Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Window Molding Car
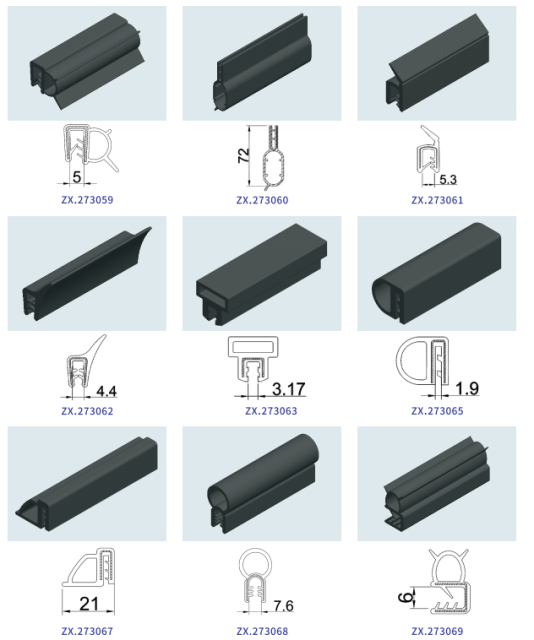

Engineering Insight: Material Science Imperatives for Automotive Window Molding Performance
Automotive window molding represents a critical interface demanding exceptional material resilience. Off-the-shelf rubber compounds frequently fail in this application due to fundamental mismatches between generic formulations and the extreme, dynamic operational environment of modern vehicles. Standard EPDM extrusions, often sourced for cost efficiency, typically lack the sophisticated polymer architecture and additive systems required to withstand the synergistic assault of ultraviolet radiation, ozone exposure, wide thermal cycling (-40°C to +120°C), repeated mechanical flexing during door closure, and exposure to road salts and cleaning agents. These generic materials prioritize basic extrudability and low cost over long-term performance, leading to premature degradation modes such as surface cracking, permanent set, hardening, and loss of sealing integrity. The consequence is not merely cosmetic; it manifests as wind noise intrusion, water leakage into cabin structures, accelerated corrosion of adjacent metal components, and ultimately, costly warranty claims that erode OEM brand reputation and profitability. Material selection is therefore not a commodity decision but a core engineering requirement.
The failure of generic solutions stems from oversimplified property targets. Achieving adequate initial durometer or tensile strength is insufficient. True performance hinges on the balance and stability of multiple interdependent properties under sustained stress. Compression set resistance is paramount; a molding must recover fully after years of constant compression against the glass to maintain a watertight seal. Low-temperature flexibility prevents brittle fracture during cold-weather operation. High elongation at break accommodates the significant deflection required during glass installation and door movement without tearing. Crucially, these properties must remain stable across the vehicle’s entire service life. Generic compounds often utilize high filler loads and basic polymer grades that sacrifice long-term resilience for initial processability, leading to rapid property decay.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses this through OEM-grade custom formulation. Our engineering process begins with a deep analysis of the specific vehicle platform’s thermal, mechanical, and environmental profile. We then develop proprietary EPDM or specialty terpolymer compounds engineered with precise crosslink density, optimized polymer molecular weight distribution, and high-performance stabilizer packages. This ensures the critical property balance required for decades of reliable service. The table below illustrates the performance gap between a typical off-the-shelf solution and our engineered OEM compound:
| Property | Generic Off-the-Shelf EPDM | Baoshida OEM Window Molding Compound | Critical Automotive Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durometer (Shore A, 23°C) | 65 ± 5 | 68 ± 3 | Consistent sealing force |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 7.0 | ≥ 10.5 | Resistance to tearing |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥ 250 | ≥ 450 | Accommodates glass deflection |
| Compression Set B (70°C/22h) | ≤ 35% | ≤ 12% | Long-term seal retention |
| Low Temp Flex (ASTM D1329) | -35°C Fail | -50°C Pass | Cold climate reliability |
The data underscores why off-the-shelf options fail: inadequate compression set and poor low-temperature performance directly cause seal loss and cracking. Baoshida’s compounds are validated through rigorous OEM test protocols, including multi-year outdoor weathering, dynamic compression cycling, and chemical resistance screening. We partner with automakers from the design phase, ensuring the rubber formulation is an integral, optimized component of the total window system, not an afterthought. This engineering-first approach eliminates the hidden costs of premature failure, delivering true value through enhanced durability and reduced lifecycle expenses.
Material Specifications

Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of rubber window molding for automotive applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision-engineered custom molded rubber parts designed to meet the stringent demands of the automotive industry. Our expertise includes the formulation and production of rubber window moldings using high-performance elastomers such as Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone. Each material offers distinct mechanical, thermal, and chemical resistance properties, making them suitable for different operating environments and vehicle systems.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a wide range of aggressive chemicals. This makes Viton an ideal choice for window moldings in high-performance or under-hood adjacent applications where exposure to engine fluids and elevated temperatures is common. With continuous service capabilities up to 230°C and excellent ozone and UV resistance, Viton ensures long-term sealing integrity in harsh conditions. However, its higher cost and lower flexibility at low temperatures may limit its use in standard consumer vehicles.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a cost-effective solution widely used in automotive sealing due to its strong resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and fuels. It offers good mechanical properties, including abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it suitable for general-purpose window molding applications. NBR performs reliably in temperature ranges from -30°C to 120°C, providing flexibility and compression set resistance under typical driving conditions. While it lacks the high-temperature resilience of Viton, NBR remains a preferred choice for cost-sensitive applications where exposure to hydrocarbons is moderate.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature environments, with a service range from -60°C to 200°C, offering unmatched low-temperature flexibility and high-temperature stability. It also demonstrates excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering, making it highly suitable for exterior window moldings exposed to sunlight and atmospheric conditions. Silicone’s inert nature and low toxicity also make it compliant with many environmental and safety standards. However, its relatively poor resistance to oils and fuels limits its use in areas with direct contact with lubricants or hydraulic fluids.
The following table summarizes the key physical and chemical properties of these materials for comparative evaluation:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–20 | 6–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–450 | 400–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 70–90 | 50–90 | 40–80 |
| Fuel/Oil Resistance | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Ozone/UV Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Cost Level | High | Low to Medium | Medium |
Selecting the optimal material requires a balance between performance requirements, environmental exposure, and cost efficiency. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we support OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers with material consultation, prototyping, and scalable production to ensure the highest quality rubber window molding solutions tailored to your automotive specifications.
Manufacturing Capabilities
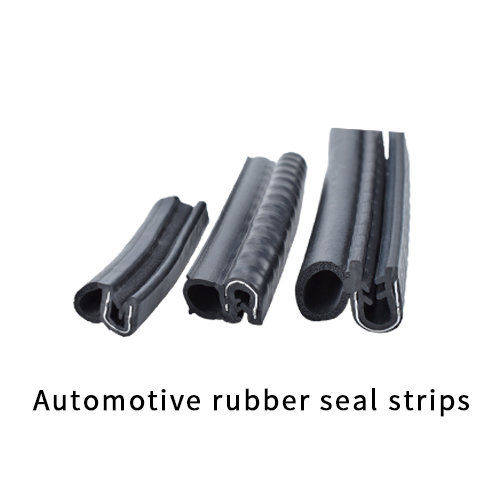

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Formulation and Mold Design for Automotive Window Seals
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber window molding solutions meeting the stringent demands of global automotive OEMs. Our core strength resides in the integrated expertise of our dedicated engineering teams: five specialized mold engineers and two advanced rubber formula engineers. This structure ensures seamless translation from material science to precise physical execution, critical for window seals operating under extreme thermal cycling, UV exposure, and dynamic compression.
Our formula engineers focus exclusively on developing and optimizing EPDM and TPE compounds tailored for automotive glazing systems. Material selection targets specific OEM requirements for low-temperature flexibility (down to -40°C), exceptional ozone and UV resistance, minimal compression set, and consistent friction coefficients for smooth glass travel. Each formulation undergoes rigorous laboratory validation against SAE J2236 and OEM-specific standards, ensuring long-term sealing integrity and aesthetic performance throughout the vehicle lifecycle. Full material traceability and batch consistency are non-negotiable elements of our quality control process.
Complementing material science, our mold engineering team possesses deep expertise in complex multi-cavity and family mold design for high-volume production. We specialize in precision tolerancing for critical sealing lips, intricate internal reinforcement channels, and co-extrusion interfaces. Advanced simulation tools (Moldflow) are employed to predict flow behavior, minimize weld lines, and optimize cooling circuits, directly impacting part dimensional stability and reducing scrap rates. This proactive approach mitigates common production challenges like flash, sink marks, and inconsistent durometer distribution across the profile.
Our OEM management framework is built for automotive integration. We operate under IATF 16949 protocols, providing full design for manufacturing (DFM) feedback during the APQP phase and establishing robust PPAP documentation packages. Closed-loop feedback mechanisms with OEM design teams ensure rapid iteration on CAD data and physical prototypes. Suzhou Baoshida manages the entire supply chain for critical raw materials, guaranteeing consistent compound performance and mitigating supply disruption risks for our partners. This end-to-end control, from molecular formulation to precision molding, delivers window seals that exceed expectations for durability, fit, and function.
Key rubber window molding specifications consistently achieved by our engineering teams include:
| Performance Parameter | Typical Value Range | Testing Standard | Significance for Window Seals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 65 ± 5 | ASTM D2240 | Optimal balance for sealing force & glass travel |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 10.0 | ASTM D412 | Resistance to tearing during installation/use |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥ 300 | ASTM D412 | Accommodates door flex and thermal expansion |
| Compression Set (70h/100°C) | ≤ 25% | ASTM D395 Method B | Critical for maintaining sealing force over time |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +130 (continuous) | Internal Validation | Ensures function in all global climates |
| Specific Gravity | 1.35 – 1.45 | ASTM D297 | Impacts weight and material cost efficiency |
This integrated engineering capability, combining deep material science with precision tooling expertise under a disciplined OEM management structure, positions Suzhou Baoshida as a strategic partner for automotive window system suppliers demanding reliability, performance, and seamless integration into high-volume manufacturing.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for rubber window molding in automotive applications begins with a comprehensive drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we evaluate technical blueprints provided by OEMs or Tier-1 suppliers to ensure dimensional accuracy, sealing interface compatibility, and compliance with vehicle assembly tolerances. Our engineering team scrutinizes critical features such as cross-sectional profiles, insertion grooves, flange geometry, and installation clearances. We also assess environmental exposure zones—such as UV radiation, temperature cycling, and exposure to road salts—to determine material suitability. This phase includes GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) verification and 3D data alignment using CAD software such as SolidWorks and AutoCAD. Any discrepancies or design risks are flagged early to prevent downstream production issues.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, we proceed to rubber compound formulation. The performance demands of automotive window moldings require elastomers with exceptional weather resistance, compression set stability, and aesthetic surface finish. Based on application requirements, we select base polymers such as EPDM, silicone (VMQ), or thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV). Additives including UV stabilizers, anti-ozonants, processing oils, and reinforcing fillers are precisely metered to achieve target hardness (typically 55–75 Shore A), tensile strength, and elongation at break. Our in-house lab conducts dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) to verify compound behavior under simulated service conditions. All formulations are engineered to meet OEM-specific material standards, including those from Ford, GM, Volkswagen, and Toyota.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the compound is finalized, we produce functional prototypes using precision compression or transfer molding techniques. Prototypes are manufactured with steel or aluminum prototype molds to mirror production conditions as closely as possible. These samples undergo rigorous testing, including fitment trials on vehicle mock-ups, weather aging (per ASTM G154), and compression deflection testing. Dimensional reports are generated using coordinate measuring machines (CMM), and surface quality is evaluated against appearance standards. Feedback from customer trials is integrated into design or material refinements, ensuring optimal performance prior to tooling release.
Mass Production
After prototype approval, we transition to full-scale manufacturing. Production molds are fabricated from high-grade tool steel with polished cavities to ensure surface consistency. Rubber window moldings are produced via high-pressure vulcanization in automated molding lines, followed by trimming, inspection, and packaging. In-process quality checks include 100% visual inspection and statistical sampling for physical properties. We maintain ISO/TS 16949-compliant production systems with full traceability, batch coding, and PPAP documentation. Our production capacity supports both low-volume specialty runs and high-volume OEM programs with JIT delivery logistics.
Typical Physical Properties of Custom Rubber Window Molding
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60 – 70 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 9.0 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 250% |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 25% |
| Operating Temperature Range | – | -40°C to +135°C |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D297 | 1.25 – 1.35 |
Contact Engineering Team
Precision Partnership for Automotive Rubber Window Molding Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands as your definitive engineering partner for custom rubber window molding in automotive applications. With over 15 years of specialized expertise in elastomer formulation and precision molding, we deliver components that meet the exacting demands of global vehicle manufacturers. Our integrated approach combines advanced material science with rigorous quality control, ensuring seamless integration into your production lines while exceeding OEM durability and sealing performance benchmarks. We recognize that window molding is not merely a component but a critical system interface requiring flawless dimensional stability, weather resistance, and aesthetic consistency across extreme operational environments.
Our technical capabilities are anchored in proprietary rubber compound development. We formulate materials to address specific challenges such as UV degradation, ozone exposure, thermal cycling from -50°C to +150°C, and long-term compression set resistance. This precision extends to secondary operations including co-extrusion, splicing, and adhesive application, all executed within our ISO/TS 16949-certified manufacturing facilities. Below are key performance specifications achievable through our custom engineering process:
| Specification Category | Performance Range | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40–90 | ASTM D2240 |
| Temperature Resistance | -50°C to +150°C | ISO 188 |
| Tensile Strength | 8–22 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | 200–600% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (70h/70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.15–1.35 | ASTM D297 |
What distinguishes Suzhou Baoshida is our commitment to collaborative engineering. We do not merely supply parts; we co-develop solutions. Our team engages directly with your design and procurement departments from initial concept through PPAP validation, leveraging finite element analysis (FEA) for seal performance prediction and rapid prototyping capabilities to accelerate time-to-market. We maintain full ownership of tooling assets, ensuring continuity and IP protection, while our lean manufacturing systems guarantee on-time delivery with <0.1% defect rates.
For automotive window molding projects demanding uncompromised quality and technical agility, initiate your partnership with Suzhou Baoshida. Contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineering lead, for an engineer-to-engineer consultation. Specify your vehicle platform requirements, performance targets, and volume projections in your initial communication. Mr. Boyce will coordinate a cross-functional team to provide material certifications, dimensional validation reports, and a tailored production timeline within 48 hours of inquiry.
Direct your technical specifications and project scope to [email protected] with the subject line Automotive Window Molding Inquiry – [Your Company Name]. Include critical parameters such as cross-section geometry, substrate adhesion requirements, and environmental exposure conditions. We respond to all qualified OEM inquiries within one business day, providing actionable data to advance your sourcing strategy. Suzhou Baoshida operates under strict NDA frameworks and adheres to all IATF 16949 traceability protocols. Partner with us to transform material science into measurable production success. Contact Mr. Boyce today at [email protected] to secure your engineering review slot.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
