Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Sealing Windshield Rubber
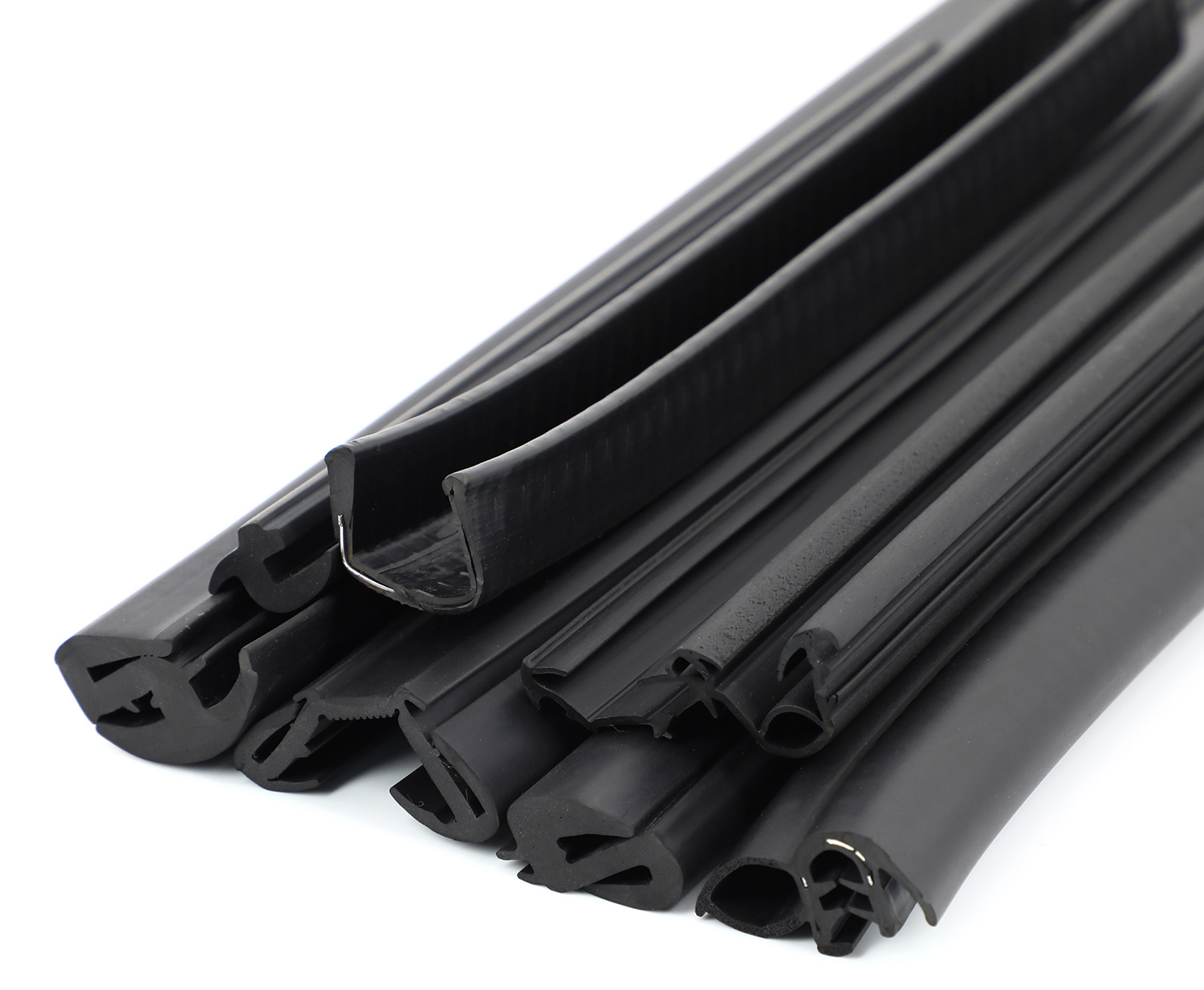

Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Sealing Windshield Rubber
In the precision domain of automotive and industrial glazing systems, the performance of a windshield seal extends far beyond simple weatherproofing. It is a dynamic interface subjected to continuous mechanical stress, thermal cycling, UV exposure, and chemical aggression from environmental contaminants and cleaning agents. The failure of a sealing windshield rubber is rarely due to a single factor but is typically rooted in inappropriate material selection. Off-the-shelf rubber profiles, while cost-attractive, often fail to meet the nuanced demands of real-world operating environments, leading to premature degradation, air/water leakage, and compromised structural integrity.
Standard elastomers such as generic EPDM or low-grade silicone may appear suitable based on basic datasheet values, but they lack the tailored compounding required for long-term resilience. For instance, unmodified EPDM compounds can exhibit poor resistance to ozone cracking in urban environments with high UV and pollutant exposure. Similarly, silicone rubber, although thermally stable, may possess insufficient tensile strength or compression set resistance when used in high-load glazing channels. These shortcomings become evident only after prolonged service, making them costly to rectify post-installation.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize application-specific formulation. Our engineered sealing windshield rubber solutions are developed through rigorous analysis of operational parameters including temperature range, mating substrate (glass, aluminum, composites), installation method (snap-fit, adhesive bonding), and expected service life. This enables precise tuning of polymer backbone, crosslink density, and additive package—elements that directly influence performance metrics such as compression set, Shore hardness, elongation at break, and aging resistance.
The following table outlines key material properties for common elastomers used in windshield sealing applications, highlighting why generic solutions fall short in demanding environments.
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Ozone Resistance | UV Stability | Typical Failure Mode in Windshield Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard EPDM | -40 to +120 | >30% | 8–10 | Moderate | Moderate | Surface cracking, hardening after 3–5 years |
| High-Performance EPDM (Baoshida Formulated) | -50 to +150 | <15% | 12–15 | Excellent | Excellent | No observable degradation at 8-year benchmark |
| General-Purpose Silicone | -60 to +200 | 20–25% | 5–7 | Good | Good | Joint separation due to low tear strength |
| Fluorosilicone | -50 to +180 | <20% | 6–8 | Excellent | Excellent | High cost limits use; over-engineered for most |
| Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) | -40 to +135 | 25–30% | 10–12 | Good | Good | Creep under continuous load after 4 years |
The data underscores a critical insight: material behavior under real-world conditions cannot be extrapolated from nominal specifications. Off-the-shelf seals frequently utilize minimum-specification compounds to meet price targets, sacrificing durability and consistency. In contrast, our precision rubber seals are formulated for mission-critical performance, ensuring dimensional stability, adhesion integrity, and long-term elastic recovery. For OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers, this translates into reduced warranty claims, enhanced brand reliability, and compliance with evolving automotive durability standards.
Material Specifications
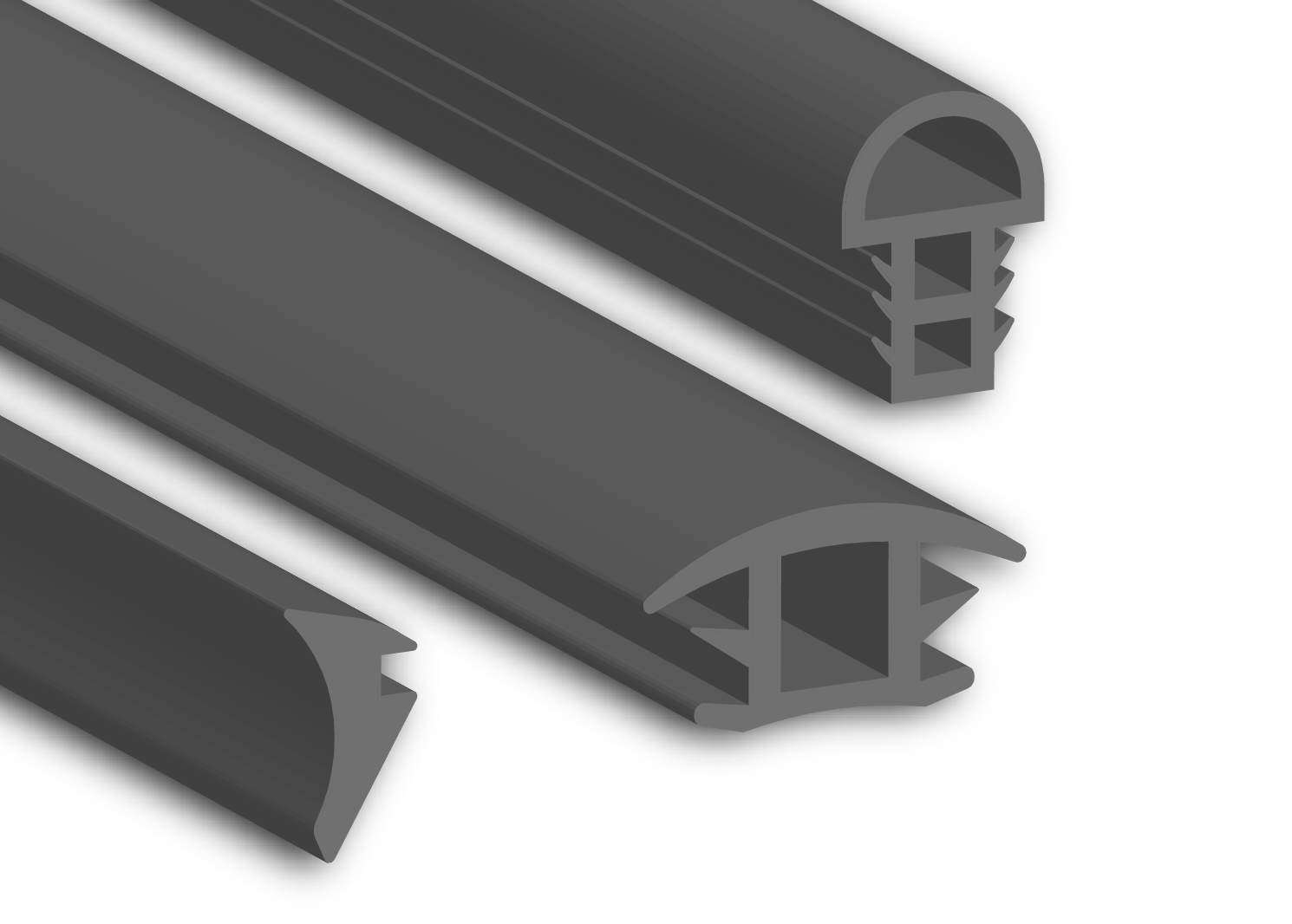
Material Specifications for Automotive Windshield Sealing Applications
Precision material selection is paramount in windshield sealing systems where dimensional stability, environmental resistance, and long-term adhesion directly impact vehicle safety and cabin integrity. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our OEM engineering team rigorously evaluates elastomer formulations to ensure compliance with global automotive standards including ISO 3302, ASTM D2000, and OEM-specific technical drawings. The three primary materials employed in high-performance windshield seals are Fluoroelastomer (Viton™ FKM), Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each compound offers distinct molecular advantages tailored to operational demands.
Viton (FKM) delivers exceptional resistance to automotive fluids, ozone, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for engine-proximate installations or luxury vehicles requiring 15+ year service life. Its perfluorinated structure maintains seal integrity against brake fluids, fuels, and washer solvents at continuous exposures up to 230°C. Nitrile (NBR/HNBR) provides optimal cost-performance balance for standard applications, exhibiting superior resistance to oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons within moderate temperature ranges. HNBR variants further enhance ozone resistance and thermal stability over standard NBR. Silicone (VMQ) excels in ultra-low temperature flexibility and UV resistance but requires formulation adjustments to mitigate compression set in dynamic sealing zones; it is preferred for cold-climate deployments where temperatures dip below -50°C.
Critical performance parameters are quantified below for direct comparison under SAE J2236 and ISO 1817 test protocols. All values reflect compression-molded test specimens cured to OEM-specified parameters.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (HNBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +230 | -40 to +120 | -60 to +200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12–18 | 20–30 | 5–9 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–250 | 200–400 | 200–600 |
| Compression Set (70h/150°C) (%) | 15–25 | 20–35 | 25–45 |
| Fuel Resistance (BIR) | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Moderate | Excellent |
| Relative Material Cost | Premium | Standard | Moderate |
Material selection must align with the vehicle’s geographic deployment, fluid exposure risks, and lifecycle requirements. Viton is non-negotiable for hybrid/electric vehicle battery compartment seals due to electrolyte resistance, while HNBR dominates mainstream production for cost efficiency. Silicone formulations require specialized primers for glass adhesion but prevent seal hardening in Arctic conditions. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM division collaborates with tier-1 suppliers to customize Shore A hardness (typically 60–75), durometer tolerances (±3 points), and pigment systems meeting OEM color codes. All compounds undergo 1,000-hour xenon-arc weathering tests per SAE J2527 and 85°C/85% RH aging per ISO 188 to validate field performance. Our ISO/TS 16949-certified supply chain guarantees batch-to-batch consistency through real-time rheometer and spectrometer monitoring, ensuring zero-defect delivery for global assembly lines.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages a specialized engineering team comprising five Mould Engineers and two Formula Engineers to deliver precision rubber seals for automotive windshields. This multidisciplinary team ensures optimal design, material selection, and manufacturing precision, meeting stringent automotive industry standards. The Mould Engineers utilize advanced CAD/CAM software and finite element analysis (FEA) to design molds with micron-level accuracy, achieving tolerances of ±0.02mm. Their expertise in thermal analysis and mold flow simulation guarantees consistent part geometry and surface finish critical for leak-proof sealing and noise reduction. The Formula Engineers focus on rubber compound development, optimizing properties such as tensile strength, compression set resistance, and temperature stability. They conduct rigorous material testing per ASTM D412, D395, and ISO 1817 standards, including UV resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) to evaluate viscoelastic behavior under varying temperatures and frequencies.
The technical capabilities of our engineering team are detailed below:
| Role | Count | Core Expertise |
|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineers | 5 | Precision mold design, FEA simulation, thermal analysis, CAD/CAM optimization |
| Formula Engineers | 2 | Rubber compound development, ASTM/ISO testing, UV/temperature resistance validation |
Our OEM capabilities extend beyond basic manufacturing. We provide end-to-end solutions including custom design support, rapid prototyping using 3D-printed tooling, and production scale-up tailored to client specifications. Each project undergoes comprehensive quality control checks, including dimensional verification, seal integrity tests, and accelerated aging assessments simulating 5+ years of environmental exposure per SAE J200. Our ISO 9001:2015-certified production facilities feature in-line monitoring systems, ensuring consistent quality across all batches. We collaborate closely with Tier 1 suppliers and OEMs to address complex engineering challenges, providing technical support from concept to production. Our team conducts root cause analysis for any quality issues, implementing corrective actions to maintain continuous improvement. By integrating advanced engineering with robust manufacturing processes, Suzhou Baoshida delivers reliable sealing solutions that enhance vehicle safety and longevity. Our commitment to precision and innovation positions us as a trusted partner for global automotive manufacturers seeking high-performance rubber components.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Automotive Windshield Sealing Systems
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our precision rubber seal customization begins with rigorous Drawing Analysis to align with OEM engineering intent. We dissect CAD files and physical samples to verify critical dimensions, cross-sectional tolerances (±0.1 mm), adhesion zones, and environmental exposure zones. This phase identifies potential stress points under dynamic load conditions, such as thermal cycling from -40°C to +120°C and UV degradation risks. Non-conformities in draft angles or parting lines are flagged early to prevent flash defects during molding. Our engineering team collaborates directly with client design departments to resolve ambiguities, ensuring the rubber profile geometry optimizes both sealing integrity and assembly efficiency.
Material Formulation follows, where compound chemistry is tailored to the windshield’s operational demands. We prioritize EPDM or thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) matrices based on ozone resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and paint compatibility requirements. Key additives include peroxide curing systems for compression set resistance (<25% at 100°C/22h) and nano-silica reinforcements for tensile strength. Below outlines critical property benchmarks for common formulations:
| Property | EPDM Standard | TPE High-Performance | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 65 ± 3 | 70 ± 3 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥12.0 | ≥10.5 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥350 | ≥400 | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (%) | ≤25 | ≤30 | ASTM D395 Method B |
Prototyping leverages CNC-machined aluminum molds for rapid validation. We produce 50–100 units per iteration, subjecting seals to SAE J2208 dynamic weathering tests and simulated installation force measurements. Dimensional verification via CMM ensures profile consistency across the entire length, with critical zones like the glass contact lip inspected at 5x magnification for surface defects. Client feedback on fitment and sealing performance under vacuum leak testing (≤0.5 cc/min) drives iterative refinements.
Mass Production commences only after PPAP Level 3 approval. Our automated 200T–500T rubber injection molding lines operate under ISO 9001-controlled parameters, with real-time monitoring of cure temperature (±2°C) and pressure profiles. Every 30 minutes, in-line tensile and hardness checks occur, while full material certification accompanies each shipment. Traceability is maintained via laser-etched batch codes linked to raw material lot numbers. This closed-loop process guarantees ≤50 PPM defect rates in serial production, meeting Tier-1 automotive durability standards for 15-year service life.
Suzhou Baoshida’s end-to-end control—from drawing validation to量产—eliminates supply chain variability, ensuring windshield seals deliver consistent acoustic insulation, water intrusion prevention, and structural bonding integrity across global vehicle platforms.
Contact Engineering Team

For manufacturers and OEMs seeking high-performance sealing solutions in automotive glass assembly, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands as a trusted partner in the precision rubber seals industry. Specializing in engineered elastomeric components, we deliver sealing windshield rubber that meets rigorous industrial standards for durability, environmental resistance, and dimensional accuracy. Our products are designed to perform under extreme temperature fluctuations, UV exposure, mechanical stress, and long-term compression, ensuring reliable performance in both passenger and commercial vehicles.
At Suzhou Baoshida, we understand that windshield sealing is not merely a structural requirement but a critical safety and comfort feature. Our sealing profiles are formulated using advanced EPDM, silicone, and thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) compounds, selected based on application-specific demands such as weather resistance, adhesion properties, and acoustic damping. Each product is manufactured under strict ISO-compliant processes, with in-house tooling, compounding, and quality control systems to guarantee consistency and repeatability across production batches.
We serve global automotive suppliers, tier-1 assemblers, and glass module integrators who require custom-engineered solutions. Whether you are developing a new vehicle platform or optimizing an existing assembly line, our technical team collaborates closely with your engineers to define material specifications, cross-sectional geometry, durometer ratings, and installation tolerances. Our rapid prototyping capabilities allow for fast validation cycles, reducing time-to-market without compromising performance.
To support your manufacturing objectives, we provide comprehensive technical documentation including material data sheets, compression set reports, aging studies, and adhesion test results. All sealing windshield rubber components undergo rigorous testing for ozone resistance, water ingress, and long-term deflection behavior to ensure compliance with OEM specifications such as GMW, Ford, VW, and JIS standards.
Below are key technical specifications commonly associated with our windshield sealing rubber profiles:
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 9.0 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 300% |
| Compression Set (22 hrs @ 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 25% |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +130°C |
| Density | ASTM D297 | 1.25 ± 0.05 g/cm³ |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracking (200 pphm, 40°C, 96 hrs) |
| Adhesion to Glass/Aluminum | Internal Method | Complete substrate bonding |
For immediate technical consultation or sample requests, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. With extensive experience in rubber formulation and automotive sealing applications, Mr. Boyce provides direct engineering support to help you select the optimal material and profile design for your windshield assembly needs. Reach out via email at [email protected] to initiate a technical discussion, request custom quotes, or schedule a factory audit. We respond to all inquiries within 24 business hours and support English, Chinese, and German communication channels. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for precision, reliability, and innovation in every seal.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
