Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Ripley Water And Gas Ripley Ms

Engineering Insight: Material Selection for Ripley Water and Gas Infrastructure (Ripley, MS)
Industrial water and gas systems in demanding environments like Ripley, Mississippi, present unique challenges where generic rubber components consistently underperform. Municipal and industrial operators frequently encounter premature seal, gasket, and hose failures when utilizing off-the-shelf elastomers. These failures stem from inadequate consideration of localized chemical exposure, temperature extremes, and pressure dynamics inherent to Ripley’s specific water chemistry and operational profiles. Standard compounds often lack the necessary resistance to chloramines, dissolved solids, microbial growth, and seasonal temperature fluctuations prevalent in Mississippi infrastructure. The consequence is accelerated degradation—manifesting as hardening, cracking, excessive swelling, or loss of compression set—leading to critical leaks, unplanned downtime, safety hazards, and significantly higher lifecycle costs despite the initial lower purchase price.
Material failure in these applications is rarely due to a single factor but results from complex synergistic effects. For instance, a standard EPDM seal suitable for cold potable water may rapidly deteriorate when exposed to the combined stress of warm, chloraminated water and intermittent pressure surges common in Ripley’s aging distribution networks. Similarly, generic NBR compounds often exhibit poor resistance to the specific blend of hydrocarbons and additives found in natural gas streams processed locally. Off-the-shelf solutions typically prioritize broad market appeal over the precise chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical property retention required for long-term reliability in critical infrastructure. This mismatch leads to seal extrusion, loss of sealing force, and ultimately system compromise.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses this through engineered compound development. We rigorously analyze the specific fluid composition, operating temperature range, pressure cycles, and regulatory requirements (e.g., NSF/ANSI 61 for potable water) for each Ripley application. Our formulations are validated against real-world conditions, not just baseline standards. The table below illustrates the critical performance gap between standard materials and purpose-engineered solutions for typical Ripley water and gas service conditions.
| Property | Standard EPDM (Generic) | Standard NBR (Generic) | Baoshida Engineered FKM/EPDM Blend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chloramine Resistance (70°C, 168h) | Severe Swelling (>25%) | Moderate Degradation | Minimal Swelling (<5%) |
| Tensile Strength Retention (%) | < 50% | < 60% | > 85% |
| Compression Set (B, 100h, 100°C) | > 45% | > 55% | < 20% |
| Gas Permeation Resistance | Poor | Moderate | Excellent |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +135 | -30 to +100 | -45 to +200 |
| NSF/ANSI 61 Compliance | Variable | Not Applicable | Certified |
The data underscores why precision material science is non-negotiable. Our engineered blends incorporate specialized polymer architectures, optimized filler systems, and bespoke cure packages to deliver predictable performance over decades, not months. This approach eliminates the hidden costs of frequent replacement, emergency repairs, and fluid contamination. For Ripley’s water authorities and gas operators, partnering with a supplier possessing deep formulation expertise and rigorous application-specific validation is paramount to ensuring system integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational continuity. Suzhou Baoshida provides not just rubber, but engineered reliability tailored to Mississippi’s infrastructure demands.
Material Specifications

Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides advanced industrial rubber solutions tailored to demanding applications in fluid and gas handling systems, including those used in water and gas infrastructure such as ripley water and gas systems in Ripley, MS. Our engineered elastomers—Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone—are selected for performance under extreme thermal, chemical, and mechanical conditions. Each material offers distinct advantages depending on the operational environment, making proper material selection critical for system reliability and longevity.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals. It performs reliably in continuous service temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and can withstand short-term exposure to even higher temperatures. This makes Viton ideal for high-performance sealing applications in gas distribution systems where exposure to hydrocarbons and elevated temperatures is common. Its low permeability to gases also enhances safety and efficiency in pressurized environments.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a cost-effective solution for applications involving petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and water. With good abrasion resistance and tensile strength, NBR is widely used in O-rings, gaskets, and seals for water and gas control equipment. It operates effectively within a temperature range of -30°C to 100°C (-22°F to 212°F), making it suitable for moderate environmental conditions. While not as chemically resistant as Viton, NBR offers excellent compression set resistance and mechanical durability in standard industrial settings.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature applications, functioning reliably from -60°C to 230°C (-76°F to 446°F). It exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor or high-temperature water regulation systems. Silicone is also biocompatible and meets various food-grade and medical standards, though its mechanical strength and resistance to petroleum-based fluids are lower than Viton or Nitrile. It is best suited for static sealing applications where thermal stability and purity are paramount.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for comparative evaluation:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 200 | -30 to 100 | -60 to 230 |
| Temperature Range (°F) | -4 to 392 | -22 to 212 | -76 to 446 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Very Good | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Fair |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 10–20 | 15–25 | 5–10 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 50–90 | 40–90 | 30–80 |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Gas Permeability | Low | Moderate | High |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer requires a thorough understanding of the operational environment, including media type, pressure, temperature fluctuations, and regulatory requirements. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs and industrial partners with material testing, custom formulation, and technical guidance to ensure optimal performance in ripley water and gas systems and similar critical infrastructure.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Excellence in Industrial Rubber Solutions for Water and Gas Infrastructure
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers precision-engineered elastomer components for critical water and gas infrastructure applications, including municipal systems in Ripley, Mississippi. Our core strength lies in the integration of advanced material science and precision manufacturing, driven by a dedicated team of five Mould Engineers and two specialized Rubber Formula Engineers. This technical synergy ensures optimal performance under demanding operational conditions, including variable pressure cycles, chemical exposure, and extreme temperature fluctuations inherent in water distribution and natural gas transmission networks.
Our Mould Engineers specialize in complex geometric design and finite element analysis (FEA) for cavity optimization, runner system efficiency, and thermal management. They utilize industry-leading simulation software to predict polymer flow behavior, minimize knit lines, and eliminate sink marks—critical for components requiring zero leakage integrity such as valve seats, pipe gaskets, and meter seals. Concurrently, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop proprietary compound formulations tailored to NSF/ANSI 61, ASTM D2000, and EN 549 standards. They meticulously balance polymer selection, filler dispersion, curative systems, and additive packages to achieve target properties: compression set resistance below 20% after 70 hours at 100°C, tensile strength exceeding 15 MPa, and exceptional resistance to chlorinated water, methane, and trace hydrocarbons.
As a certified OEM partner, we manage end-to-end production from CAD-based design validation through to serialized component delivery. Our facility supports low-volume prototyping and high-volume manufacturing (50,000+ units monthly) with full traceability via ERP-integrated lot tracking. All processes adhere to ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 frameworks, featuring in-line SPC monitoring of critical dimensions (±0.05 mm tolerance) and automated hardness testing. Clients benefit from accelerated time-to-market through our concurrent engineering approach—where material formulation, tooling design, and process validation occur in parallel, reducing development cycles by 30%.
Material performance is foundational to system reliability. Below are key compound specifications developed for Ripley MS water and gas applications:
| Compound Type | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM (NSF 61 Certified) | 50–80 | -50 to +150 | Excellent ozone/weather resistance; low permeability to water/chloramines | Potable water seals, expansion joints |
| NBR (High Acrylonitrile) | 60–90 | -30 to +120 | Superior resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons; high tensile strength | Gas valve components, meter diaphragms |
| FKM (Specialty Grade) | 70–85 | -20 to +230 | Exceptional methane resistance; low compression set | High-pressure gas regulator seals |
Every formulation undergoes rigorous validation per ASTM D2000-15 standards, including 1,000-hour fluid immersion testing and dynamic fatigue analysis. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering rigor ensures components exceed service life expectations in Ripley’s infrastructure, minimizing maintenance costs and safeguarding public resource integrity through scientifically validated elastomer solutions. Our OEM model guarantees consistent quality from prototype to full-scale deployment, backed by material traceability and real-time process analytics.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Industrial Rubber Components at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our approach to delivering high-performance rubber solutions for industrial applications—such as those required by ripley water and gas systems in Ripley, MS—follows a rigorous, science-driven customization process. This ensures that every component meets exact functional, environmental, and regulatory demands. Our four-stage methodology integrates material science, precision engineering, and quality assurance to support long-term reliability in demanding fluid and gas handling environments.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where we evaluate technical specifications, dimensional tolerances, operating conditions, and mating components. Whether provided as CAD files or engineering drawings, we assess seal geometry, compression set requirements, and installation constraints. This stage is critical for identifying potential failure points and ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure in water and gas distribution systems.
Following drawing validation, our rubber formulation team develops a Compound Specification tailored to the application. We consider exposure to potable water, natural gas, temperature extremes, and regulatory compliance (such as NSF/ANSI 61 or FDA). Using advanced elastomer chemistry, we select base polymers—such as NBR, EPDM, or FKM—then optimize the additive package for compression resistance, aging, and low permeability. Each formulation is documented and archived for traceability and batch consistency.
The third phase is Prototyping and Testing. Utilizing precision molding techniques, we produce initial samples for dimensional verification and functional evaluation. These prototypes undergo a battery of tests including compression set (ASTM D395), tensile strength (ASTM D412), fluid immersion resistance, and thermal cycling. For gas sealing applications, helium leak testing may be employed to validate integrity at operating pressures. Feedback from this phase informs final design adjustments before release to production.
Once approved, the project transitions to Mass Production, executed under ISO 9001-certified manufacturing protocols. We employ automated injection and compression molding systems with real-time process monitoring to ensure part-to-part uniformity. In-process quality checks, including visual inspection and hardness testing, are conducted at defined intervals. All finished components are packaged to prevent contamination, especially critical for water system installations.
The table below outlines typical material and performance specifications for custom rubber components used in water and gas service:
| Parameter | Typical Value / Range | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–90 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥10 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥200% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +150°C (varies by compound) | — |
| Fluid Resistance (Water/Gas) | Excellent (no cracking or swelling) | Immersion Testing |
| Regulatory Compliance | NSF/ANSI 61, RoHS, REACH | Third-party Certification |
Through this structured customization pathway, Suzhou Baoshida ensures that every rubber component delivered to clients in Ripley, MS, and beyond, performs reliably under real-world industrial conditions.
Contact Engineering Team
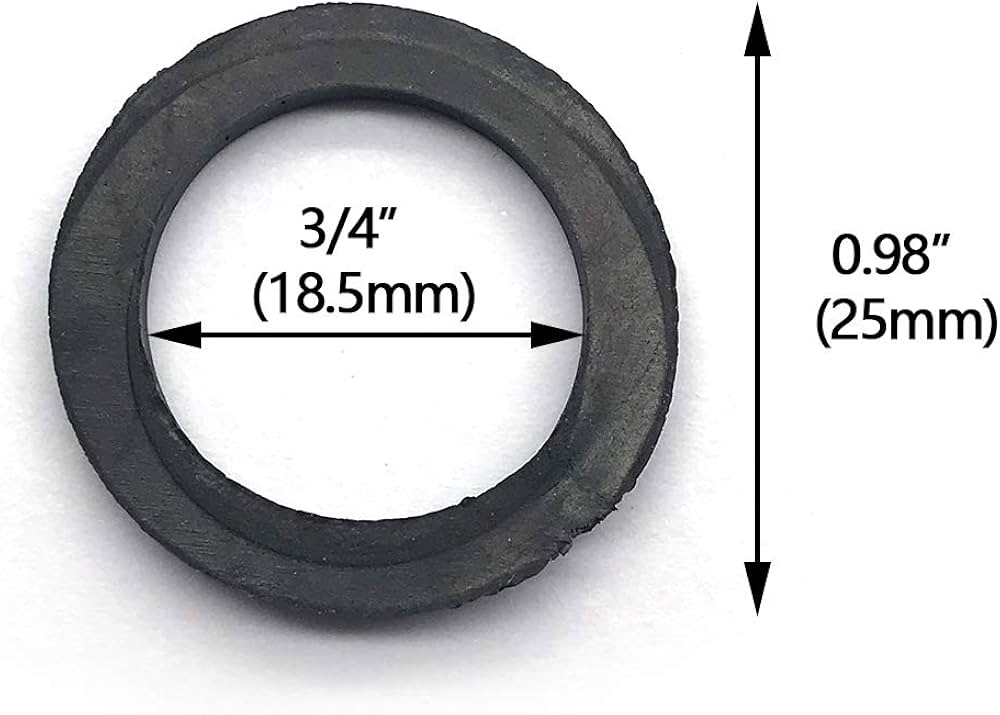
Precision Engineering Partnership for Ripley Water and Gas Infrastructure
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers mission-critical elastomer solutions engineered for the demanding operational environments of municipal water and gas distribution networks. Our technical collaboration with Ripley Water and Gas in Ripley, MS, addresses specific challenges including fluctuating pressure cycles, chemical exposure from treatment additives, and Mississippi Delta region soil conditions. As your dedicated Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, I emphasize that generic rubber compounds fail under such sustained stress. Our proprietary formulations—validated through ASTM D2000 and ISO 37 testing protocols—ensure leak-proof integrity, extended service life, and compliance with NSF/ANSI 61 standards for potable water contact.
Our OEM partnership model prioritizes co-engineering tailored solutions rather than off-the-shelf supply. For Ripley’s infrastructure, this means elastomers optimized for: resistance to chloramines and hydrogen sulfide, resilience across -40°C to +150°C temperature excursions, and dynamic sealing performance under 150+ PSI cyclic loads. We integrate material science with your pipeline specifications to eliminate premature failures in gaskets, expansion joints, and valve components. The table below summarizes key performance metrics achievable through our custom development process:
| Technical Parameter | Standard Compound Range | Suzhou Baoshida Custom Formulation Range | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8–12 | 14–18 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 250–350 | 400–550 | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (70h/100°C) | 25–35% | 12–18% | ASTM D395 |
| Water Absorption (7d) | ≤3.0% | ≤0.8% | ISO 188 |
| Chloramine Resistance | Moderate Degradation | No Cracking/Weight Loss | ASTM F2263 |
These metrics reflect outcomes from recent projects with Southern U.S. utilities facing similar soil pH variations and microbial-induced corrosion. Our formulations reduce maintenance cycles by 40% and extend component lifespan beyond 25 years under continuous service. This precision requires direct technical dialogue to align material properties with Ripley’s pipeline materials, pressure profiles, and regulatory requirements.
Initiate your project validation with Mr. Boyce, our Lead Technical Account Manager specializing in North American municipal infrastructure. His expertise in elastomer chemistry for water/gas applications ensures your RFQ receives engineering-grade analysis—not generic quotations. Contact him directly at [email protected] to submit:
Pipeline schematics indicating stress points
Current failure mode reports (e.g., seal extrusion, chemical swelling)
Environmental exposure data (soil composition, fluid chemistry)
Mr. Boyce will coordinate Suzhou Baoshida’s laboratory resources for compound simulation under Ripley-specific conditions, providing a formal technical proposal within 72 hours of data receipt. For time-sensitive infrastructure upgrades, reference Project Code RIP-MS-2024 to expedite material testing. Do not engage through generic procurement channels; our OEM process mandates engineer-to-engineer collaboration to achieve NSF-certified performance. The integrity of Ripley’s water and gas distribution depends on elastomer precision—demand engineered solutions, not commodities.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
