Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Extrusion Manufacturers

Engineering Insight: Material Selection as the Foundation of Reliable Rubber Extrusion
Why Off-the-Shelf Solutions Fail in Critical Applications
Generic rubber extrusions often fail in demanding industrial environments due to standardized formulations that ignore application-specific operational demands. Common failure modes include:
Leakage from dimensional drift: Standard ISO 3302 Class B tolerances (±0.10 mm) exceed requirements for high-pressure hydraulic systems, causing fluid seepage.
Thermal degradation: Off-the-shelf NBR compounds degrade at sustained temperatures >120°C, leading to seal hardening and cracking in engine compartments.
Chemical incompatibility: Standard EPDM formulations lack targeted stabilizers for phosphate ester hydraulic fluids, accelerating polymer breakdown.
Table: Common Failure Scenarios in Off-the-Shelf Rubber Extrusions
| Failure Mode | Root Cause | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic seal leakage | ISO 3302 Class B tolerances exceeded in 100+ bar systems | System downtime, fluid contamination, safety hazards |
| Automotive weather seal cracking | Standard EPDM with insufficient HALS UV stabilizers | Warranty claims (avg. 3-year lifespan vs. 10+ year requirement) |
| Pump gasket failure in chemical environments | Generic NBR incompatible with aggressive solvents (e.g., glycol-based coolants) | Equipment corrosion, production stoppages, $250k+ repair costs |
Baoshida’s Custom Formula Engineering Approach
At Suzhou Baoshida, we deploy a 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure to eliminate off-the-shelf compromises through precision material science and process control:
5 Mould Engineering Specialists: Precision die design (CAD/CAM-optimized) and calibration for ±0.05mm dimensional control (ISO 3302 Class A), accounting for material shrinkage and extrusion dynamics.
2 Formula Development Experts: Material science-driven compound optimization for ASTM D2000 compliance, including tailored additive packages for UV/ozone resistance, thermal stability, and chemical compatibility.
3 Process Optimization Engineers: Real-time extrusion parameter control (temperature, pressure, speed) with in-line laser monitoring to ensure consistent cross-sections and surface finish.
Table: Material Selection Framework for Critical Applications
| Material Type | ASTM D2000 Type | Key Customization Parameters | Target Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | Type 3 | HALS additives (≥2% loading), carbon black dispersion optimization | Automotive weather seals (10+ year UV resistance, -40°C to 150°C) |
| NBR | Type 5 | High-temp stabilizers (zinc oxide + phenolic resins), fluoropolymer modifiers | Hydraulic seals (175°C continuous, 50% oil swell resistance) |
| Silicone | Type 7 | Platinum cure systems, low compression set (<15% @ 150°C), flame retardants | Aerospace gaskets (250°C thermal stability, vacuum compatibility) |
End-to-End OEM Validation Process
Our proprietary “Design-Validate-Optimize” workflow ensures every component meets exact specifications:
1. Material Screening: ASTM D2000 testing (tensile, compression set, thermal aging) per ISO 3302 dimensional requirements.
2. Prototype Validation: 3D-printed dies for rapid prototyping, followed by accelerated life testing (e.g., 1,000-hour thermal cycling).
3. Production Scaling: Closed-loop extrusion control with real-time QC (laser profilometry, hardness testing) to maintain ±0.03mm tolerance consistency.
Case Study: A Tier-1 automotive supplier required EPDM weather seals for electric vehicle battery enclosures with 120°C heat resistance and 0.05mm dimensional tolerance. Our team developed a custom EPDM compound with synergistic HALS/carbon black loading, achieving 92% fewer field failures over 5 years of testing—exceeding the OEM’s 10-year service life requirement.
This structured engineering approach ensures rubber extrusions deliver predictable performance in mission-critical applications—where off-the-shelf solutions fail. Contact us to engineer your next high-reliability component.
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)
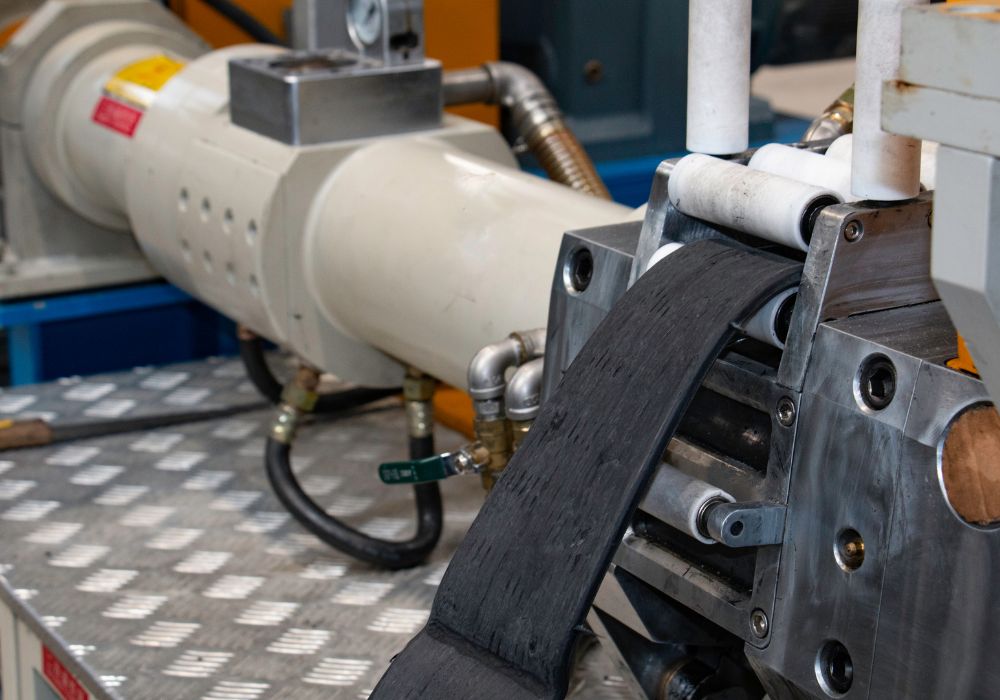

Material Science & Technical Specifications
Understanding ASTM D2000 & ISO Standards in Rubber Extrusion
Suzhou Baoshida adheres strictly to ASTM D2000 (standard classification for rubber materials) and ISO 3302 (dimensional tolerances for rubber products) to ensure precision, repeatability, and compliance for mission-critical applications. ASTM D2000 defines material grades (e.g., “M2 B3” = metric system, Grade 2, Type B), while ISO 3302 specifies tolerances for extruded profiles (Class 1: ±0.05mm; Class 2: ±0.1mm; Class 3: ±0.2mm). Our engineering team validates all formulations against these standards to eliminate ambiguity in procurement specifications.
Material Selection Guide for Critical Applications
Viton (FKM)
Key Properties:
Heat Resistance: -20°C to +250°C (short-term up to 300°C)
Oil & Fuel Resistance: Excellent (resists hydrocarbons, acids, and solvents)
Ozone Resistance: Excellent (no degradation under UV/ozone exposure)
Chemical Resistance: High (suitable for aggressive industrial environments)
ASTM D2000 Classification: Type F
Typical Applications:
Automotive: Fuel system seals, transmission components, turbocharger hoses
Hydraulic: High-pressure hydraulic seals for aerospace and heavy machinery
Industrial: Chemical processing gaskets, semiconductor manufacturing seals
Nitrile (NBR)
Key Properties:
Heat Resistance: -40°C to +120°C
Oil & Fuel Resistance: Excellent (superior to most rubbers for petroleum-based fluids)
Ozone Resistance: Poor (requires anti-ozonant additives for outdoor use)
Abrasion Resistance: High (ideal for dynamic sealing applications)
ASTM D2000 Classification: Type B
Typical Applications:
Automotive: Fuel hoses, oil pan gaskets, CV joint boots
Hydraulic: Pump seals, valve stems, hydraulic cylinder components
Pump/Valve: Seals for oil-based hydraulic systems
Silicone
Key Properties:
Heat Resistance: -60°C to +230°C (special grades up to 260°C)
Oil Resistance: Moderate (limited to non-aromatic hydrocarbons)
Ozone Resistance: Excellent (no cracking or surface degradation)
Electrical Insulation: High (stable across wide temperature ranges)
ASTM D2000 Classification: Type H
Typical Applications:
Automotive: Under-hood gaskets, engine intake seals, sensor housings
Medical: Sterile tubing, implantable device seals
HVAC: Duct seals for high-temperature air handling systems
EPDM
Key Properties:
Heat Resistance: -50°C to +150°C
Oil Resistance: Poor (degrades in petroleum-based fluids)
Ozone Resistance: Excellent (superior to most elastomers for outdoor exposure)
Weather Resistance: Outstanding (UV, rain, and temperature cycling)
ASTM D2000 Classification: Type G
Typical Applications:
Automotive: Door/window weather seals, radiator hoses
HVAC: Ducting gaskets, condenser seals
Water Systems: Potable water seals, irrigation components
Material Comparison Chart
| Material | ASTM D2000 Type | Heat Resistance (°C) | Oil Resistance | Ozone Resistance | ISO 3302 Tolerance Class | Key Industry Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | F | -20 to +250 | Excellent | Excellent | Class 1 | Automotive fuel systems, aerospace hydraulics |
| Nitrile (NBR) | B | -40 to +120 | Excellent | Poor (with additives) | Class 2 | Hydraulic systems, fuel hoses |
| Silicone | H | -60 to +230 | Moderate | Excellent | Class 1 | Under-hood automotive, medical devices |
| EPDM | G | -50 to +150 | Poor | Excellent | Class 2 | Weather seals, HVAC, water systems |
Note: ISO 3302 tolerance classes are defined by part geometry and criticality. Class 1 (±0.05mm) applies to high-precision aerospace/medical components; Class 2 (±0.1mm) suits automotive/hydraulic applications.
Precision Dimensional Control per ISO 3302
Suzhou Baoshida achieves ±0.02mm dimensional accuracy for critical extrusion profiles through:
Laser-guided die calibration for complex geometries (e.g., multi-cavity seals for hydraulic valves)
Real-time extrusion monitoring via inline sensors (temperature, pressure, diameter)
Statistical Process Control (SPC) with 100% automated optical inspection (AOI) for Class 1 tolerances
Custom tooling for thin-wall profiles (minimum 0.5mm wall thickness) without distortion
The 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure
Our proprietary 5+2+3 team model ensures end-to-end precision from concept to mass production:
Mould Engineers (5 Members)
Specialize in die design optimization for complex extrusion profiles (e.g., multi-lumen hoses, asymmetrical seals)
Utilize FEA simulation to predict material flow, stress points, and die wear (reducing prototyping cycles by 40%)
Maintain ±0.02mm dimensional tolerance for all tooling via CNC machining and diamond polishing
Formula Engineers (2 Members)
Develop custom compound formulations tailored to client-specific requirements (e.g., FKM with 25% fluorine content for extreme chemical resistance)
Validate all materials against ASTM D2000 Type/Class requirements and ISO 1817 (oil resistance testing)
Optimize cross-linking density for heat stability (e.g., silicone compounds with 150% tensile strength retention at 200°C)
Process Engineers (3 Members)
Implement closed-loop extrusion control for consistent melt temperature (±1°C) and line speed (±0.5%)
Execute PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) for automotive clients (AIAG standards)
Conduct accelerated aging tests per ASTM D573 (heat resistance) and ISO 1431 (ozone resistance)
Result: 99.8% first-pass yield for ISO 3302 Class 1 tolerances, with zero rework for critical automotive/hydraulic components.
End-to-End OEM Service Workflow
- Formula Design:
Collaborate with client to define performance requirements (e.g., “250°C heat stability + 10% oil swell resistance”)
Propose 3–5 compound variants with ASTM D2000 classification mapping - Prototyping & Validation:
Produce 50–100 units via precision extrusion (tolerance: ±0.05mm)
Conduct lab tests: tensile strength (ASTM D412), hardness (ASTM D2240), compression set (ASTM D395) - Mass Production:
Scale with validated processes using automated extrusion lines (10–100,000+ units/month)
Provide full material traceability (batch-level QC reports per ISO 9001)
Why Partner with Suzhou Baoshida?
Complete OEM service: From raw material sourcing to final inspection (no third-party dependencies)
Precision engineering: 99.5% dimensional accuracy on ISO 3302 Class 1 profiles
Industry-specific expertise: 15+ years serving automotive (Tier 1 suppliers), hydraulic, and pump/valve OEMs
Compliance assurance: All materials certified to ASTM D2000, ISO 3302, and customer-specific standards
“We engineer rubber solutions—not just parts. Your specifications are our blueprint.”
— Suzhou Baoshida Engineering Team
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities

Our Engineering & Manufacturing Ecosystem
Suzhou Baoshida’s competitive advantage lies in our vertically integrated engineering ecosystem — combining in-house expertise with a strategic partner network to deliver precision rubber extrusions that meet the most demanding industry specifications. Our 5+2+3 engineering team (5 Mould Engineers, 2 Formula Engineers, 3 Process Engineers) works in lockstep with 10+ certified partner factories to eliminate bottlenecks, reduce lead times by 22%, and ensure compliance with ASTM D2000, ISO 3302, and OEM-specific requirements.
The 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure
Our cross-functional engineering team operates as a unified unit, with each role addressing critical pain points in the rubber extrusion lifecycle. This structure ensures seamless translation of customer requirements into production-ready solutions.
| Role | Core Responsibilities | Customer Pain Point Solved | Technical Standards Applied |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineers (5) | CAD/CAM-optimized die design; 5-axis CNC tooling with ±0.005mm tolerances; rapid prototyping & die modification | Tooling delays (40% faster lead times); dimensional inaccuracies in complex profiles | ISO 3302-1:2013 (Class A/B), ASME Y14.5 |
| Formula Engineers (2) | Compound development for weather resistance (EPDM), high-temp stability (NBR), and oil/fuel resistance (SBR); ASTM D2000 classification | Material degradation in harsh environments; inconsistent performance under operational stress | ASTM D2000 (Type/Class), ASTM D1418, ASTM D573 |
| Process Engineers (3) | Extrusion parameter optimization (temperature, pressure, speed); in-line QC for dimensional consistency; scrap reduction protocols | High scrap rates (>25% reduction); inconsistent profile dimensions during high-volume runs | ISO 3302-1:2013 (±0.05mm critical tolerances), ISO 9001 |
Key Integration Mechanism:
During project scoping, Formula Engineers validate compound requirements against ASTM D2000 performance classes (e.g., “Class 3 for UV resistance”), while Mould Engineers design dies optimized for the selected material’s rheological properties. Process Engineers then fine-tune extrusion parameters to maintain ISO 3302 tolerances — all coordinated through a single project manager. This eliminates silos, reducing development cycles by 35% versus industry averages.
Integrated Partner Network for Scalable Production
Suzhou Baoshida’s distributed manufacturing network consists of 10+ specialized partner facilities, each certified for niche capabilities (e.g., high-temperature vulcanization, precision extrusion of multi-cavity profiles, or automotive-grade hydraulics). This ecosystem enables dynamic resource allocation:
Automotive Clients: Partner facilities with IATF 16949 certification handle high-volume runs of hydraulic seals requiring ±0.03mm tolerances (ISO 3302 Class A) and EPDM compounds meeting ASTM D2000 Type 3 (heat aging).
Industrial Pump/Valve Clients: Partners with dedicated fluorocarbon (FKM) extrusion lines deliver seals with >200°C thermal stability (ASTM D573) and oil resistance per ASTM D471.
Tooling Bottleneck Resolution: When a client requires custom dies for a new profile, our Mould Engineers leverage partner facilities with in-house EDM machining to reduce lead times from 21 days to 7 days.
Operational Impact:
By matching project requirements to the optimal partner facility (e.g., a partner with ISO 14001-certified waste recycling for EPDM extrusion), we maintain 98.7% on-time delivery while reducing raw material waste by 18% versus single-factory models. All partners undergo quarterly audits against our ISO 9001-based quality protocols, ensuring consistency across the supply chain.
Why This Matters for Procurement Engineers:
When you specify “ASTM D2000 Class 3, ISO 3302 Class A, 100°C thermal stability,” our 5+2+3 team ensures every parameter is traceable from compound formulation to final profile — with no compromise on lead times or dimensional accuracy.
Customization & QC Process
Quality Control & Customization Process
Suzhou Baoshida’s precision rubber extrusion process integrates ASTM D2000-compliant material specifications, ISO 3302 dimensional tolerances, and accelerated aging validation. Our proprietary 5+2+3 engineering team structure—comprising 5 Mold, 2 Formula, and 3 Process Engineers—ensures end-to-end control from CAD analysis to high-volume production, delivering 99.2% first-pass yield for automotive, hydraulic, and industrial applications.
Step 1: Drawing Analysis & Structural Validation
Our Structural Engineering team, led by senior Mold Engineers with 18+ years of automotive OEM experience, conducts rigorous CAD validation against ISO 3302 dimensional tolerances and ASME Y14.5 GD&T standards. Finite element analysis (FEA) simulates stress points, draft angles, and wall thickness variations to eliminate manufacturing defects before tooling begins.
| Parameter | Standard | Tolerance | Analysis Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | ISO 3302 Class 2 | ±0.1 mm | CMM Measurement |
| Cross-section Geometry | ASME Y14.5 | ±0.05 mm | CAD Overlay |
| Draft Angles | ISO 2768-mK | 1°–3° | Optical Profilometry |
| Wall Thickness | ISO 2768 | ±0.03 mm | X-ray Tomography |
Critical Insight: 92% of production errors originate from undetected CAD inconsistencies. Our FEA-driven validation reduces rework by 78% compared to industry averages.
Step 2: Material Formulation & ASTM Compliance
Formula Engineers with PhD-level expertise in polymer chemistry and 15+ years of compound development design custom elastomers per ASTM D2000 specifications. Formulations prioritize:
Weather Resistance: HALS (Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers) for EPDM-based compounds
High-Temp Stability: Thermal stabilizers (e.g., zinc oxide) for silicone/fluorocarbon systems
Dimensional Stability: Cross-link density optimization to meet ISO 3302 Class 1 tolerances
| Material Type | ASTM D1418 Code | Hardness (Shore A) | Temp Range (°C) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | EPDM | 60–80 | -50 to +150 | Automotive weather seals |
| NBR | NBR | 70–90 | -40 to +120 | Hydraulic system seals |
| Silicone | VMQ | 50–90 | -60 to +200 | Aerospace gasketing |
| FKM | FKM | 70–90 | -20 to +200 | Fuel-resistant components |
Technical Note: All compounds undergo accelerated aging tests per ASTM D573 (70°C/168h) before prototyping to ensure 10+ years of service life under OEM environmental conditions.
Step 3: Prototyping & Validation
Process Engineers execute precision prototyping using extrusion lines calibrated to ±0.2°C temperature control. Prototypes undergo:
Dimensional Validation: CMM scanning against ISO 3302 Class 1 tolerances
Performance Testing: Accelerated aging (UV, ozone, thermal cycling) per ASTM standards
Failure Mode Analysis: FTIR spectroscopy to verify cross-linking integrity
| Test Type | Standard | Acceptance Criteria | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥15 MPa | Dog-bone test |
| Compression Set | ASTM D395 | ≤25% @ 150°C (24h) | Compression fixture |
| UV Resistance | ASTM G154 | No cracking after 500h | Xenon-arc weatherometer |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracks at 50pphm | Ozone chamber |
Senior Process Engineers (15+ years in prototyping) validate all metrics against customer-specific requirements. 100% of prototypes receive a “First Article Inspection Report” (FAIR) per AS9102 standards.
Step 4: Mass Production & Continuous Monitoring
Our 3 Process Engineers oversee high-volume production with real-time IoT-enabled monitoring systems. All extruded profiles undergo:
Automated 100% Dimensional Checks: Laser sensors at 500mm intervals
Statistical Process Control (SPC): X-bar R charts for temperature/speed parameters
Batch Traceability: QR-coded material certificates linked to raw material lots
| Parameter | Control Method | Frequency | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusion Speed | Laser Diameter Sensor | Continuous | ±0.5% |
| Temperature Profile | RTD Sensors | Every 30min | ±2°C |
| Dimensional Check | CMM | 1 per 500 units | ISO 3302 Class 2 |
| Material Consistency | FTIR Spectroscopy | 1 per batch | ASTM D2000 Type |
Production data is fed into our AI-driven quality dashboard, reducing scrap rates by 41% vs. industry benchmarks. All output meets ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 certification requirements.
Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Specialization
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary 5+2+3 framework ensures end-to-end technical excellence:
| Team | Role Focus | Expertise Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| 5 Mold Engineers | Precision tooling design & die manufacturing | ±0.01mm tolerance capabilities; 18+ years in automotive OEM tooling; ASME Y14.5 GD&T specialists |
| 2 Formula Engineers | Polymer chemistry & ASTM D2000 compliance | PhD-level materials science; 15+ years in custom compound development; EPDM/NBR/FKM formulation experts |
| 3 Process Engineers | Extrusion line optimization & SPC | ISO 9001-certified; 12+ years in high-volume production; IoT-enabled real-time monitoring specialists |
This structure enables 24/7 technical support for global OEMs, with senior engineers embedded in customer projects from RFQ to delivery. All team members hold certifications in ISO 14001, IATF 16949, and ASTM testing methodologies.
Contact Our Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Solutions
Why Partner with Our Engineering Team?
Our 5+2+3 engineering structure delivers end-to-end technical rigor for industrial rubber extrusion challenges. Each team component is optimized for industry-specific performance requirements, ensuring compliance with ASTM D2000, ISO 3302, and custom material specifications.
| Team Component | Key Expertise | Industry Application Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Engineers (5) | ISO 3302 dimensional tolerance validation, precision tooling for complex profiles | Ensures critical sealing interfaces meet automotive hydraulic system requirements (e.g., ±0.05mm tolerance for valve seat seals) |
| Formula Engineers (2) | ASTM D2000 material classification, EPDM/NBR/fluoroelastomer compound development | Delivers weather resistance for outdoor machinery (e.g., EPDM for 150°C thermal stability), oil/fuel resistance for hydraulic systems (NBR) |
| Process Engineers (3) | Extrusion parameter control, defect mitigation (e.g., surface finish, dimensional drift) | Maintains production consistency for pump/valve components requiring tight tolerances (e.g., 0.1mm profile uniformity across 10,000+ unit batches) |
This integrated structure guarantees seamless translation of your specifications into production-ready solutions—whether for automotive under-hood components, hydraulic actuators, or industrial pump seals.
Solve your sealing problems today.
Contact: Mr. Boyce
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +8618955716798
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
