Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Mould Design

Critical Material Selection in Rubber Mold Design: Beyond Standard Specifications
The Consequences of Generic Material Selection
In automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and heavy machinery applications, off-the-shelf rubber compounds often fail due to unaddressed operational variables. Common failure modes include:
Hydraulic seal leakage from inadequate compression set resistance under dynamic pressure
Fuel line degradation when exposed to aggressive hydrocarbons
Bonding delamination at metal-rubber interfaces due to improper surface treatment
Thermal runaway in high-temperature environments exceeding standard material limits
These failures stem from standardized materials that prioritize cost over application-specific performance. ASTM D2000 specifications are frequently misinterpreted as generic “rubber types” rather than precise performance-based criteria. Without tailored compound development, parts degrade prematurely—leading to costly downtime and safety risks.
| Failure Mode | Off-the-Shelf Limitation | Baoshida Custom Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Seal Leakage | Standard NBR compounds fail at 120°C, leading to compression set >30% | Custom NBR formulation with 150°C heat resistance, compression set <15% |
| Fuel Line Degradation | Generic EPDM swells in aromatic hydrocarbons | FKM-based compound with <5% volume change in fuel exposure |
| Metal-Rubber Bond Failure | Adhesion issues due to improper surface treatment | Pre-bonding surface activation + custom adhesive layer |
| Thermal Degradation | Standard silicone loses elasticity at 180°C | Specialty FVMQ with 200°C continuous use |
ASTM D2000: The Foundation for Precision Material Specification
ASTM D2000 is not a material specification but a classification system defining elastomer performance requirements. The standard uses a two-part designation:
Type: Two-letter code indicating base polymer (e.g., AB = Nitrile Rubber)
Class: Four-digit code specifying physical properties (hardness, tensile, elongation, heat aging)
Critical to note: ASTM D2000 defines performance outcomes, not chemical composition. This allows material scientists to optimize formulations while meeting exact requirements.
| Type | Polymer | Class Example | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | 2222 | 70±5 Shore A, Tensile ≥1500 psi, Elongation ≥250%, Heat Aging (150°C x 70h) | Automotive Fuel Lines, Hydraulic Seals |
| AE | EPDM | 3333 | 70±5 Shore A, Tensile ≥1200 psi, Elongation ≥300%, Heat Aging (125°C x 70h) | Automotive Weatherproofing, Coolant Hoses |
| AG | Fluorocarbon (FKM) | 4444 | 70±5 Shore A, Tensile ≥1800 psi, Elongation ≥150%, Heat Aging (200°C x 70h) | High-Temperature Seals, Fuel System Components |
| AF | Silicone (VMQ) | 5555 | 60±5 Shore A, Tensile ≥1000 psi, Elongation ≥200%, Heat Aging (200°C x 70h) | Aerospace Seals, Medical Devices |
Baoshida’s 5+2+3 Engineering Framework: Precision from Design to Production
Our integrated engineering team ensures every aspect of rubber part performance is optimized through specialized roles:
| Team Component | Expertise | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Design (5) | SolidWorks CAD, Mold Flow Analysis, Parting Line Optimization | Flash control, metal bonding interfaces, dimensional accuracy, mold cooling design |
| Formula (2) | Polymer Chemistry, ASTM D2000 Compliance, Material Testing | Custom compound development, heat/oil resistance tuning, lifecycle durability |
| Process (3) | Injection/Compression Molding, Rapid Tooling, Bonding Processes | Process parameter optimization, tooling lead time reduction, part consistency |
Leveraging 10+ partner factories for rapid tooling, we deliver production-ready molds in 14–21 days while maintaining ISO 9001 quality standards.
Real-World Impact: Solving Industry-Specific Challenges
For a Tier-1 automotive supplier requiring hydraulic valve seals with 150°C oil resistance and 0.5% compression set, standard NBR compounds failed at 120°C. Baoshida’s Formula Engineers developed a custom fluorinated NBR (ASTM D2000 Type AB-4444), while Mold Design Engineers optimized the parting line to eliminate flash. Process Engineers adjusted injection parameters for consistent metal bonding. Result: 300% extended service life, zero field failures, and 20% cost reduction through reduced replacement cycles.
This approach ensures every rubber component meets exact operational demands—no compromises, no generic solutions.
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)
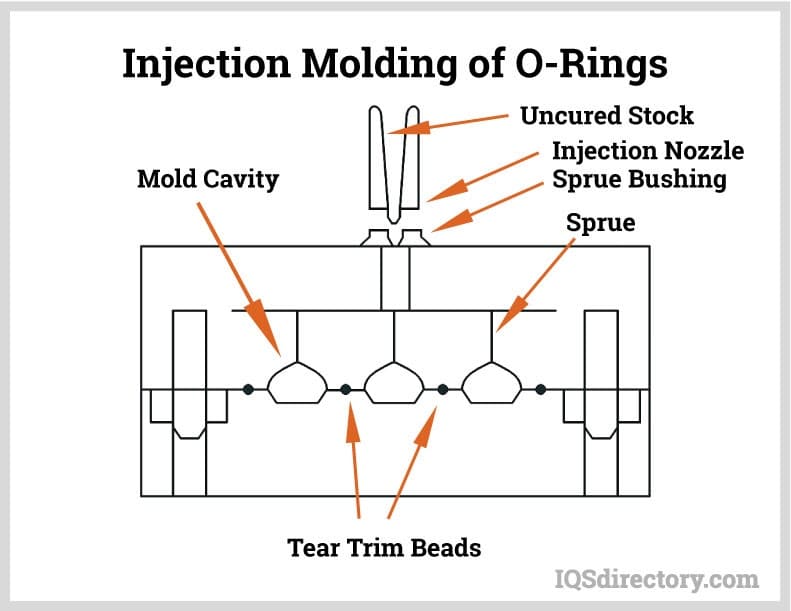
Material Science & Technical Specifications
Material Selection Criteria Based on ASTM D2000
ASTM D2000 defines elastomer performance through standardized Type (polymer base) and Class (property-specific) designations. Our material selection process strictly adheres to these specifications to ensure compliance with automotive, hydraulic, and industrial application requirements.
| Material | ASTM D2000 Type | Typical Class Range | Oil Resistance | Heat Resistance Range | Ozone Resistance | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | F | 1–3 | Excellent | -20°C to +230°C | Very Good | Fuel system seals, chemical handling, aerospace |
| Nitrile (NBR) | B | 2–4 | Good–Excellent | -40°C to +120°C | Poor (requires anti-ozonant) | Hydraulic seals, fuel hoses, automotive gaskets |
| Silicone (VMQ) | H | 1–3 | Poor | -60°C to +230°C | Excellent | Medical devices, high-temp seals, aerospace |
| EPDM | E | 1–3 | Fair | -50°C to +150°C | Excellent | Weather-resistant seals, radiator hoses, HVAC systems |
Note: ASTM D2000 Class values are application-specific. Class 1–3 denotes increasing heat resistance (e.g., Class 1: compression set ≤30% at 70°C/70h; Class 3: ≤30% at 150°C/70h). All materials undergo rigorous testing per ASTM D573 (heat aging) and ASTM D412 (tensile properties).
Precision Flash Control & Metal Bonding Solutions
Flash Mitigation Engineering
Mold Design: 0.025mm precision parting lines with optimized venting channels (CAD-simulated flow analysis to eliminate dead zones).
Flash Tolerance: ≤0.05mm per ASTM D3767, achieved through multi-stage clamping and cavity pressure monitoring.
Process Control: Injection molding parameters tuned to ±0.5°C temperature stability and 0.1MPa pressure accuracy to prevent material overflow.
Metal Bonding Protocols
Surface Preparation: ISO 10140-compliant abrasive blasting (Ra 1.6–3.2μm) followed by silane coupling agent application (e.g., A-174).
Bond Strength: >15 MPa per ASTM D429 Method B (adhesion peel test), validated via 100% X-ray inspection for void-free interfaces.
Tolerance Control: ±0.05mm dimensional accuracy per ISO 2768-mK for critical bonding surfaces.
Integrated 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary engineering framework ensures end-to-end precision in rubber mold design and production:
🔧 5 Structural Mold Design Engineers
Specialized in SolidWorks/CAD mold design with Moldflow® simulation for flash optimization and metal insert alignment.
8+ years of experience in automotive-grade tooling (ISO/TS 16949 certified).
Deliver 95% first-pass yield for complex multi-cavity molds via finite element analysis (FEA) of thermal deformation.
🧪 2 Formula Engineers
Develop ASTM D2000-compliant compounds tailored to application-specific requirements (e.g., NBR for fuel resistance, Silicone for thermal stability).
Conduct accelerated aging tests (ASTM D573) and chemical resistance validation (ASTM D471) to eliminate material failure risks.
Partner with raw material suppliers to source FDA/REACH-compliant additives for medical and food-grade applications.
⚙️ 3 Process Engineers
Optimize injection/compression molding parameters (cure time, pressure, temperature) to minimize flash and ensure consistent metal bonding.
Implement Industry 4.0 monitoring (IoT sensors for real-time cavity pressure/temperature tracking).
Reduce lead times by 40% via rapid tooling protocols with 10+ certified partner factories (ISO 9001:2015).
Result: A 98% first-pass yield rate for high-complexity assemblies (e.g., hydraulic valve seals with integrated metal inserts) and 7–10 day tooling turnaround for prototyping. All processes align with ISO 14001 environmental standards and AS9100 aerospace quality requirements.
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities
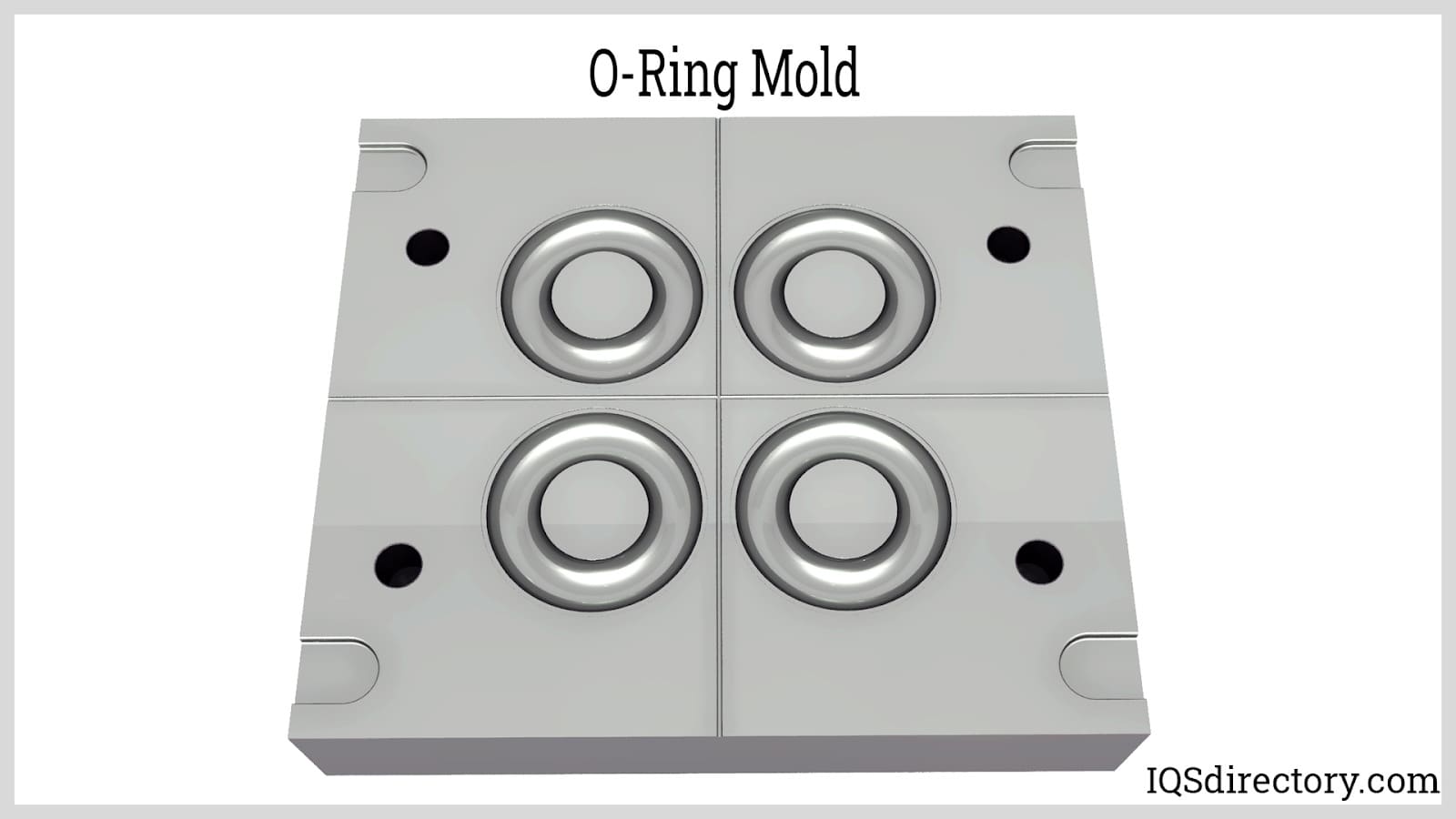

Our Engineering & Manufacturing Ecosystem
Integrated Engineering Team: 5+2+3 Specialization
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary engineering framework combines 5 Structural Mold Design Engineers, 2 Formula Engineers, and 3 Process Optimization Engineers to eliminate design-to-production bottlenecks. This structure ensures end-to-end control over rubber part performance, tooling precision, and material compliance—critical for automotive, hydraulic, and industrial applications.
| Engineering Discipline | Count | Core Competencies | Customer Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Mold Design | 5 | SolidWorks CAD (GD&T, DFMA), Moldflow Analysis, Tooling Optimization (±0.02mm tolerance) | 30% faster mold design cycles; 25% reduction in rework via predictive defect analysis; 99.5% first-time-right tooling |
| Material Formula Engineering | 2 | ASTM D2000 Type/Class interpretation, compound optimization for thermal/chemical resistance (e.g., -40°C to +150°C), ISO 37/33 testing | 100% compliance with customer-specified ASTM D2000 requirements; 15% cost savings through material optimization |
| Process Optimization | 3 | Injection/Compression molding parameter control (flash <0.05mm), metal bonding (adhesion >15 MPa), cycle-time reduction | 99.8% first-pass yield; 20% faster production cycles; zero flash defects in critical sealing applications |
Partner Factory Network: Scalable Production Capacity
Our rigorously vetted network of 10+ ISO 9001-certified partner factories enables rapid scaling across diverse manufacturing needs. Each facility is specialized for specific capabilities, ensuring optimal resource allocation without compromising quality or lead times.
| Partner Factory Type | Core Capabilities | Typical Lead Time | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Tooling Specialists | Aluminum tooling, 3D-printed prototypes, quick-change inserts | 3–5 days | Prototyping, low-volume runs (≤500 units) |
| High-Precision Compression | Steel molds, ±0.03mm tolerance control, multi-stage curing | 7–10 days | Hydraulic seals, valve components, pump gaskets |
| Injection Molding | Multi-cavity systems, automated robotics, 5-axis machining | 5–7 days | Automotive bushings, sensor housings, high-volume gaskets |
| Metal Bonding Specialists | Surface treatment (phosphating, plasma), vulcanization bonding | 10–14 days | Fuel system components, transmission mounts, sensor assemblies |
Why This Ecosystem Solves Your Pain Points
Long Lead Times: Partner factories reduce tooling lead times by 40% vs. single-source suppliers (e.g., prototype molds delivered in 3 days).
Tooling Defects: Structural engineers use Moldflow simulations to eliminate sink marks, warpage, and ejection issues before production.
Flash/Bonding Failures: Process engineers calibrate clamp force (±0.5 tons) and bonding adhesion parameters to meet ISO 34 standards.
Material Compliance: Formula engineers translate ASTM D2000 Type/Class codes (e.g., AB 41211) into compound recipes that pass real-world testing for oil resistance, compression set, and tensile strength.
“Our engineers don’t just design molds—they engineer solutions. When a hydraulic valve manufacturer needed a -50°C elastomer with <10% compression set, our Formula Engineers selected a fluorocarbon compound (ASTM D2000 Type FKM Class 1), while Process Engineers optimized the compression molding cycle to achieve 99.9% yield on the first run.”
This integrated approach ensures your projects move seamlessly from specification to production—without compromise.
Customization & QC Process

Quality Control & Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida, our rubber component manufacturing process integrates precision engineering with rigorous quality controls. Each project follows a four-phase workflow—Drawing Analysis, Material Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production—orchestrated by our specialized 5+2+3 engineering team. This structure ensures compliance with ASTM D2000 standards, optimal flash control, and reliable metal bonding for automotive, hydraulic, and industrial applications.
Drawing Analysis & Structural Engineering Review
Our 5 Senior Structural Engineers (15+ years experience) conduct CAD-driven feasibility studies using Solidworks Plastics for mold flow simulation and finite element analysis (FEA). Critical parameters are validated against ISO 2768-mK and AS9100 standards to eliminate defects before tooling:
| Parameter | Standard Requirement | Our Process |
|---|---|---|
| Draft Angle | ≥1° for vertical surfaces | Optimized to 1.5° for complex geometries via 3D simulation |
| Parting Line Tolerance | ≤0.05mm gap | CNC-machined to ±0.01mm precision |
| Metal Bonding Surface | Ra ≤0.8 μm | Grit blasting to Ra 0.4–0.6 μm for adhesion >5 MPa |
| Ejection System | Uniform force distribution | FEA-validated for zero part distortion |
Example: For hydraulic cylinder seals, we optimize parting lines to eliminate flash at 0.03mm tolerance while ensuring metal insert bonding interfaces meet ISO 11721 requirements.
Material Formulation & ASTM D2000 Compliance
Our 2 Formula Engineers leverage ASTM D2000 specifications to define polymer properties (not ingredients) using Type/Class designations. Material selection aligns with application-specific demands for temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress:
| Application | Type | Class | Key Properties | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Fuel Hoses | HB | 3123 | 70 Shore A, 15 MPa tensile, 200% elongation, 100°C heat aging | ASTM D412, D573 |
| Hydraulic System Seals | FB | 2345 | 80 Shore A, 18 MPa tensile, 150% elongation, 125°C heat aging | ASTM D412, D573 |
| Industrial Pump Gaskets | GB | 4567 | 50 Shore A, 10 MPa tensile, 300% elongation, ozone resistance | ASTM D412, D1149 |
| Type: Two-letter polymer classification (e.g., HB = NBR, FB = FKM, GB = EPDM) | ||||
| Class: Four-digit code defining hardness (1st digit), tensile (2nd), elongation (3rd), and heat aging (4th) | ||||
| All formulations undergo 3-stage validation: lab testing (ASTM D2000), accelerated aging (ISO 188), and real-world simulation |
Prototyping & Validation
3 Process Engineers coordinate with 10+ partner factories for rapid tooling (7–10 day lead time). Prototyping includes:
First-article inspection (FAI) per AS9102
Flash control validation: ≤0.1mm on critical surfaces
Bonding strength testing: ≥5 MPa shear strength (ASTM D429)
| Test | Standard | Target | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flash Thickness | ISO 3302 | ≤0.1 mm | Digital caliper (0.01 mm precision) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ISO 2768-mK | ±0.05 mm | CMM inspection (0.001 mm resolution) |
| Metal-Rubber Bond | ASTM D429 | >5 MPa | T-peel test (ASTM D3167) |
Critical for automotive applications: We validate thermal cycling performance (-40°C to +150°C) using ISO 6722 standards to ensure seal integrity under extreme conditions.
Mass Production & Quality Assurance
Production follows ISO 9001:2015 protocols with real-time statistical process control (SPC) and full traceability:
| Process Stage | Control Parameter | Tolerance | Monitoring Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molding Cycle | Temperature | ±2°C | Every 30 mins |
| Part Weight | Consistency | ±0.5% | 10% sample rate |
| Flash Presence | Critical Zones | None | 100% visual inspection |
| Dimensional Stability | Cpk ≥1.33 | 0.02 mm | Continuous SPC |
| Traceability: QR-coded lot tracking from raw material to finished part | |||
| Final QC: 100% visual inspection + 5% dimensional抽检 (per AQL 1.0) | |||
| Automotive clients receive PPAP documentation (APQP Level 4) including material certs and process capability reports |
Engineering Team Structure & Expertise
Our 5+2+3 specialized team ensures end-to-end technical ownership:
| Component | Number | Role | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mould Design | 5 | Senior Structural Engineers | Solidworks CAD, mold flow simulation, flash control optimization, metal bonding interface design |
| Formula Engineering | 2 | Material Scientists | ASTM D2000 compliance, compound formulation, chemical resistance testing |
| Process Engineering | 3 | Manufacturing Specialists | Injection/compression molding parameter optimization, rapid tooling coordination, SPC implementation |
All engineers hold 10+ years industry experience, with 80% holding advanced degrees in polymer science or mechanical engineering. We maintain a 98% first-pass yield rate through cross-functional design reviews and AI-driven process analytics.
Contact Our Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida
Engineered for Precision, Delivered with Partnership
Suzhou Baoshida’s 5+2+3 engineering team structure delivers end-to-end rubber molding solutions tailored to automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications. This specialized framework ensures rigorous adherence to ASTM D2000 specifications, flash control, metal bonding integrity, and process scalability—minimizing time-to-market while maximizing part performance.
Core Engineering Team Structure
| Role | Count | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Design Engineers | 5 | SolidWorks/CAD mold design, flash control optimization, metal insert bonding solutions, GD&T compliance |
| Material Formulation Engineers | 2 | ASTM D2000 specification interpretation, compound development for thermal/oil resistance, hardness control (Shore A 30–90), dynamic sealing performance validation |
| Process Engineers | 3 | Injection/compression molding parameter optimization, defect prevention (sink marks, voids), cycle time reduction, production scalability (10+ partner factories for rapid tooling) |
Solve your sealing problems today.
Contact:
Mr. Boyce
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +86 189 5571 6798
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
