardness Retention (Shore A) | ±8 points | ±3 points | ASTM D2240 |
This data underscores why material selection transcends procurement cost considerations. Off-the-shelf fenders fail because they treat rubber as a homogeneous commodity rather than a system-specific engineering component. Baoshida’s collaborative formulation process begins with OEM application mapping—analyzing load spectra, environmental exposure, and lifecycle requirements—to develop compounds where molecular stability directly correlates with operational uptime. We integrate accelerated aging protocols per ISO 188 and real-world validation to guarantee that every fender maintains its energy dissipation profile throughout its service life. In industrial contexts where reliability is non-negotiable, engineered elastomer science is not an option—it is the foundation of risk mitigation. Partner with us to transform pneumatic fenders from failure points into mission-critical assets through proactive materials engineering.
Material Specifications

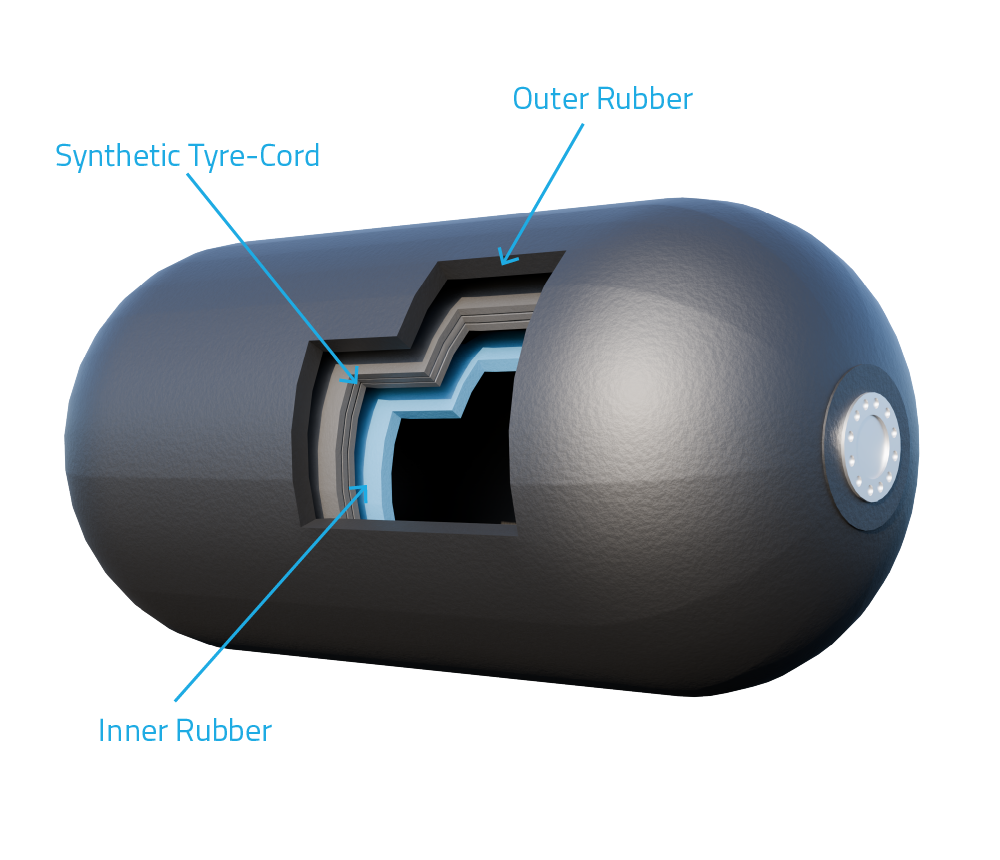
Pneumatic fenders are critical components in industrial applications requiring resilient, airtight sealing under dynamic pressure conditions. The performance and longevity of these fenders are directly influenced by the elastomeric material used in their construction. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision-engineered pneumatic fenders utilizing high-performance rubber compounds tailored to operational demands. Among the most widely specified materials are Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each offering distinct chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties suitable for specific industrial environments.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to 200°C (up to 250°C intermittently), Viton is the preferred choice for pneumatic fenders operating in extreme thermal and chemical environments, such as in petrochemical processing, aerospace systems, and high-temperature automation equipment. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics further enhance reliability in pressurized applications.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is a cost-effective solution offering superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. It performs reliably within a temperature range of -30°C to 100°C, with short-term excursions up to 120°C. Nitrile is widely used in general industrial pneumatic systems, automotive manufacturing, and hydraulic sealing applications where exposure to lubricants and greases is common. While less resistant to ozone and UV degradation compared to other elastomers, NBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for dynamic sealing duties.
Silicone rubber exhibits outstanding thermal stability across a wide range, from -60°C to 200°C, and maintains flexibility at low temperatures where other rubbers become brittle. It is highly resistant to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, making it suitable for outdoor and medical-grade applications. However, silicone has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton and Nitrile, and it swells in contact with hydrocarbon oils. Its use is typically optimized in clean environments such as food processing, pharmaceutical systems, and electronic enclosures where purity and thermal cycling are critical.
Selection of the appropriate elastomer must consider fluid compatibility, temperature profile, mechanical stress, and regulatory requirements. Our engineering team at Suzhou Baoshida supports OEM clients with material validation testing and custom compounding to meet exact performance criteria.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 200 (250 intermittent) | -30 to 100 (120 intermittent) | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–20 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–400 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A, 70–80) | 70–90 | 60–80 | 40–80 |
| Fluid Resistance | Excellent (oils, fuels, acids) | Excellent (petroleum oils) | Poor (hydrocarbons) |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Ozone/UV Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Gas Permeability | Low | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, chemical seals | Automotive, hydraulics | Medical, food, electronics |
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Excellence in Pneumatic Fender Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise to deliver precision-engineered pneumatic fenders for global maritime and industrial applications. Our integrated engineering team—comprising five dedicated mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers—ensures every product meets stringent performance, durability, and safety standards. This collaborative structure bridges material science with advanced manufacturing, eliminating silos between compound development and production tooling.
Our mould engineering team excels in complex cavity design, finite element analysis (FEA), and rapid prototyping. Utilizing Siemens NX and Moldflow simulation software, we optimize wall thickness uniformity, material flow, and curing kinetics to prevent defects like voids or uneven compression. Each mould undergoes rigorous thermal cycling validation to guarantee dimensional stability across 50,000+ production cycles. This precision directly translates to fenders with consistent Shore hardness, minimal flash, and exact geometric tolerances critical for berthing energy absorption.
Complementing this, our rubber formula engineers develop proprietary elastomer compounds tailored to operational extremes. Through iterative lab testing and ASTM D2000 classification adherence, we formulate EPDM and CR blends resistant to ozone, seawater, UV degradation, and temperatures from -40°C to +120°C. Each compound is engineered for specific shore hardness ranges, elongation properties, and rebound resilience—ensuring optimal energy dissipation during vessel impact. Material batches undergo full traceability via QR-coded lot tracking, with third-party validation of tensile strength, tear resistance, and compression set per ISO 37 and ISO 815 standards.
As a certified OEM partner, we manage end-to-end customization—from concept to serial production. Clients provide operational parameters (e.g., vessel displacement, berthing velocity), and our engineers co-develop fenders meeting ISO 17357-1:2018 requirements. This includes finite element modeling of energy absorption curves, accelerated aging tests, and on-site installation support. Our facility supports low-volume bespoke runs (1–50 units) and high-volume contracts (500+ units) with identical quality control protocols, including 100% hydrostatic pressure testing at 1.5x working pressure.
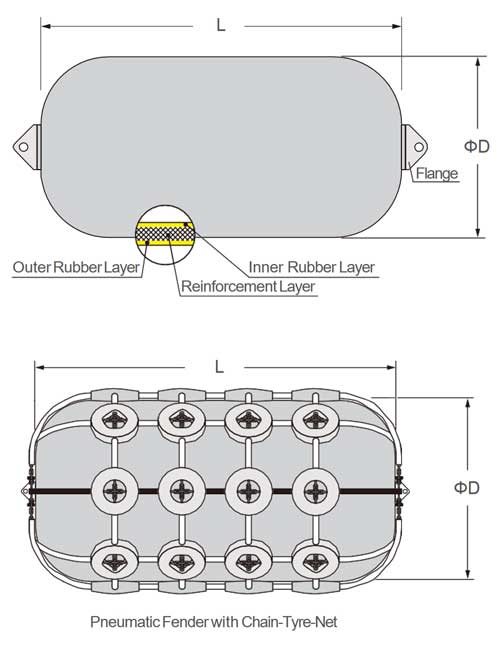
Critical Pneumatic Fender Specifications
| Parameter | Standard Range | Testing Standard | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore Hardness (A) | 70–90 | ASTM D2240 | ±3 points |
| Operating Pressure | 0.3–0.8 MPa | ISO 17357-1 | ±0.05 MPa |
| Temperature Resistance | -40°C to +120°C | ISO 188 | Full property retention |
| Ozone Resistance | 50 pphm, 40°C, 200 hrs | ASTM D1149 | No cracking |
| Tensile Strength | ≥12 MPa | ISO 37 | ±1.5 MPa |
This engineering synergy—validated through 15+ years of OEM partnerships with major port operators and shipbuilders—ensures pneumatic fenders that exceed lifecycle expectations. Suzhou Baoshida’s commitment to material innovation and tooling precision delivers not just components, but mission-critical safety solutions engineered for real-world resilience.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for pneumatic fenders begins with a rigorous drawing analysis to ensure dimensional accuracy, performance compliance, and integration readiness with the client’s system. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team evaluates technical drawings provided by OEM partners, focusing on critical parameters such as outer diameter, inner bore, wall thickness, flange configuration, and tolerance specifications. We assess material contact surfaces, pressure zones, and dynamic stress points to anticipate operational challenges. This phase includes cross-referencing international standards such as ISO 22013 and DIN 28184, ensuring compliance with industrial safety and performance benchmarks. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities are flagged for collaborative review, enabling design refinement before material selection.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our rubber formula engineers initiate material formulation tailored to the operational environment of the pneumatic fender. The selection of polymer base—typically NR (Natural Rubber), EPDM, or NBR—is determined by factors including temperature range, ozone exposure, fluid resistance, and mechanical stress. For marine or offshore applications, EPDM is preferred for its superior weather and UV resistance, while NR offers optimal elasticity and rebound resilience for high-impact buffer systems. Additives such as carbon black, sulfur, and anti-degradants are precisely metered to enhance tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and aging performance. Each compound is modeled using rheological simulation software to predict cure behavior and compression set characteristics. The final formulation is documented and archived for batch traceability and reproductivity.
Prototyping and Validation
A functional prototype is manufactured using precision molding techniques, including compression or transfer molding, under controlled vulcanization conditions. The prototype undergoes a battery of physical and mechanical tests, including hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, elongation at break, and dynamic deflection under load. We perform air retention testing at 1.5 times the rated working pressure to verify seal integrity. Dimensional inspection is conducted via CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) to ensure conformity within ±0.5 mm tolerance. Clients receive a comprehensive test report alongside prototype samples for field evaluation. Feedback is integrated into a final design freeze, confirming readiness for scale-up.
Mass Production and Quality Assurance
Once approved, the project transitions to mass production in our ISO-certified facility. Automated batching systems ensure consistent compound mixing, while mold monitoring systems track temperature, pressure, and cure time in real time. Each pneumatic fender is visually inspected and subjected to 100% air pressure testing. Batch samples undergo periodic third-party validation for long-term performance. Traceability is maintained through laser marking and digital logs.
| Parameter | Standard Value | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60 ± 5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥12 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥350% | ASTM D412 |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C to +80°C | ISO 1817 |
| Working Pressure | 0.4–0.8 MPa | Internal Hydrostatic |
| Compression Set (24h) | ≤20% | ASTM D395 |
Contact Engineering Team
Initiate Technical Collaboration for Precision Pneumatic Fender Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the forefront of industrial rubber compound development and OEM manufacturing, specializing in mission-critical pneumatic fenders for maritime, offshore, and heavy industrial applications. Our engineering team possesses deep expertise in formulating elastomers that withstand extreme cyclic stress, UV degradation, ozone exposure, and aggressive chemical environments inherent to marine operations. We do not merely supply components; we deliver engineered resilience through rigorous material science and process validation. Each pneumatic fender solution is developed under ISO 9001-certified protocols, integrating finite element analysis (FEA) for structural optimization and accelerated aging tests to guarantee 20+ years of service life under operational duress.
Our competitive differentiation lies in proprietary rubber formulations that balance Shore A hardness, energy absorption efficiency, and fatigue resistance—parameters non-negotiable for vessel berthing safety and infrastructure protection. Unlike commoditized alternatives, Baoshida’s compounds undergo dynamic compression testing at 500,000+ cycles to simulate real-world impact scenarios, ensuring zero delamination or permanent set. We collaborate directly with naval architects and terminal operators to tailor fender performance to specific vessel displacement profiles, tidal ranges, and berthing velocities. This precision engineering approach minimizes downtime, reduces replacement costs, and meets stringent classification society standards (DNV, ABS, LR).
Below outlines core technical specifications achievable through our custom formulation process:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Durometer (Shore A) | 55–75 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥18 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥450% | ASTM D412 |
| Tear Resistance | ≥90 kN/m | ASTM D624 |
| Compression Set (70°C) | ≤22% (22h) | ASTM D395 |
| Ozone Resistance | No cracks (200 pphm) | ASTM D1149 |
| Adhesion Strength | ≥8 kN/m | ISO 813 |
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida eliminates the risk of substandard elastomer performance in high-stakes environments. We manage end-to-end production—from raw material sourcing (including halogen-free and recycled content options) to vulcanization control and non-destructive testing—ensuring batch-to-batch consistency for global OEM programs. Our facility supports volumes from prototype validation to 50,000+ units annually, with dedicated tooling for complex geometries up to Ø3.5m diameter.
To integrate Baoshida’s engineering precision into your pneumatic fender supply chain, contact Mr. Boyce, our OEM Strategic Account Manager. He will facilitate a technical consultation to assess your operational requirements, material specifications, and compliance frameworks. Mr. Boyce possesses direct authority to mobilize our R&D team for custom compound development and expedite feasibility studies within 72 hours of engagement. Provide your berthing load diagrams, environmental exposure data, and target lifecycle metrics to receive a validated performance proposal with cost-in-use analysis.
Initiate this critical dialogue via email at [email protected]. Include your company name, project timeline, and specific technical challenges for prioritized review. Suzhou Baoshida does not offer generic solutions; we engineer certainty for your most demanding impact protection scenarios. Engage our expertise to transform pneumatic fender reliability from an operational concern into a competitive advantage. All technical inquiries receive a detailed engineering response within one business day.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
