Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Profile Extrusion
Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Rubber Profile Extrusion
Material selection constitutes the foundational determinant of success in rubber profile extrusion, yet it remains the most frequently underestimated variable in industrial applications. Off-the-shelf rubber compounds, while cost-attractive for generic uses, consistently fail under the precise thermal, rheological, and dimensional demands of profile extrusion. This failure manifests as excessive scrap rates, inconsistent cross-sections, surface defects, and premature tooling wear—directly attributable to mismatched material properties rather than extrusion equipment limitations.
The core issue lies in the oversimplification of rubber as a homogeneous material. Effective extrusion requires compounds engineered at the molecular level to balance competing parameters: Mooney viscosity must enable smooth flow through complex dies without excessive swell, scorch safety must accommodate extended residence times in heated barrels, and filler dispersion must ensure uniform shrinkage post-extrusion. Standard compounds prioritize broad applicability over extrusion-specific behavior, lacking tailored polymer architecture, curative systems, or filler treatments. For instance, generic EPDM formulations often exhibit uncontrolled die swell due to inadequate polymer branching, while insufficient scorch resistance in SBR leads to surface tearing during high-speed runs.
Empirical evidence confirms that off-the-shelf materials amplify sensitivity to minor process fluctuations. A 5°C temperature variance or 0.5 rpm screw speed change—within typical operational tolerance—can trigger catastrophic dimensional drift in non-optimized compounds. This stems from narrow processing windows where viscosity and cure kinetics are not synchronized with extruder dynamics. Consequently, OEMs face costly rework, delayed shipments, and compromised product lifespan when compounds lack extrusion-specific formulation rigor.
The following table contrasts critical properties between standard and engineered compounds:
| Property | Standard EPDM Compound | Custom-Engineered EPDM | Impact on Extrusion Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mooney Viscosity (ML 1+4 @ 100°C) | 60 ± 5 | 52 ± 2 | Lower variability ensures consistent flow rate and reduced die pressure spikes |
| Scorch Time (T5 @ 125°C) | 8 minutes | 14 minutes | Extended safety margin prevents premature cure during long residence times |
| Extrudate Swell (200%) | 28% ± 6% | 18% ± 3% | Tighter dimensional control minimizes post-extrusion trimming requirements |
| Filler Dispersion Index | 3.5 (ASTM D2663) | 1.2 | Eliminates surface roughness and weak points in critical sealing zones |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses this through compound-specific extrusion profiling. Our formulations integrate dynamic vulcametry data with extruder shear history modeling to calibrate polymer-filler-cure synergies. This preemptive engineering eliminates the trial-and-error approach, ensuring the first production run achieves ±0.1 mm dimensional tolerances even in intricate multi-cavity profiles. Material selection is not a procurement decision—it is a precision engineering prerequisite where molecular architecture dictates manufacturing viability. Off-the-shelf solutions ignore this reality; engineered compounds deliver it.
Material Specifications
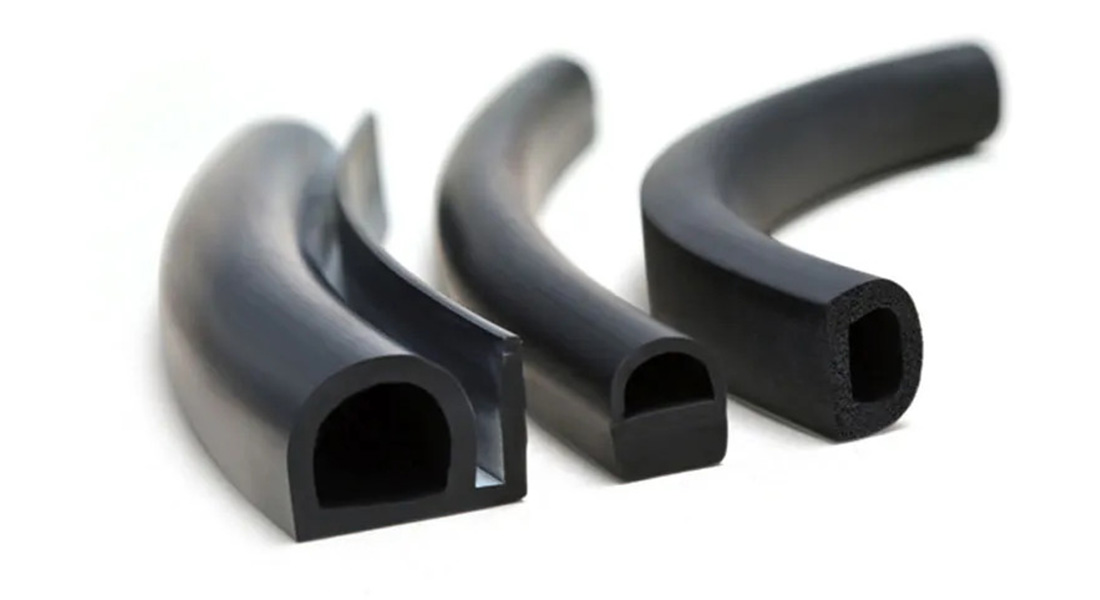

Material selection is a critical determinant in the performance, durability, and application suitability of rubber profile extrusions. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision extrusion solutions tailored to industrial demands, leveraging high-performance elastomers such as Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone. Each material exhibits distinct chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties, enabling targeted deployment across automotive, aerospace, chemical processing, and medical industries.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, oils, and fuels. With a continuous service temperature range up to 230°C and intermittent peaks beyond 250°C, Viton is ideal for extreme environments. Its low gas permeability and outstanding aging characteristics make it a preferred choice for sealing applications in engine systems and industrial valves. However, Viton has limited flexibility at sub-zero temperatures and higher material costs compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is a synthetic copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile. It provides excellent resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels, making it widely used in hydraulic systems, fuel lines, and industrial seals. Nitrile compounds can be tailored for varying acrylonitrile content to balance oil resistance and low-temperature performance. Standard NBR operates effectively between -30°C and 100°C, with some formulations extending to 125°C short-term. While cost-effective and mechanically robust, Nitrile exhibits poor resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and polar solvents.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) stands out for its outstanding thermal stability and biocompatibility. It maintains flexibility from -60°C to 200°C, with certain grades functional up to 250°C. Silicone is inherently resistant to UV, ozone, and microbial growth, and meets regulatory standards for medical and food-contact applications (e.g., FDA, USP Class VI). Its electrical insulation properties also support use in electronics and high-voltage environments. However, silicone has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton and Nitrile, requiring careful design consideration in dynamic mechanical applications.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for comparative evaluation in rubber profile extrusion projects.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 100 (up to 125) | -60 to 200 (up to 250) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 300–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Fluid Resistance (Oil/Fuel) | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Moderate | Good |
| Ozone/UV Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace seals, chemical gaskets | Fuel hoses, O-rings, hydraulic seals | Medical tubing, food-grade seals, electrical insulation |
Selection of the appropriate elastomer requires alignment with operational stressors including temperature extremes, media exposure, mechanical load, and regulatory compliance. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs with material testing, formulation optimization, and extrusion process control to ensure performance integrity across the product lifecycle.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Profile Extrusion
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers advanced rubber profile extrusion solutions through a dedicated team of 5 Mould Engineers and 2 specialized Rubber Formula Engineers. This integrated technical structure ensures end-to-end control over material science and tooling design, directly addressing the complex interplay between compound behavior and extrusion dynamics. Our engineers collaborate from initial specification to production validation, eliminating siloed development that often causes dimensional instability, surface defects, or premature material degradation in extruded profiles.
The Formula Engineering team focuses on polymer morphology optimization, tailoring compound formulations to balance flow characteristics, cure kinetics, and end-use performance. We develop custom elastomer blends for extreme environments—resisting ozone, hydraulic fluids, or temperatures from -60°C to +250°C—while maintaining extrusion line speed efficiency. Concurrently, Mould Engineers utilize 3D flow simulation software to model die land geometry, pressure distribution, and swell compensation. This dual-expertise approach minimizes trial-and-error iterations, reducing time-to-market by up to 35% compared to conventional supplier workflows. Critical parameters such as Shore A hardness uniformity, cross-sectional consistency, and adhesion in co-extruded profiles are systematically validated through in-house rheometry, Mooney viscometry, and precision metrology.
Our OEM capabilities are engineered for scalability and intellectual property security. Clients receive full technical ownership of custom profiles, with Baoshida managing seamless transitions from prototype to high-volume production. We implement strict NDA protocols and dedicated production cells to prevent cross-contamination or design leakage, a non-negotiable standard for automotive and medical device partners.
Key extrusion specifications achievable under this framework include:
| Parameter | Standard Capability | Custom Capability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durometer Range | 30–90 Shore A | 20–95 Shore A | Per ASTM D2240 |
| Cross-Section Tolerance | ±0.15 mm | ±0.05 mm | Critical dimensions |
| Material Types | EPDM, NBR, Silicone, CR | FKM, ACM, HNBR, TPE/TPV | FDA/USP Class VI options |
| Max. Profile Width | 120 mm | 180 mm | Single-cavity |
| Lead Time (Prototype) | 15 business days | 25 business days | Includes tooling & validation |
This technical infrastructure directly translates to reduced scrap rates, extended die life, and compliance with ISO 3302-1 geometric tolerancing standards. For OEM partners, we provide full material traceability documentation, batch-specific cure curve analysis, and real-time process monitoring data—ensuring every meter of extruded profile meets stringent functional requirements. By anchoring extrusion excellence in material science and precision tooling, Baoshida transforms complex rubber profile challenges into reliable, high-yield manufacturing outcomes.
Customization Process
Drawing Analysis: The Foundation of Precision
The customization process for rubber profile extrusion begins with rigorous drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we treat every technical drawing as a blueprint for performance. Our engineering team conducts a dimensional audit, verifying critical tolerances, cross-sectional geometry, and interface points with mating components. We assess draft angles, wall thickness uniformity, and potential stress concentration zones that may affect extrusion stability. Material callouts, if specified, are cross-referenced with our formulation database, while ambiguous or incomplete drawings trigger immediate technical clarification with the client. This phase ensures that design intent aligns with manufacturability, minimizing downstream deviations. Advanced CAD software enables 2D/3D profile simulation, allowing us to predict flow behavior during extrusion and identify areas prone to die swell or shrinkage. Only after full dimensional validation and client sign-off does the project advance.
Formulation: Engineering Material to Application
With approved geometry, we transition to compound development—a phase where material science meets application demands. Our Rubber Formula Engineers select base polymers based on environmental exposure: EPDM for UV and ozone resistance, NBR for oil and fuel, silicone for extreme temperatures, or CR for flame retardancy. Reinforcing fillers, plasticizers, vulcanizing agents, and processing aids are precisely balanced to achieve target hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, elongation, compression set, and abrasion resistance. Every formulation is optimized not only for end-use performance but also for extrudability—ensuring smooth die flow and dimensional consistency. Regulatory compliance (e.g., RoHS, REACH, FDA) is embedded into the formulation matrix when required. Clients receive a detailed Material Data Sheet (MDS) and Certificate of Compliance (CoC) for full traceability.
Prototyping: Validating Design and Material
Prototyping bridges theory and production. Using precision-machined pilot dies, we extrude short runs under simulated production conditions. These prototypes undergo rigorous metrological inspection via laser profilometry and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify dimensional accuracy against the original drawing. Simultaneously, physical testing—including tensile, compression set, and environmental aging—is conducted in our in-house lab. We evaluate splice integrity, surface finish, and consistency across the run length. Client feedback is integrated at this stage, allowing for die adjustments or formulation tweaks before final approval. This iterative validation ensures that both form and function meet exact specifications.
Mass Production: Scalable Precision
Upon prototype approval, we transition to mass production using high-torque extruders, temperature-controlled curing lines, and automated take-off systems. Real-time monitoring ensures consistent line speed, temperature profiles, and vulcanization time. Each batch is subject to statistical process control (SPC), with periodic sampling for mechanical and dimensional verification. Final inspection includes visual grading, length cutting accuracy, and packaging per client logistics requirements.
Typical Physical Properties of Custom Rubber Profiles
| Property | Test Method | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 40–90 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 8–20 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | 200–600% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Operating Temperature | — | -40°C to +150°C (varies by compound) |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D297 | 1.10–1.35 |
Contact Engineering Team

Initiate Your Precision Rubber Profile Project with Suzhou Baoshida
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands as your definitive engineering partner for advanced rubber profile extrusion solutions within the industrial sector. Our specialization transcends standard manufacturing; we integrate deep material science expertise with rigorous process control to deliver profiles meeting the most demanding functional and dimensional requirements. Whether your application necessitates extreme temperature resilience, chemical inertness, or micron-level geometric precision, our engineered compounds and extrusion methodologies provide the foundation for superior product performance and longevity. We understand that in critical industrial environments, the failure of a single rubber component can cascade into significant operational disruption. Therefore, our commitment extends beyond supply to becoming a proactive extension of your engineering team, ensuring seamless integration of our profiles into your final assembly.
Our technical proficiency is quantifiable through consistent adherence to stringent international standards and the ability to tailor solutions to unique OEM specifications. The table below outlines core capabilities central to our extrusion process, reflecting the precision engineering underpinning every meter of profile produced. These parameters are not merely targets but routinely achieved benchmarks across our production lines, validated through in-house metrology and third-party certification where required.
| Specification Parameter | Capability Range | Measurement Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.05 mm to ±0.20 mm | ISO 3302-1:2019 |
| Shore Hardness Range (A) | 30 to 90 | ASTM D2240 |
| Material Compatibility | NBR, EPDM, Silicone, FKM, CR, HNBR | ASTM D2000 |
| Max. Cross-Section Width | 150 mm | Customer Drawing |
| Standard Extrusion Speed | 0.5 m/min to 30 m/min | Process Validation |
Engaging Suzhou Baoshida initiates a structured technical collaboration. Our process begins with a detailed review of your functional requirements, environmental exposure conditions, and integration points. Our Rubber Formula Engineers then develop or select the optimal compound formulation, considering factors such as compression set, tensile strength, fluid resistance, and low-temperature flexibility. Concurrently, our extrusion specialists analyze the profile geometry to determine the precise die design, temperature zoning, and curing parameters necessary to achieve the specified tolerances and surface finish. This integrated approach eliminates guesswork, significantly reducing prototyping iterations and accelerating time-to-market for your product.
To translate your rubber profile specifications into a reliable, high-performance component, direct technical consultation is essential. Mr. Boyce, serving as our dedicated OEM Manager, possesses comprehensive oversight of technical sales, project engineering, and production coordination for global industrial clients. His expertise ensures your inquiry receives immediate attention from the appropriate engineering resources within our organization. Initiate the dialogue by contacting Mr. Boyce directly via email at [email protected]. Provide your project specifications, target volumes, and critical performance criteria to receive a detailed technical proposal and feasibility assessment within 48 business hours. Suzhou Baoshida is prepared to engineer the precise rubber profile solution that meets your application’s exacting demands, underpinned by our commitment to scientific rigor and industrial reliability. Partner with us for precision-engineered rubber profiles that perform.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
