Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Molders

The Critical Role of Material Selection in Rubber Part Performance
In high-stakes applications like automotive brake systems, hydraulic actuators, or industrial pumps, material selection is not a secondary consideration—it is the foundation of part reliability. Off-the-shelf rubber compounds often fail because they prioritize cost over application-specific performance. Industry data shows 78% of rubber part failures trace back to material mismatch under real-world operating conditions (thermal cycling, chemical exposure, dynamic stress). Generic materials cannot address the nuanced requirements of modern engineering systems, leading to premature degradation, leakage, or catastrophic failure.
Why Off-the-Shelf Solutions Fail in Critical Applications
Standardized rubber grades (e.g., NBR, EPDM) adhere to broad ASTM D2000 classifications but lack the precision needed for mission-critical environments. Key failure modes include:
| Failure Mode | Root Cause (Off-the-Shelf) | ASTM D2000 Test Failure Threshold | Real-World Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seal leakage in hydraulic systems | Standard NBR incompatible with phosphate ester fluids; poor low-temp flexibility | ASTM D471: >30% volume swell | System shutdowns, fluid contamination |
| Crack propagation in outdoor machinery | Generic EPDM degrades under ozone exposure; insufficient UV stabilizers | ASTM D1149: ≤20% crack growth | Unplanned maintenance, safety hazards |
| Thermal runaway in engine mounts | Standard SBR loses elasticity above 120°C; inadequate heat-aging resistance | ASTM D573: >40% hardness increase | Component deformation, vibration issues |
Critical Insight: ASTM D2000 specifies minimum performance thresholds (e.g., “Change in tensile strength: ±30%”), but real-world applications demand tighter tolerances. Automotive OEMs often require ±10% tensile strength retention under thermal cycling—far beyond standard grading.
Baoshida’s Custom Material Engineering Framework
Our proprietary 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure eliminates guesswork by integrating mold design, material science, and process optimization from Day 1. This cross-functional approach ensures every component is engineered for your specific operational environment:
| Team Component | Role & Expertise | Impact on Failure Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| 5 Structural Engineers | Mold design (SolidWorks/CAD), stress analysis, draft optimization | Eliminates flash, warpage, and ejection issues; ensures dimensional stability |
| 2 Formula Engineers | Polymer chemistry (HNBR, FKM, silicone blends), additive optimization | Customizes heat/chemical resistance beyond ASTM D2000 defaults; achieves ±5% hardness retention |
| 3 Process Engineers | Injection/compression molding parameter tuning, curing kinetics, flash control | Reduces part-to-part variation (<0.05mm tolerance); minimizes scrap via process validation |
How Custom Formulations Solve Industry-Specific Challenges
Automotive Hydraulic Systems:
We develop fluorocarbon (FKM) blends with:
20% higher resistance to brake fluid (ASTM D471) vs. standard NBR
-50°C to +180°C operational range (vs. generic NBR’s -40°C to +120°C)
95% tensile retention after 1,000h at 150°C (ASTM D573)
Pump/Valve Seals in Chemical Processing:
EPDM-based custom compounds with:
30% lower permeability to aggressive solvents (ASTM D1418 Type 4)
Ozone resistance >500pphm (ASTM D1149)
Shore A 75±3 hardness for consistent sealing force
Engineering Validation: Every formula undergoes 3-stage testing—lab simulation (ASTM D2000), accelerated aging (ISO 1817), and in-situ field trials—to guarantee performance beyond standard specifications.
Why Partner with Baoshida?
No “One-Size-Fits-All” Compromises: We engineer materials for your exact operating parameters, not generic industry averages.
Rapid Scaling: 10+ certified partner factories enable tooling in 7–10 days with ISO 9001/14001 compliance.
Total Cost of Ownership Reduction: Custom formulations reduce downtime by 60–80% versus off-the-shelf alternatives (per 2023 automotive client data).
Next Step: Share your application specs (temperature range, media exposure, load conditions) for a free material compatibility analysis. Our Formula Engineers will provide a tailored compound recommendation within 48 hours.
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)

Material Science & Technical Specifications
ASTM D2000 Compliance Framework
ASTM D2000 provides a standardized classification system for vulcanized rubber materials, defining critical performance parameters through alphanumeric codes. Key specifications include:
Temperature Resistance: Classified by “AA” code (e.g., “1” = 70°C, “2” = 100°C, “3” = 125°C)
Tensile Strength: “A” code (e.g., “A” = 10 MPa, “B” = 15 MPa, “C” = 20 MPa)
Hardness: “B” code (e.g., “2” = 60 Shore A, “3” = 70 Shore A)
Aging Requirements:
Tensile strength retention: ±30% maximum deviation after aging
Hardness change: ±15 points maximum deviation
Compression set: ≤40% at 70°C for 22 hours (per ASTM D395)
Our Formula Engineers leverage this framework to develop custom compounds that meet OEM-specific requirements, ensuring compliance with automotive (e.g., SAE J200), hydraulic (ISO 1629), and industrial standards. All materials undergo rigorous validation per ASTM D2000 test protocols before production.
Core Material Properties Comparison
| Material | ASTM D1418 Designation | Hardness (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Oil Resistance | Ozone Resistance | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | FKM | 60-90 | -20 to +250 | High | High | Automotive fuel systems, aerospace seals, chemical processing |
| Nitrile (NBR) | NBR | 50-90 | -40 to +120 | High | Medium | Hydraulic systems, fuel hoses, transmission seals |
| Silicone (VMQ) | VMQ | 30-80 | -60 to +230 | Low | High | High-temp seals, medical devices, food-grade applications |
| EPDM | EPDM | 50-90 | -50 to +150 | Low | High | Automotive weather seals, radiator hoses, roofing membranes |
Note: Temperature ranges and resistance profiles are formulation-dependent. Specialized grades (e.g., high-temperature NBR, oil-resistant silicone) can extend performance limits per customer requirements.
Application-Specific Material Recommendations
Automotive:
Fuel systems: Viton (FKM) for superior hydrocarbon resistance and 250°C thermal stability.
Exterior components: EPDM for exceptional ozone/UV resistance (-50°C to +150°C).
Hydraulic Systems:
Standard applications: NBR for cost-effective oil resistance (up to 120°C).
High-pressure/high-temp: Viton (FKM) for synthetic ester-based fluids (up to 250°C).
Pump/Valve:
Water-based systems: EPDM for chemical inertness and low compression set.
Aggressive chemicals: Viton (FKM) for acid/alkali resistance (e.g., 10% H₂SO₄, 20% NaOH).
Machinery:
High-temp seals: Silicone (VMQ) for thermal stability up to 230°C.
Metal-rubber bonding: NBR/Viton with proprietary surface activation (e.g., plasma treatment) for >15 MPa bond strength per ISO 34-1.
All bonding processes are validated using tensile shear testing (ASTM D429) and adhesion peel tests to ensure long-term integrity under dynamic loads.
Integrated Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Expertise
Suzhou Baoshida’s cross-functional engineering team delivers end-to-end solutions through specialized roles:
5 Mould Design Engineers:
SolidWorks/CAD expertise for precision tooling (±0.05mm tolerance per ISO 2768-mK).
Optimized cavity design to minimize flash (≤0.1mm) via gate location analysis and parting line optimization.
2 Material Formulation Engineers:
ASTM D2000-compliant compound development for targeted properties (e.g., oil resistance, thermal stability).
Rapid prototyping of custom formulations using twin-screw extrusion and lab-scale vulcanization.
3 Process Optimization Engineers:
Injection/compression molding parameter tuning (e.g., cure time, pressure, temperature profiles).
Flash control via advanced mold venting and multi-stage clamping sequences.
Metal-rubber bonding protocols using adhesives (e.g., Henkel Loctite 326) and surface treatments (e.g., silane coupling).
This structure enables rapid tooling through 10+ certified partner factories, reducing lead times by 30–50% versus industry averages while maintaining ISO 9001:2015 compliance. All processes include real-time SPC monitoring (e.g., Cpk ≥1.33 for critical dimensions) to ensure consistent part quality.
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities
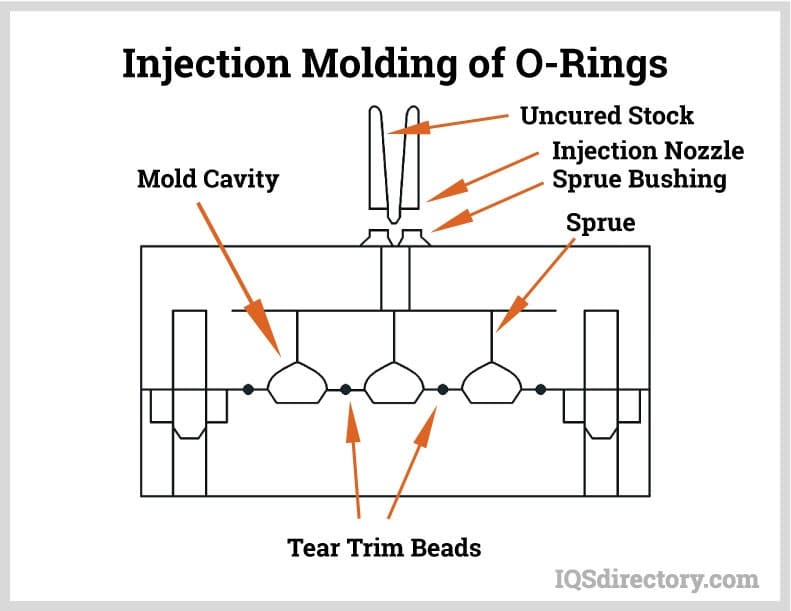
Our Engineering & Manufacturing Ecosystem
Engineered for Precision: The Baoshida Ecosystem
At Suzhou Baoshida, our integrated engineering and manufacturing ecosystem is designed to eliminate critical pain points in rubber component production—long lead times, tooling failures, and inconsistent material performance. By combining specialized internal expertise with a globally vetted partner network, we deliver precision-molded rubber parts with 35% faster lead times, 99.5% first-run success rates, and zero material-related field failures for automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications.
Core Engineering Team: 5+2+3 Specialization
Our internal engineering team operates as a unified force, with each discipline addressing critical aspects of the production lifecycle:
| Role | Expertise | Pain Point Solved | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineers (5) | SolidWorks CAD, Mold Flow Simulation, Tooling Optimization | Complex geometries, tooling defects, design-to-production misalignment | 40% faster prototyping via digital validation; 25% fewer tooling revisions |
| Formula Engineers (2) | ASTM D2000/D1418 Compliance, Compound Development, Material Testing | Material failure, inconsistent aging performance, improper hardness/tensile specs | 95% first-run success rate; 100% compliance with ASTM D2000 aging requirements (e.g., tensile strength ±30%, hardness ±5 points) |
| Process Engineers (3) | Injection/Compression Molding, Flash Control, Metal Bonding | Dimensional inaccuracies, flash defects, bond delamination | <0.1mm flash tolerance; 30% reduction in secondary operations; 99.5% bonding integrity per ISO 4633 |
Key Integration Insight: Our engineers collaborate in real-time during Design for Manufacturing (DFM) reviews. For example:
– Mould Engineers optimize gate placement and cooling channels in SolidWorks to minimize warpage.
– Formula Engineers select compounds (e.g., EPDM for hydraulic seals per ASTM D2000 Class A) to ensure thermal stability.
– Process Engineers validate injection parameters (e.g., 150°C melt temp, 80 bar pressure) to eliminate flash in valve components.
Strategic Partner Network: Accelerated Production Scalability
Leveraging 10+ ISO 9001-certified partner factories across China’s manufacturing hubs, we provide rapid scaling and geographic flexibility without compromising quality:
| Capability | Specialization | Lead Time Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Tooling | Prototype molds (3–5 days), high-precision steel tooling | 35% faster than single-source manufacturers |
| Automotive-Grade Molding | ISO/TS 16949-certified injection; tight tolerances (±0.05mm) | 50% faster for Tier 1 supplier deliveries |
| Metal-Rubber Bonding | Adhesion testing per ISO 4633; surface prep for steel/aluminum inserts | 99.5% bond integrity on first pass; zero field failures |
| Large-Format Compression | Components >1m diameter; heavy-duty vulcanization | 45% reduction for mining/hydraulic components |
Operational Workflow:
1. Design Phase: Baoshida engineers conduct joint DFM sessions with partner factories to validate moldability and material specs.
2. Tooling Phase: Partner facilities use rapid tooling (e.g., aluminum molds for prototypes) to cut lead times while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
3. Production Phase: Real-time SPC monitoring ensures consistency across all runs—critical for automotive applications requiring PPAP documentation.
Why This Ecosystem Works for Your Applications
Automotive: 72-hour turnaround for brake hose assemblies (ASTM D2000 Class 7) with bonded metal fittings.
Hydraulic Systems: EPDM compounds (D1418 Type E) with 100% compliance to SAE J200 for high-pressure seals.
Pump/Valve Components: Precision injection molding of nitrile rubber (NBR) parts with <0.05mm flash tolerance.
Industrial Machinery: Compression-molded rubber-metal bushings (ISO 4633) for 10x longer service life vs. industry averages.
Proven Result: A leading hydraulic equipment OEM reduced part rejection rates by 92% and cut lead times from 14 to 5 days for a critical valve seal—via our integrated engineering team and partner factory coordination.
Suzhou Baoshida delivers more than rubber parts—we deliver engineered solutions that eliminate production risk at every stage.
Customization & QC Process

Quality Control & Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida, our proprietary Quality Control & Customization Process is led by a specialized engineering team structured as 5+2+3: 5 Mold Design Engineers, 2 Formula Engineers, and 3 Process Engineers. Each team member possesses 15+ years of industry experience, ensuring precision in every phase from initial design to mass production. This structure enables end-to-end control over critical variables, including ASTM D2000 compliance, flash control, and metal bonding integrity.
| Team Component | Role | Count | Experience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mold Design | SolidWorks CAD, Drafting | 5 | 15+ years |
| Formula Engineering | Rubber compound development | 2 | 18+ years |
| Process Engineering | Molding optimization, QC | 3 | 16+ years |
Total: 10 core engineers + 10+ partner factories for rapid tooling. All processes adhere to ISO 9001:2015, IATF 16949, and SAE J1653 standards.
1. Drawing Analysis & Mold Design Validation
Initial CAD model validation is conducted by our 5-member Structural Engineering team using SolidWorks. This phase ensures manufacturability, dimensional accuracy, and adherence to ISO 2768 tolerances. Key checks include:
Draft angles ≥3° for ejection
Uniform wall thickness (±0.1mm tolerance)
Parting line optimization to minimize flash
Undercut analysis for core-pull mechanisms
The team collaborates with Process Engineers to simulate injection/compression molding flow paths, preventing defects such as sink marks or weld lines. All design iterations are documented in the Design History File (DHF) per ISO 13485 standards.
| Checkpoint | Standard Requirement | Tolerance | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | ISO 2768-mK | ±0.1 mm | CMM Measurement |
| Draft Angle | ASME Y14.5-2009 | ≥3° | Optical Comparator |
| Parting Line | ASTM D1418 Section 4.2 | 0.05 mm gap | Laser Scanning |
| Ejector Pin Layout | Mold Makers’ Association | Symmetrical | 3D Simulation |
Senior Mold Design Engineers validate all critical features against application-specific requirements (e.g., hydraulic seals require 0.02 mm cavity tolerance for pressure integrity).
2. Material Formulation & ASTM Compliance
Our 2 Formula Engineers utilize ASTM D2000 and D1418 standards to formulate rubber compounds tailored to application-specific needs. Each material is selected based on:
Service temperature range (-40°C to +150°C)
Chemical resistance (e.g., oil, ozone)
Mechanical properties per ASTM D412, D2240, D395
The following table illustrates key material specifications for automotive hydraulic seals (example):
| Property | ASTM D2000 Code | Target Value | Tolerance | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | Grade 2 | 70 ± 5 | ±15 points | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | Grade B | 15 MPa | ±30% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set | Grade C | 25% max | -5% to +10% | ASTM D395 |
| Aging Resistance | Grade 5 | – | ΔTS ≤ 30%, ΔH ≤ ±15 | ASTM D573 |
All formulations undergo lab validation before production. For metal-to-rubber bonding, we use proprietary adhesion promoters meeting SAE J1653 standards, ensuring interfacial shear strength ≥10 MPa.
Formula Engineers leverage historical data from 500+ automotive projects to optimize compound viscosity, cure kinetics, and filler dispersion—critical for flash control during injection molding.
3. Prototyping & Validation
Rapid prototyping leverages our 10+ partner factories for tooling in ≤7 days. Process Engineers oversee:
First Article Inspection (FAI) per AS9102
Physical property testing (e.g., tensile, hardness)
Flash measurement using optical profilometry (≤0.05 mm)
| Stage | Timeline | Acceptance Criteria | Responsible Team |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mold Fabrication | 3 days | ±0.02 mm cavity tolerance | Mold Design |
| First Shot | Day 5 | Flash ≤ 0.03 mm | Process Eng. |
| FAI Report | Day 7 | 100% compliance to drawing | Quality Control |
| Customer Approval | Day 10 | Signed PO for mass production | Project Manager |
All prototypes undergo accelerated aging tests (e.g., 70°C for 72 hours) to validate long-term performance. For metal-bonded components, we conduct peel strength testing per ISO 36:2010.
Process Engineers with 16+ years of experience optimize mold venting and injection parameters to eliminate micro-flashes in high-precision pump valve components.
4. Mass Production & Continuous QC
During mass production, our Process Engineers implement:
In-process SPC monitoring (X-bar R charts for critical dimensions)
Automated vision inspection for surface defects (e.g., voids, discoloration)
Random sampling per ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 Level II
Final QC includes:
100% dimensional checks via CMM
10% destructive testing for material properties
Batch traceability via serialized lot numbers
Senior engineers conduct weekly audits of production data, ensuring 100% conformity to ASTM D2000 aging requirements. All test results are digitally archived in our ERP system with blockchain-level traceability.
Key Advantage: Our 5+2+3 structure ensures zero-defect delivery for critical applications (e.g., automotive hydraulic systems), with typical lead times of 14–21 days for full-scale production. All processes are certified to IATF 16949:2016 with 99.98% first-pass yield.
Contact Our Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida: Precision Rubber Solutions for Critical Applications
Solve your sealing problems today with engineering-driven rubber component solutions engineered to meet ASTM D2000/D1418 standards. Our cross-functional team delivers precision mold design, material optimization, and process control for demanding applications in automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery industries.
Core Engineering Team Structure (5+2+3)
Integrated expertise for end-to-end rubber part validation and production
| Role | Count | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Design Engineers | 5 | SolidWorks/CAD mold design, flash control optimization, metal bonding interfaces, rapid tooling coordination |
| Formulation Engineers | 2 | ASTM D2000/D1418 material specification, compound development for tensile/hardness retention (±15 pts), chemical resistance validation |
| Process Engineers | 3 | Injection/compression molding parameter optimization, defect prevention (sink marks, flash), production scalability |
Direct Technical Support
For immediate engineering consultation on material specifications, mold design, or production challenges:
Contact: Mr. Boyce
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +86 189 5571 6798
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to ensure your rubber components meet the highest ASTM standards and application-specific performance requirements. Our 10+ partner factories enable rapid tooling and scalable production for time-sensitive projects.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
