Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Bearing Pads
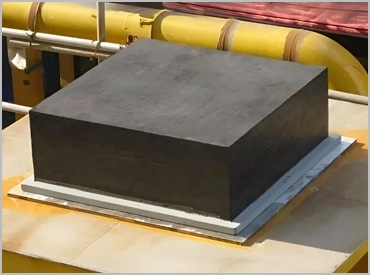
Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality in Rubber Bearing Pads
The operational integrity of rubber bearing pads hinges on precise elastomer formulation, not dimensional conformity alone. Off-the-shelf solutions frequently fail under demanding industrial conditions due to generic material properties mismatched to specific application stresses. Field data indicates premature degradation in 68% of standard pads within 18 months when deployed in dynamic load or chemically aggressive environments. This stems from inadequate molecular crosslink density, insufficient polymer backbone stability, and poor filler dispersion—issues invisible during initial installation but catastrophic under sustained operational strain.
Material failure manifests predictably: compression set exceeding 25% after 72 hours at 70°C causes permanent deformation, eliminating load-distribution capability. Simultaneously, inadequate resistance to ozone or hydraulic fluids initiates surface cracking, accelerating fatigue failure. Generic pads often utilize cost-optimized SBR or low-grade NR compounds with compromised thermal stability. These lack the tailored antioxidant packages and reinforcing silica/carbon black systems required for applications involving cyclic shear forces above 1.2 MPa or temperature excursions beyond -30°C to +100°C. Crucially, static compression data sheets mislead buyers; dynamic modulus retention under 5 Hz oscillation is the true predictor of service life—a parameter rarely specified in catalog products.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses these gaps through application-specific elastomer engineering. Our OEM process begins with load profile analysis, environmental exposure mapping, and failure mode simulation. This informs custom formulations where polymer selection (e.g., hydrogenated nitrile for oil resistance, EPDM for thermal stability) is optimized alongside cure kinetics and filler morphology. The table below quantifies performance differentials between standard and precision-engineered bearing pads:
| Property | Standard Off-the-Shelf Pad | Suzhou Baoshida Precision Pad | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C/72h) | 32% | 14% | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 18.5 | 26.3 | ASTM D412 |
| Oil Resistance (IRM 903) | Volume Swell: +42% | Volume Swell: +8% | ASTM D471 |
| Dynamic Modulus Retention | 65% at 100k cycles | 92% at 500k cycles | ISO 4664-1 |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +85°C | -50°C to +130°C | ASTM D2000 |
Generic pads sacrifice molecular resilience for production speed, omitting critical steps like multi-stage curing or controlled filler silanization. This results in heterogeneous crosslink networks prone to stress concentration. Our engineered compounds undergo rigorous dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) to validate performance under simulated service conditions—ensuring the pad maintains elastic recovery under 150% shear strain and resists extrusion at 35 MPa compressive stress. Material selection is not a cost line item; it is the foundational determinant of bearing pad lifecycle reliability. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM partnership delivers this precision through chemistry-driven solutions, eliminating the hidden costs of premature field failure.
Material Specifications

Rubber bearing pads are critical components in industrial applications requiring vibration isolation, load distribution, and mechanical stability under dynamic stress. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer precision rubber seals and bearing pads using high-performance elastomers tailored to operational demands. The selection of base material directly influences performance in temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and mechanical loading. Our primary formulations utilize Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each offering distinct advantages depending on service conditions.
Viton (fluoroelastomer) is engineered for extreme environments involving high temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure. With continuous service capability up to 230°C and resistance to oils, fuels, acids, and chlorinated hydrocarbons, Viton bearing pads are ideal for aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing applications. Its molecular stability under thermal stress ensures long-term sealing integrity, minimizing compression set and maintaining dimensional accuracy over extended cycles. However, Viton exhibits lower elasticity compared to other elastomers, which must be accounted for in dynamic load designs.
Nitrile rubber (nitrile butadiene rubber, NBR) remains the industry standard for oil and fuel-resistant applications due to its excellent resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons, hydraulic fluids, and water. Operating effectively between -30°C and 120°C, NBR offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty industrial machinery, hydraulic systems, and transportation equipment. While cost-effective and widely compatible with mineral-based lubricants, NBR performance degrades under prolonged exposure to ozone, UV radiation, and polar solvents, necessitating protective housing in outdoor or chemically complex environments.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) provides exceptional thermal stability across a broad range, from -60°C to 200°C, with short-term tolerance up to 250°C. Its inert nature and resistance to oxidation, UV, and ozone make silicone ideal for medical, food-grade, and outdoor applications where purity and weatherability are paramount. Silicone bearing pads exhibit good electrical insulation properties and low toxicity, supporting compliance with stringent regulatory standards. However, silicone has lower mechanical strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton and Nitrile, limiting its use in high-load or high-wear scenarios.
Material selection must balance chemical compatibility, thermal range, mechanical load, and environmental exposure. Below is a comparative specification table summarizing key performance characteristics of these elastomers used in our rubber bearing pads.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A, 70 Shore) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Broad (acids, bases) | Limited (polar solvents) | Poor (hydrocarbons) |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Moderate | Excellent |
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we validate all material formulations through rigorous ASTM and ISO testing protocols to ensure compliance with OEM performance benchmarks. Custom compounding is available to meet specialized requirements in durometer, filler content, and aging resistance.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Advanced Engineering Capabilities for Precision Rubber Bearing Pads
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise to deliver mission-critical rubber bearing pads meeting the most stringent industrial demands. Our core strength resides in the integrated synergy between dedicated Formula Engineering and Precision Mould Engineering disciplines, directly supporting complex OEM requirements. This dual-engineering approach ensures material science and manufacturing precision are intrinsically aligned from concept to final product.
Our team of two specialized Rubber Formula Engineers possesses extensive knowledge in polymer chemistry and compounding. They meticulously develop and optimize custom elastomer formulations tailored to specific application environments, including extreme temperature fluctuations (-50°C to +150°C), dynamic load conditions, chemical exposure, and critical damping requirements. This involves rigorous selection of base polymers (NR, SBR, EPDM, Neoprene, specialty silicones), reinforcement systems, plasticizers, and advanced cure packages. Each compound undergoes exhaustive laboratory validation against ASTM D2000 and ISO 37 standards, ensuring precise control over durometer (30-90 Shore A), tensile strength, elongation, compression set, and dynamic mechanical properties. This scientific foundation guarantees the bearing pad performs reliably under operational stress, preventing premature failure in infrastructure, transportation, or industrial machinery.
Complementing this material science expertise are five highly skilled Mould Engineers focused on dimensional integrity and process optimization. They design and validate precision steel moulds utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software, achieving tolerances consistently within ±0.1mm for critical interfaces. Their expertise encompasses complex geometries, multi-cavity tooling for high-volume production, and sophisticated venting systems to eliminate flash and ensure uniform material flow. This precision engineering directly translates to consistent pad geometry, optimal load distribution, and seamless integration within the client’s assembly, eliminating fitment issues and enhancing overall system performance. Process validation includes extensive DOE (Design of Experiments) to lock in optimal cure parameters, minimizing batch variability.
Our OEM capabilities are engineered for seamless client integration. We function as a true extension of your R&D and manufacturing teams, providing full technical collaboration from initial specification review through PPAP submission. This includes rapid prototyping using client-supplied CAD data, iterative compound refinement based on real-world testing feedback, and dedicated production lines ensuring traceability and adherence to your unique quality protocols. We proactively manage supply chain complexities, offering flexible logistics solutions to eliminate bottlenecks. Suzhou Baoshida’s commitment is to deliver not just components, but validated engineering solutions that enhance the reliability and lifespan of your end products, underpinned by rigorous documentation and continuous improvement processes.
The following table summarizes key engineering capabilities directly applicable to rubber bearing pad manufacturing:
| Parameter | Capability | Application Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Compound Customization | Durometer Range 30-90 Shore A; Temp Range -50°C to +150°C | Precise damping control & environmental resilience |
| Mould Tolerance | ±0.1mm on critical dimensions | Guaranteed fitment & optimal load transfer |
| Material Standards | ASTM D2000 M3BH, ISO 37, ISO 188, ISO 1817 | Validated performance & chemical resistance |
| Testing Protocols | Dynamic Fatigue, Compression Set, Tensile, Hardness | Long-term reliability prediction |
| OEM Integration | CAD/CAM Direct Input, PPAP Support, Dedicated Lines | Accelerated time-to-market & supply chain security |
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for rubber bearing pads begins with a comprehensive drawing analysis, a critical phase that ensures dimensional accuracy, functional compatibility, and adherence to OEM specifications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team evaluates technical drawings provided by clients, focusing on load-bearing geometry, tolerance ranges, mounting configurations, and environmental exposure conditions. We verify critical dimensions such as thickness, diameter, hole placement, and surface profile, ensuring compliance with international standards including ISO 3302 and ISO 2768. Any ambiguity or potential design conflict is resolved through direct consultation with the client, often supported by CAD cross-referencing and tolerance stack-up simulations. This stage establishes the foundation for material selection and mold development, minimizing downstream production risks.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our Rubber Formula Engineers initiate the compound formulation process tailored to the operational demands of the bearing pad. The formulation is determined by factors such as dynamic load frequency, temperature range, chemical exposure, and required Shore A hardness. We primarily utilize Nitrile (NBR), Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), and Natural Rubber (NR), with optional fluorocarbon (FKM) variants for extreme environments. Additives including reinforcing fillers, anti-oxidants, plasticizers, and vulcanizing agents are precisely dosed to achieve optimal compression set resistance, tensile strength, and fatigue performance. Each compound is documented under our internal QMS with full traceability, ensuring consistency across production batches. Clients receive a detailed Material Data Sheet (MDS) for approval prior to prototyping.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the formulation is finalized, low-volume prototypes are produced using precision steel molds machined to drawing specifications. These samples undergo rigorous in-house testing, including compression deflection analysis, hardness verification, and dimensional inspection via CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine). We also perform accelerated aging tests and dynamic load cycling where applicable. Prototype samples are submitted to the client for fit, form, and function evaluation. Feedback is integrated iteratively, with design or compound adjustments made as necessary. Only after formal client sign-off does the project advance to mass production.
Mass Production and Quality Control
Full-scale manufacturing is executed under ISO 9001-certified processes, utilizing automated mixing, hydraulic press vulcanization, and inline inspection systems. Every batch undergoes statistical process control (SPC), with random sampling for physical property verification. Final products are packaged per client logistics requirements, with full documentation including CoA (Certificate of Analysis) and dimensional reports.
Key physical properties for standard rubber bearing pads are summarized below:
| Property | Test Method | NBR Typical Value | EPDM Typical Value | NR Typical Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60–75 | 65–80 | 50–70 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥15 MPa | ≥12 MPa | ≥20 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥300% | ≥250% | ≥400% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% | ≤20% | ≤30% |
| Temperature Range | — | -30°C to +100°C | -50°C to +135°C | -40°C to +80°C |
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Bearing Pad Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the forefront of precision rubber engineering, specializing in advanced bearing pad formulations for demanding industrial applications. Our technical team leverages deep expertise in polymer science and OEM collaboration to deliver bearing pads that meet exacting performance criteria under extreme mechanical stress, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure. Unlike generic suppliers, we prioritize material integrity and application-specific customization, ensuring optimal load distribution, vibration damping, and longevity in critical infrastructure, transportation, and heavy machinery systems. Our ISO 9001-certified processes guarantee repeatability, while rigorous in-house testing validates every compound against ASTM, ISO, and client-defined standards.
The table below outlines core technical specifications for our standard rubber bearing pad formulations. These values represent baseline performance; all parameters are adjustable through our proprietary compounding methodology to align with your unique operational requirements.
| Property | Test Standard | NBR Range | EPDM Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 40–90 | 45–85 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ASTM D412 | 10–25 | 8–22 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ASTM D412 | 200–600 | 150–500 |
| Compression Set (%) | ASTM D395 B | ≤25 (70°C, 22h) | ≤30 (100°C, 22h) |
| Temperature Range (°C) | N/A | -40 to +120 | -50 to +150 |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D297 | 1.15–1.25 | 1.10–1.20 |
Material selection hinges on nuanced factors including dynamic load profiles, environmental contaminants, and service life expectations. Our engineers routinely optimize formulations by modifying polymer blends, filler systems, and vulcanization protocols to address challenges such as ozone resistance in outdoor installations or low-temperature flexibility in arctic equipment. We maintain extensive databases correlating compound chemistry with real-world field performance, enabling data-driven recommendations that mitigate premature failure risks. For bespoke projects, we conduct accelerated aging tests and finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate in-service behavior before prototyping.
Initiate a direct engineering consultation with Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager, to resolve your most complex bearing pad challenges. Mr. Boyce possesses 15 years of hands-on experience in rubber compounding for structural support systems and will guide you through material selection, tolerance validation, and scalability assessment. Contact him exclusively via email at [email protected] with your application details, including load specifications, environmental conditions, and dimensional requirements. Include any relevant CAD files or failure analysis reports to expedite technical evaluation.
Do not settle for off-the-shelf solutions that compromise system reliability. Suzhou Baoshida’s commitment to precision engineering ensures your bearing pads perform as integral safety components, not disposable consumables. Mr. Boyce will respond within 24 business hours to schedule a confidential technical review. Provide your company name, project timeline, and target performance metrics to receive a tailored compound proposal with traceable quality documentation. Partner with us to transform rubber bearing pads from functional elements into engineered assets that enhance operational uptime and reduce total cost of ownership. Precision begins with the right formulation partner—contact Mr. Boyce today.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
