Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Pneumatic Rubber Fender
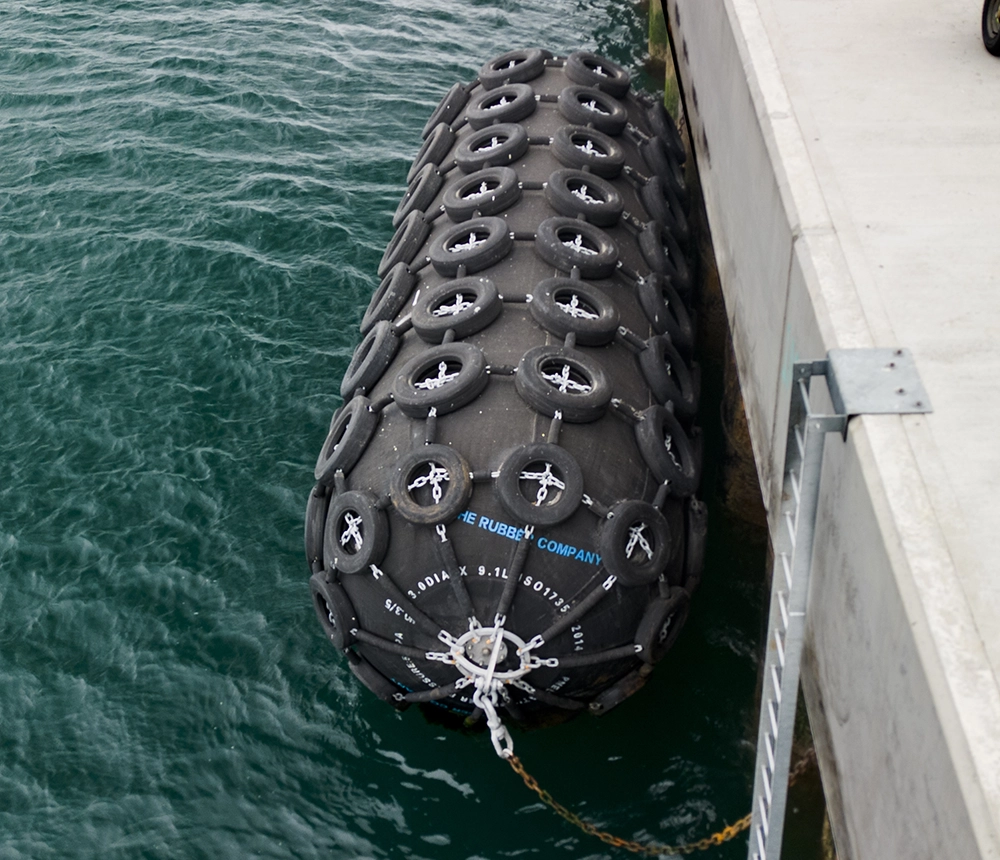

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Pneumatic Rubber Fenders
The performance and longevity of pneumatic rubber fenders are fundamentally determined by material selection. These components serve as critical impact-absorbing interfaces in marine, offshore, and industrial handling applications, where they mitigate kinetic energy during vessel berthing or equipment contact. Despite their seemingly simple construction, the operational demands placed on pneumatic fenders—extreme environmental exposure, cyclic loading, abrasion, and chemical contact—require a highly engineered approach to elastomer formulation. Off-the-shelf solutions often fail because they rely on generic rubber compounds optimized for cost rather than durability under real-world stress conditions.
Standard pneumatic fenders frequently utilize natural rubber (NR) or low-grade synthetic blends that lack resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and saltwater degradation. These materials may exhibit adequate initial elasticity and air retention but deteriorate rapidly when exposed to prolonged sunlight or marine atmospheres. Cracking, chalking, and loss of tensile strength are common failure modes observed within 12 to 18 months of deployment. Additionally, such compounds often lack the required resilience to repeated compression cycles, leading to permanent set deformation and reduced energy absorption efficiency.
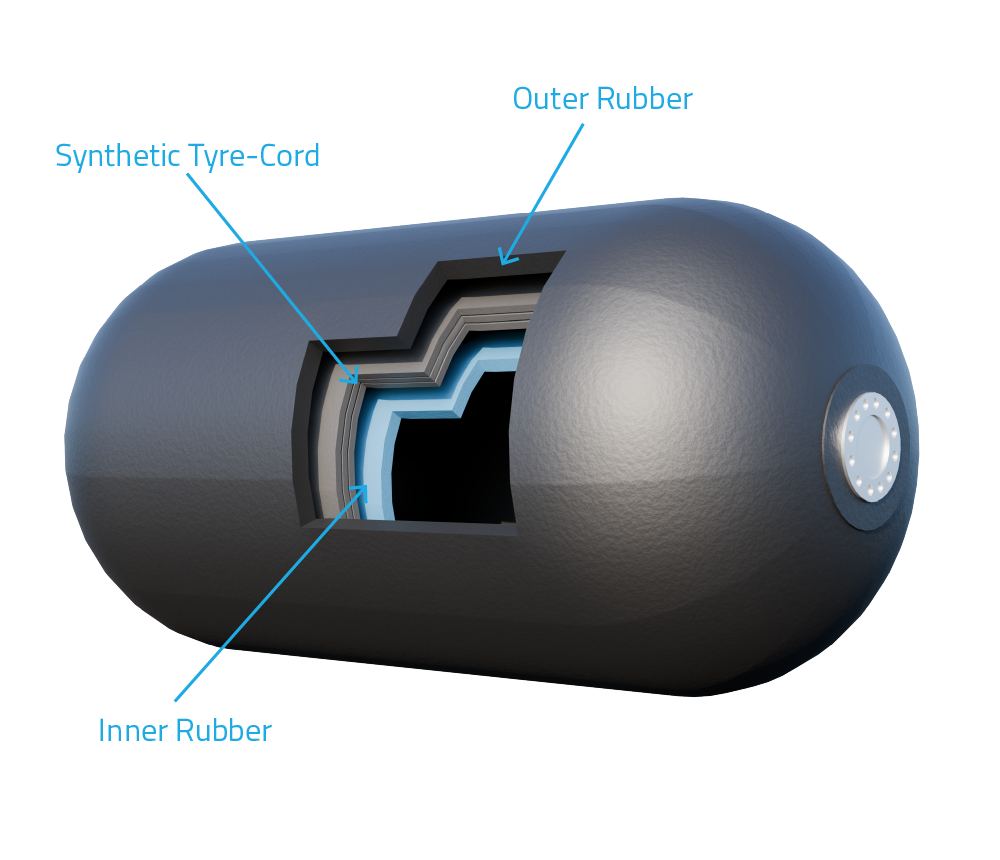
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering approach prioritizes high-saturation synthetic rubbers such as Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) and advanced chloroprene (CR) formulations. These materials offer superior resistance to weathering, oxidation, and marine corrosion. EPDM, in particular, demonstrates exceptional stability under prolonged UV exposure and maintains flexibility across a wide temperature range (–45°C to +135°C), making it ideal for offshore and arctic applications. Reinforcement with high-tenacity textile cords—typically nylon or aramid—ensures structural integrity under high internal pressure and external impact loads.
Another critical factor is the compatibility of rubber compounds with internal air pressure systems. Poorly formulated seals and valve interfaces in generic fenders lead to micro-leakage and gradual pressure loss, compromising fender performance. Our proprietary compounding process integrates co-cured valve seats and seamless inner liners made from halogenated butyl rubber (BIIR), which provides excellent air retention and chemical resistance.
Customization is not a luxury—it is a necessity in high-stakes industrial environments. Standardized fenders cannot account for site-specific variables such as tidal range, vessel tonnage, or berth frequency. By tailoring rubber hardness (durometer), wall thickness, and cord orientation to application requirements, we ensure optimal energy distribution and service life exceeding 15 years under routine maintenance.
The following table outlines key material specifications used in our engineered pneumatic rubber fenders compared to typical off-the-shelf alternatives:
| Property | Baoshida Engineered Fender | Standard Off-the-Shelf Fender |
|---|---|---|
| Base Elastomer | EPDM / CR Blend | Natural Rubber (NR) |
| Durometer (Shore A) | 60–70 | 50–60 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥25 MPa | 15–18 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥450% | 300–350% |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent (No cracking at 50 pphm, 40°C) | Poor (Cracking within 72 hours) |
| Operating Temperature Range | –45°C to +135°C | –10°C to +70°C |
| Air Retention (Pressure Loss/year) | <5% | 15–25% |
| Reinforcement Layer | Woven Nylon + Aramid | Polyester or Cotton |
Material selection is not merely a component decision—it is a system-level engineering imperative. At Suzhou Baoshida, we apply industrial rubber science to deliver fenders that perform reliably in the world’s most demanding maritime and industrial environments.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Pneumatic Rubber Fenders
Material selection critically determines the operational resilience and service life of pneumatic rubber fenders in demanding marine and industrial environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we rigorously evaluate elastomer formulations to ensure optimal performance under extreme mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and temperature fluctuations. Our engineering team prioritizes three primary compounds: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers distinct advantages and constraints, necessitating precise alignment with application-specific requirements.
Viton fluorocarbon rubber delivers exceptional resistance to aggressive chemicals, including hydrocarbons, acids, and ozone, making it ideal for fenders exposed to fuel, hydraulic fluids, or corrosive marine atmospheres. Its thermal stability supports continuous service up to 200°C, though costs are elevated compared to other elastomers. Viton fenders maintain structural integrity in high-temperature berthing operations but exhibit reduced flexibility at sub-zero conditions.
Nitrile rubber provides superior resistance to oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons at a competitive cost. With acrylonitrile content typically optimized at 34%, our NBR formulations achieve balanced abrasion resistance and tensile strength (15–25 MPa), suitable for standard port and offshore applications. However, NBR’s vulnerability to ozone, UV radiation, and polar solvents necessitates protective coatings in harsh environments. Its operational temperature range is limited to -30°C to 100°C, restricting use in extreme climates.
Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature applications, functioning reliably from -60°C to 230°C. Its inherent flexibility ensures consistent energy absorption in cryogenic or high-heat scenarios, while excellent electrical insulation properties benefit specialized industrial deployments. Silicone’s low surface energy resists adhesion from marine organisms, yet its comparatively low tensile strength (6–12 MPa) and susceptibility to tearing require reinforcement in high-impact zones.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. validates all materials against ISO 17357-1 standards for pneumatic fenders, ensuring compliance with international marine safety protocols. The comparative analysis below guides OEM selection based on quantifiable performance metrics.
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Resistance Properties | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Critical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | -20 to 200 | Fuels, acids, ozone, hydraulic fluids | 10–20 | 60–80 | High cost; poor low-temperature flexibility |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -30 to 100 | Oils, greases, aliphatic hydrocarbons | 15–25 | 50–75 | Vulnerable to ozone, UV, ketones, esters |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to 230 | Extreme temperatures, water, steam | 6–12 | 40–70 | Low tear strength; susceptible to abrasion |
Material choice directly impacts fender longevity, safety margins, and lifecycle costs. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. collaborates with OEM partners to conduct application-specific stress testing, ensuring the selected elastomer withstands dynamic compression, cyclic loading, and environmental degradation unique to each operational profile. Consult our engineering team for customized compound validation under ISO 37 and ASTM D2000 protocols.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Excellence in Pneumatic Rubber Fender Development
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, particularly in the design and production of high-performance pneumatic rubber fenders. Our team integrates deep material science expertise with advanced mold design to deliver OEM solutions that meet the rigorous demands of marine, offshore, and heavy industrial applications. Central to our technical strength is a dedicated engineering unit comprising five specialized mold engineers and two certified rubber formulation engineers. This multidisciplinary team ensures that every fender is optimized for performance, durability, and manufacturing efficiency.
Our mold engineers utilize state-of-the-art CAD/CAM software, including SolidWorks and AutoCAD, to develop precision steel molds with exacting dimensional control and optimized flow channels for uniform vulcanization. Each mold is engineered for long service life, minimal flash generation, and ease of maintenance—critical factors in high-volume OEM production. Finite element analysis (FEA) is routinely applied during the design phase to simulate stress distribution and deformation under load, ensuring that the final product meets international standards such as ISO 17357 and PIANC guidelines.
Complementing our mold engineering is our in-house rubber formulation expertise. Our two rubber formula engineers specialize in compounding elastomers for extreme environmental resistance, including seawater exposure, UV degradation, ozone attack, and wide temperature fluctuations. We primarily work with natural rubber (NR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), tailoring each compound to balance tensile strength, elongation at break, rebound resilience, and abrasion resistance. Our lab conducts iterative testing on cure kinetics, compression set, and aging behavior to validate formulation stability before full-scale production.
Our OEM capabilities allow us to develop custom fender systems tailored to client specifications—whether in geometry, load-deflection profile, or attachment interface. We support clients from concept validation through prototyping, tooling, and serial manufacturing, maintaining full traceability and documentation per ISO 9001 standards. This end-to-end control ensures consistency, reduces time-to-market, and supports compliance with classification society requirements including CCS, ABS, and DNV.
The following table outlines the standard technical specifications achievable with our current engineering and production platform:
| Parameter | Standard Range / Value | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 50–70 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥15 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥400% | ASTM D412 |
| Tear Resistance | ≥25 kN/m | ASTM D624 (Die B) |
| Compression Set (70°C × 24h) | ≤20% | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -30°C to +70°C | Internal Validation |
| Ozone Resistance | No cracking (200 pphm, 20%) | ASTM D1149 |
| Accelerated Aging (7 days) | Tensile retention ≥85% | ASTM D573 |
Through the synergy of advanced mold design and precision rubber chemistry, Suzhou Baoshida delivers engineered reliability in every pneumatic rubber fender. Our technical team remains committed to innovation, quality, and responsive OEM collaboration across global industrial markets.
Customization Process
Pneumatic Rubber Fender Customization Process: Precision Engineering from Concept to Deployment
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our pneumatic rubber fender customization adheres to a rigorously defined four-stage workflow, ensuring compliance with ISO 17357 marine safety standards and client-specific operational demands. This systematic approach eliminates design ambiguities and guarantees material-performance alignment before scaling to production.
Drawing Analysis initiates the process. Our engineering team conducts a granular review of client-provided CAD schematics and technical specifications, focusing on dimensional tolerances, pressure ratings, and environmental exposure parameters. Critical checks include verifying wall thickness consistency for hydrostatic load distribution, assessing flange geometry for vessel compatibility, and confirming material compatibility with seawater, UV, and ozone conditions. Any deviations from manufacturable tolerances (±0.5 mm for critical diameters) or structural weaknesses are flagged for collaborative redesign, preventing downstream tooling rework. This phase typically concludes within 72 hours with a formal feasibility report.
Formulation leverages our 15+ years of compound development expertise. Based on the validated design parameters, our rubber chemists select base polymers (EPDM for ozone resistance or SBR for abrasion tolerance) and engineer a bespoke compound balancing hardness, resilience, and fatigue life. Key properties are optimized through controlled adjustments of sulfur crosslink density, carbon black reinforcement, and antioxidant packages. The target specifications are non-negotiable; for instance, Shore A hardness must sustain 60–65 across -30°C to +70°C operational ranges without plasticizer migration.
| Property | ISO 17357 Requirement | Baoshida Control Range |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 55–70 | 62 ± 2 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥12 MPa | 14.5–16.0 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥300% | 380–420% |
| Ozone Resistance | 50 pphm, 40°C, 96h | Zero cracks |
| Hydrostatic Pressure | 1.5x working pressure | 2.0x with zero creep |
Prototyping transforms the formulation into physical validation. Using client-approved CAD data, we produce 3–5 units via precision molding under controlled vulcanization cycles (155°C ± 2°C, 18–22 minutes). Each prototype undergoes accelerated life testing: 10,000 compression cycles at 50% deflection, salt-spray exposure per ASTM B117, and burst pressure verification. Data from hydraulic pressure decay tests and Shore hardness mapping across the fender body are compiled into a test dossier. Client sign-off requires zero failures in critical metrics before progression.
Mass Production commences only after prototype validation. Our ISO 9001-certified facility employs real-time process monitoring, with every batch traceable via RFID tags logging cure temperature, pressure, and compound batch numbers. In-line checks include ultrasonic wall thickness scanning and 100% hydrostatic testing at 1.25x working pressure for 30 minutes. Statistical process control (SPC) charts track hardness and tensile deviations, maintaining CpK >1.67. Final inspection includes dimensional verification against the original drawing using CMM equipment, with certified material test reports (MTRs) supplied per shipment. This disciplined sequence ensures pneumatic fenders deliver consistent energy absorption and longevity in berthing operations, with zero tolerance for field failure.
Contact Engineering Team
For industrial operations requiring reliable, high-performance impact protection, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands as a leading provider of engineered rubber solutions. Our pneumatic rubber fenders are precision-designed for marine, offshore, and heavy industrial applications where energy absorption, durability, and consistent performance under dynamic loads are critical. As a trusted OEM partner, we combine advanced material science with rigorous quality control to deliver fenders that meet international standards and customized operational demands.
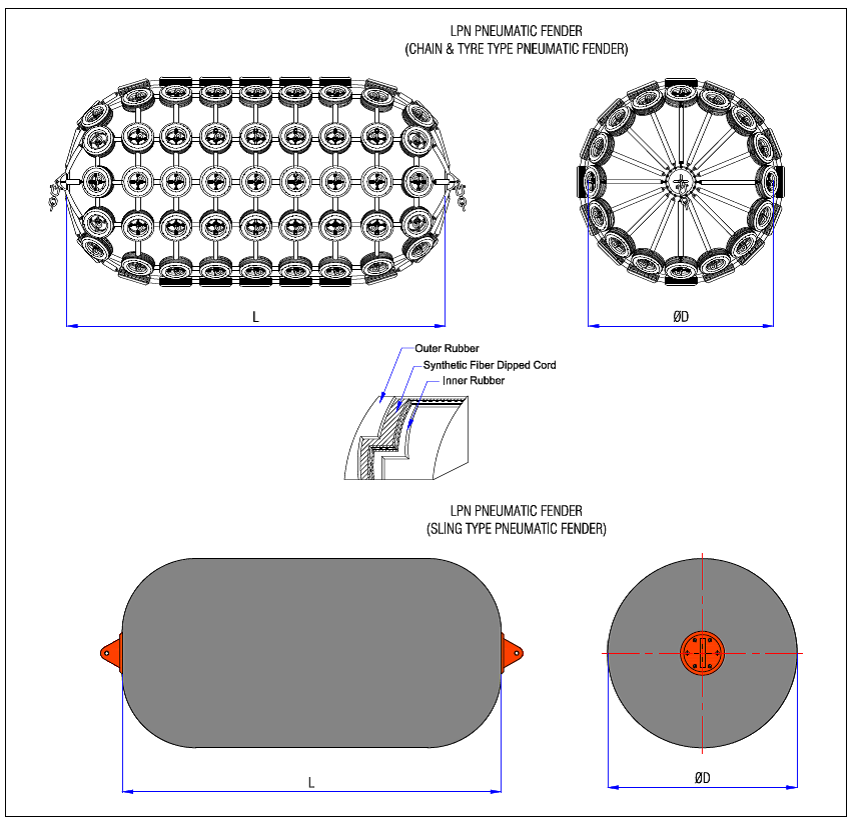
Our pneumatic rubber fenders are constructed using high-tensile synthetic rubber compounds, reinforced with multi-ply textile cord layers, and engineered for resistance to ozone, UV exposure, seawater, and extreme temperature fluctuations. Each unit undergoes hydrostatic and pneumatic testing to ensure leak integrity and structural resilience under operational pressure. Whether for ship-to-ship transfer, dockside berthing, or offshore platform protection, our fenders provide predictable reaction force curves and superior energy absorption characteristics.
We offer standard models in diameters ranging from 300 mm to 2000 mm, with working pressures calibrated between 0.2 bar and 0.8 bar, ensuring compatibility across a broad spectrum of vessel sizes and berthing energies. Custom configurations—including specialized flange fittings, integrated pressure monitoring systems, and enhanced abrasion-resistant covers—are available upon request. Our engineering team collaborates directly with clients to validate load profiles, environmental conditions, and installation parameters, ensuring optimal fender system performance.
All products are manufactured under ISO 9001-certified processes and comply with IACS UR S21, ISO 17357, and OCIMF guidelines. We provide full certification packages, including material test reports, pressure test documentation, and traceability records for every production batch.
For technical inquiries, project specifications, or OEM collaboration opportunities, contact Mr. Boyce, Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, directly at [email protected]. Mr. Boyce leads our application engineering division and specializes in custom elastomer formulation, finite element analysis (FEA) validation, and lifecycle optimization for industrial rubber components. He is available to support feasibility studies, prototype development, and on-site technical consultation.
| Specification | Range/Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 300 mm – 2000 mm |
| Working Pressure | 0.2 bar – 0.8 bar |
| Material Compound | NR/SBR blend with ozone-resistant additives |
| Reinforcement | 2–6 ply textile cord fabric (polyester/nylon) |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C to +70°C |
| Standards Compliance | ISO 17357, IACS UR S21, OCIMF |
| Test Protocol | 100% hydro-pneumatic testing, 72-hour pressure hold |
| Customization Options | Flange types, pressure sensors, protective chains, color coding |
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to integrate robust, scientifically formulated rubber fender systems into your next industrial or marine project. Reach out today to initiate technical dialogue and receive a performance-driven solution tailored to your operational environment.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
