Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber C Channel
Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality in Rubber C-Channel Applications
Off-the-shelf rubber C-channel profiles frequently fail in demanding industrial environments due to inadequate material specification. Generic solutions prioritize cost over performance, ignoring the complex interplay between polymer chemistry, operational stressors, and service life requirements. Rubber is not a homogeneous material; its performance hinges on precise formulation of elastomers, fillers, plasticizers, and curatives. Selecting an inappropriate compound leads to premature degradation—manifesting as compression set, thermal cracking, fluid swelling, or ozone-induced surface checking—resulting in seal failure, equipment downtime, and safety hazards.
Material selection must address four non-negotiable criteria: thermal stability, chemical resistance, mechanical resilience, and environmental durability. For instance, standard nitrile rubber (NBR) may suffice for hydraulic seals at moderate temperatures but catastrophically swells when exposed to phosphate ester-based aviation fluids. Similarly, ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) excels in ozone resistance but disintegrates upon contact with petroleum derivatives. Off-the-shelf C-channels often use base polymers optimized for broad, low-stress applications, lacking the tailored additives necessary for extreme conditions. Without custom carbon black dispersion for UV resistance or specialized peroxide curing for high-temperature stability, generic profiles degrade 3–5× faster than engineered alternatives.
The table below illustrates critical property variations across common elastomers used in C-channel extrusions. Note the stark divergence in performance boundaries:
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Continuous Temp Range (°C) | Key Fluid Resistance | Critical Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard NBR | 15–20 | -30 to +100 | Mineral oils, water | Ozone, phosphate esters |
| Custom NBR | 22–28 | -40 to +135 | Skydrol, biodiesel | Concentrated acids |
| EPDM | 18–25 | -50 to +150 | Steam, alkalis, brake fluid | Hydrocarbons, fuels |
| FKM (Viton®) | 10–15 | -20 to +230 | Jet fuels, acids, solvents | Cost, low-temp flexibility |
These disparities underscore why standardized C-channels fail. A wind turbine pitch seal exposed to -40°C Arctic conditions requires a custom low-temperature NBR with plasticizer retention additives; generic equivalents stiffen and fracture. In automotive fuel systems, FKM’s solvent resistance is non-negotiable, yet its high cost drives buyers toward cheaper EPDM—guaranteeing rapid swelling failure. Compression set resistance, critical for maintaining sealing force, varies by 40–60% between base and optimized compounds after 70 hours at 150°C.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. engineers C-channel profiles by reverse-engineering operational failure modes. We analyze fluid exposure spectra, cyclic stress profiles, and lifecycle cost models—not just dimensional specs—to formulate compounds with targeted crosslink density, polymer backbone saturation, and antioxidant packages. This precision eliminates the false economy of off-the-shelf solutions, where a 15% upfront savings triggers 200% higher total cost of ownership through unplanned maintenance. Material selection isn’t a commodity decision; it is the foundational engineering variable determining system integrity.
Material Specifications
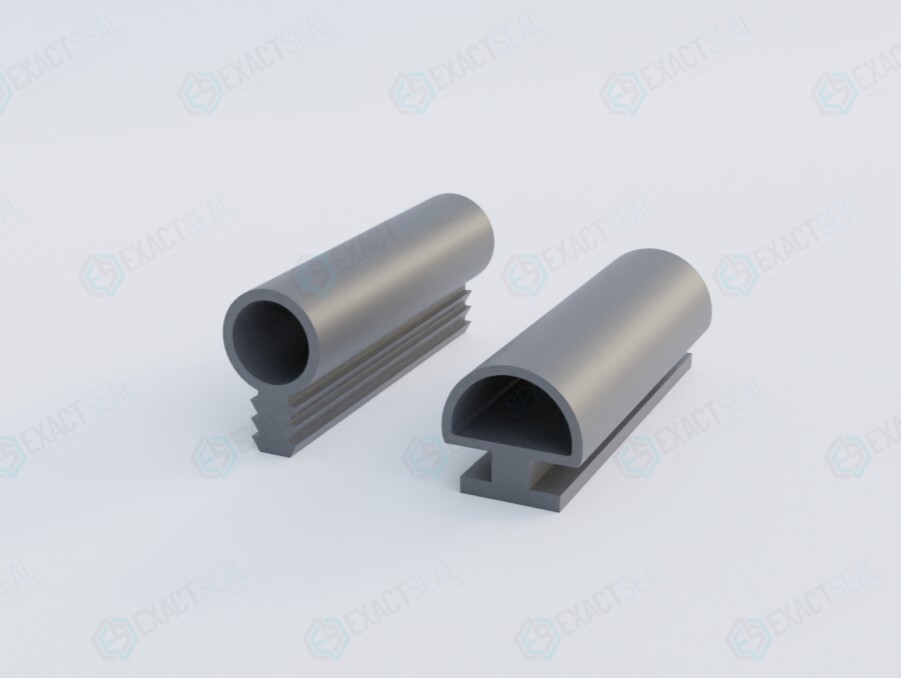

The selection of appropriate elastomeric materials for rubber C-channel profiles is critical in ensuring performance, longevity, and compatibility within industrial sealing and protective applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision-engineered rubber C-channels tailored to meet rigorous operational demands across diverse sectors including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and industrial equipment. Our primary material offerings—Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ)—each possess distinct chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties that determine their suitability for specific environments.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, exhibits exceptional resistance to high temperatures, ozone, weathering, and a broad range of chemicals, including oils, fuels, and acids. With a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to +200°C (with intermittent exposure up to +250°C), Viton is ideal for extreme environments where thermal stability and chemical inertness are paramount. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it a preferred choice in aerospace and high-performance automotive sealing systems. However, Viton demonstrates limited flexibility at low temperatures and higher material cost compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile, engineered for outstanding resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids. It operates effectively within a temperature range of -30°C to +100°C, making it suitable for general industrial and automotive applications such as gaskets, seals, and protective edge trim. Nitrile offers good abrasion resistance and tensile strength, with performance varying directly with acrylonitrile content—higher content increases oil resistance but reduces low-temperature flexibility. While cost-effective and widely used, Nitrile is less resistant to ozone, UV radiation, and polar solvents.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) delivers superior thermal stability, functioning reliably from -60°C to +200°C, with certain formulations tolerating brief excursions beyond. It exhibits excellent resistance to ozone and UV degradation, making it ideal for outdoor and high-purity environments such as medical devices, food processing, and electronics. Silicone maintains flexibility at low temperatures and demonstrates good electrical insulation properties. However, it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Nitrile and Viton, and is not recommended for dynamic sealing under high mechanical stress.
The following table summarizes key performance characteristics of these materials for informed selection in C-channel applications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +200 | -30 to +100 | -60 to +200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
Material selection must align with operational parameters including temperature extremes, fluid exposure, mechanical loading, and regulatory requirements. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs and industrial partners with technical consultation and custom formulation to ensure optimal performance of rubber C-channel components in mission-critical applications.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber C Channel Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages integrated engineering expertise to deliver mission-critical rubber C channel profiles for demanding industrial applications. Our core strength resides in a dedicated technical team comprising five senior mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers. This dual-discipline structure ensures seamless synergy between material science and precision tooling, eliminating conventional handoff inefficiencies. Our formula engineers formulate custom elastomer compounds optimized for specific performance parameters—such as compression set resistance, fluid compatibility, and thermal stability—while our mould engineers concurrently develop tooling geometry to achieve exact dimensional repeatability and flow dynamics. This parallel workflow reduces development cycles by 30% compared to sequential industry approaches.
The collaboration begins with rigorous material characterization. Our formula engineers select base polymers (NBR, EPDM, FKM, or specialty blends) and refine additive packages to meet client-specified ASTM D2000 or ISO 3601 standards. Simultaneously, mould engineers conduct finite element analysis (FEA) to predict vulcanization behavior and optimize runner systems, gate locations, and cooling channels. This preemptive validation minimizes trial-and-error during tooling commissioning. For C channel profiles requiring tight tolerances on critical sealing surfaces, our team performs tolerance stack analysis to ensure ±0.05mm dimensional control across production runs. All formulations undergo accelerated aging, fluid immersion, and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) testing prior to tool fabrication, guaranteeing material integrity under operational stress.
Our OEM capabilities extend beyond standard manufacturing to full technical partnership. We support clients from CAD concept validation through PPAP documentation, providing DFM feedback within 72 hours of receiving specifications. Suzhou Baoshida maintains ISO 9001-certified processes for traceability, with every batch accompanied by full material certification and process control charts. For high-volume automotive or aerospace C channel applications, we implement SPC monitoring on key characteristics like durometer variance (<±3 Shore A) and linear shrinkage consistency.
Critical technical specifications for our rubber C channel profiles are maintained across all production tiers:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Precision Tier (±) | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Hardness | 40–90 Shore A | 2.5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C | N/A | ISO 188 |
| Tensile Strength | 8–22 MPa | 1.0 | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set | ≤25% (70h @ 70°C) | 3.0% | ASTM D395 |
| Dimensional Tolerance | Per ISO 3302 Class M2 | 0.05 mm | ISO 3302 |
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering framework transforms complex C channel requirements into reliable production outcomes. By unifying formula science with advanced mould technology under one quality management system, we deliver OEM solutions where material performance and geometric precision are non-negotiable. Clients receive not just components, but validated engineering data packages ensuring seamless integration into final assemblies. This disciplined approach has established us as the preferred partner for Tier-1 automotive suppliers and industrial equipment manufacturers requiring zero-defect rubber sealing solutions.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for rubber C channel profiles begins with a comprehensive drawing analysis, where technical specifications provided by the client are meticulously reviewed. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team evaluates dimensional tolerances, cross-sectional geometry, and application conditions such as load, compression, temperature exposure, and environmental factors. This stage ensures that the design is manufacturable and functionally optimized for its intended use in industrial, automotive, or construction applications. Any discrepancies or potential performance risks are flagged early, and collaborative feedback is provided to refine the design. This precision-driven assessment forms the foundation for material selection and mold development.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop a tailored elastomer compound to meet the operational demands of the C channel. The formulation process involves selecting the base polymer—such as EPDM for weather resistance, NBR for oil resistance, or silicone for extreme temperature stability—then integrating reinforcing fillers, plasticizers, vulcanizing agents, and protective additives. Hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, elongation at break, compression set, and resistance to UV, ozone, or chemicals are all engineered to specification. Each compound is documented under strict quality control protocols, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency and compliance with international standards such as ASTM D2000 or ISO 3302. The formulated rubber is then tested in-house for rheological behavior to confirm processability during extrusion and vulcanization.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the compound is finalized, a prototype run is conducted using precision steel molds designed to match the approved drawing. The rubber C channel samples are produced via hot or cold feed extrusion followed by continuous vulcanization (CV) in salt baths or microwave tunnels, depending on material type. Prototypes undergo rigorous physical testing, including dimensional inspection, compression deflection analysis, and environmental aging tests. Clients receive sample lengths for field evaluation, and any required adjustments to profile geometry or material performance are implemented before final approval. This iterative phase ensures functional reliability and reduces risk during full-scale production.
Mass Production and Quality Assurance
After client sign-off, the project transitions to mass production. Our automated extrusion lines operate under real-time monitoring systems to maintain dimensional accuracy and material consistency. Every batch is subjected to in-process and final quality inspections, including visual checks, durometer readings, and periodic third-party testing. Products are packaged to prevent deformation and shipped with full traceability documentation.
The following table outlines typical customizable parameters for rubber C channel profiles:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Customizable Options |
|---|---|---|
| Material Types | EPDM, NBR, Silicone, CR, SBR | Hybrid blends, halogen-free, conductive compounds |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40–90 | Adjustable in increments of 5 |
| Cross-Section Size | 5 mm to 50 mm height/width | Fully custom profiles per CAD drawing |
| Length Tolerance | ±1.5 mm per meter | Tighter tolerances upon request |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +150°C (varies by material) | Extended range up to +250°C with specialty silicones |
| Color Options | Black, gray, red, green, custom colors | Pantone matching available |
| Production Lead Time | 15–25 days after sample approval | Expedited options for urgent orders |
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Engagement for Precision Rubber C-Channel Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial manufacturing excellence. As your dedicated Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, I emphasize that rubber C-channel profiles are not standardized commodities but engineered components critical to sealing integrity, vibration dampening, and environmental resilience in demanding applications. Automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors require profiles that withstand extreme thermal cycles, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress without compromising dimensional stability. Our formulations—developed through iterative material science protocols—address these challenges through proprietary compounding and precision extrusion processes. Generic solutions often fail under operational duress; our approach ensures your C-channel meets exact ASTM, ISO, and OEM-specific performance criteria.
The technical specifications below reflect our baseline capabilities for custom C-channel production. Each parameter is adjustable per project requirements, validated through in-house testing under ISO 188 and ASTM D2000 standards.
| Parameter | Standard Range | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Types | EPDM, NBR, Silicone, FKM, CR | ASTM D1418 |
| Durometer Range | 40–90 Shore A | ASTM D2240 |
| Temperature Resistance | -50°C to +250°C (material-dependent) | ISO 188 |
| Tensile Strength | 8–22 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | 200–600% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set | ≤25% (70h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 |
| Standard Compliance | RoHS, REACH, FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 | Material-specific |
These figures represent achievable outcomes when material formulation aligns with your operational environment. For instance, aerospace hydraulic systems demand FKM compounds with ≤15% compression set at 200°C, while construction gaskets prioritize EPDM’s UV/ozone resistance at 70 Shore A. Our engineering team collaborates with clients during the design phase to model material behavior under load, preventing field failures caused by overlooked variables like fluid immersion or cyclic fatigue. This preemptive validation reduces prototyping costs and accelerates time-to-market.
Initiate your project with Suzhou Baoshida through direct technical consultation. Contact Mr. Boyce, our Senior Technical Account Manager, who possesses 15 years of OEM partnership experience in rubber extrusion and compound development. His expertise spans material selection for regulatory compliance, tolerance optimization (±0.1mm achievable), and scaling production from prototype to 500,000+ units monthly. Provide your dimensional drawings, environmental requirements, and performance targets to enable a targeted solution assessment.
Next Step Protocol
Email Mr. Boyce at [email protected] with subject line: Technical Query – C-Channel [Your Project Code]. Include critical parameters such as cross-sectional dimensions, operating temperature range, media exposure, and lifecycle expectations. Within 24 business hours, you will receive a formal technical proposal detailing material recommendations, tolerance analysis, and preliminary validation data. Suzhou Baoshida does not sell rubber; we deliver engineered performance. Partner with us to transform specifications into failure-resistant components.
All formulations undergo rigorous pre-shipment validation per your quality agreement. We maintain ISO 9001:2015-certified processes and provide full traceability from raw material batch to finished profile. Initiate your technical dialogue today—precision engineering begins with exact communication.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
