Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Shield Molding
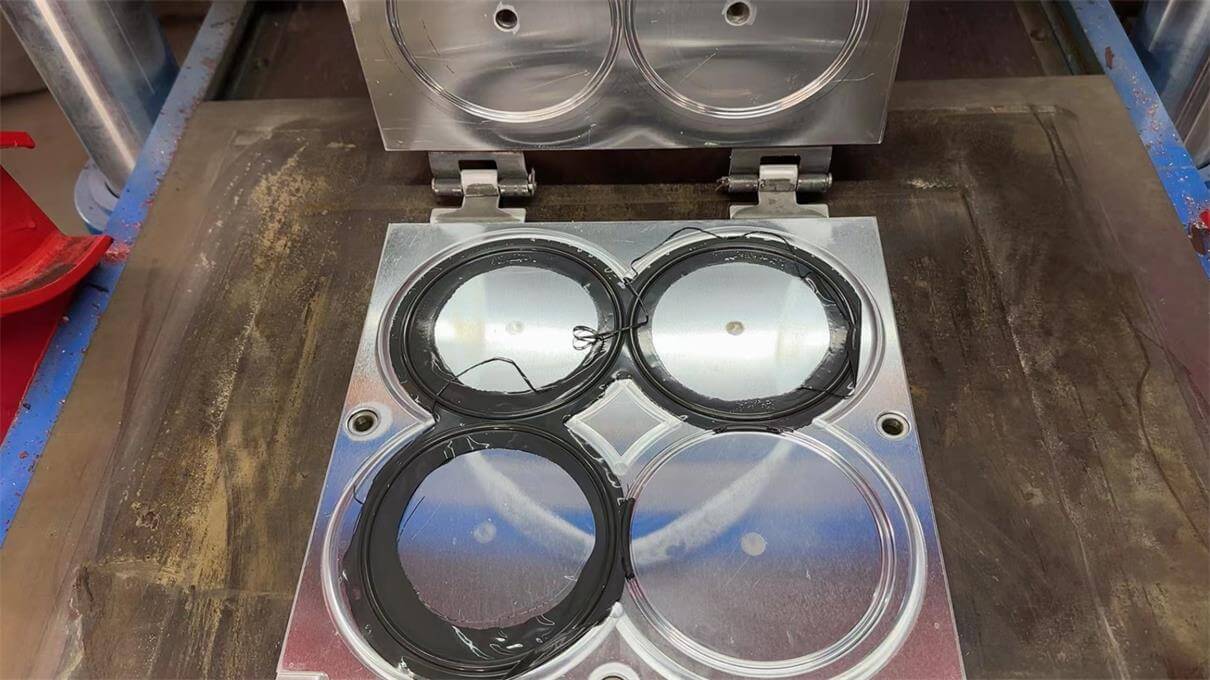

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Shield Molding for EMI/RFI Applications
Shield molding for electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI) applications demands precise integration of environmental sealing and electrical conductivity. Off-the-shelf rubber compounds frequently fail in these critical roles due to inherent compromises in standardized formulations. Generic materials prioritize broad compatibility and cost reduction over the stringent, application-specific requirements of shield molding. This results in catastrophic performance degradation under real-world operational stresses, including thermal cycling, chemical exposure, and mechanical compression.
The core failure mechanism lies in inconsistent conductivity. Standard conductive elastomers often utilize carbon black or metal-filled systems with non-uniform dispersion, leading to anisotropic conductivity and shielding effectiveness (SE) drift. When subjected to thermal excursions beyond 85°C or exposure to automotive fluids like brake fluid or transmission oil, off-the-shelf compounds exhibit resistivity increases of 40–60%. This directly compromises SE, allowing EMI leakage that disrupts sensitive electronics. Simultaneously, inadequate compression set resistance—common in generic EPDM or silicone blends—causes permanent deformation after prolonged sealing force. Gaps form, eliminating both environmental sealing and electrical contact continuity. Field failures in automotive sensor housings or aerospace connectors often trace back to these material limitations, triggering costly warranty claims and recalls.
Material selection must therefore address three interdependent parameters: stable electrical performance across the operational envelope, resilience against specified environmental agents, and long-term mechanical integrity. Custom formulation is non-negotiable. At Suzhou Baoshida, we engineer compounds with tightly controlled filler morphology (e.g., nickel-coated graphite in fluoroelastomers) to maintain volume resistivity below 0.1 Ω·cm after 500 hours of thermal aging per ASTM D865. This ensures SE retention exceeding 90 dB across 30 MHz–10 GHz per MIL-DTL-83528, even after fluid immersion. Crucially, compression set is optimized to ≤12% (70 hrs @ 100°C, ASTM D395) through peroxide curing systems, preventing seal failure under dynamic loads.
The table below contrasts critical performance metrics between generic and custom-engineered solutions:
| Parameter | Off-the-Shelf Compound | Baoshida Custom Formulation | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) | 0.5–2.0 (post-aging) | ≤0.1 (post-aging) | ASTM D257 |
| SE Retention after Aging | 60–70 dB | ≥90 dB | IEEE-STD-299 |
| Compression Set (%) | 25–35 | ≤12 | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Fluid Resistance (Brake) | Severe Swelling (>25%) | Minimal Swelling (<8%) | ASTM D471 |
Relying on commoditized materials ignores the physics of shield molding: conductivity, sealing, and durability are co-dependent. A 5% cost saving on raw material can escalate into a 200x cost in field failures. Precision-engineered compounds from Suzhou Baoshida eliminate this risk through OEM-collaborative formulation, ensuring your shielded assemblies perform reliably across lifecycle demands. Material selection is not a procurement decision—it is the foundation of electromagnetic integrity.
Material Specifications
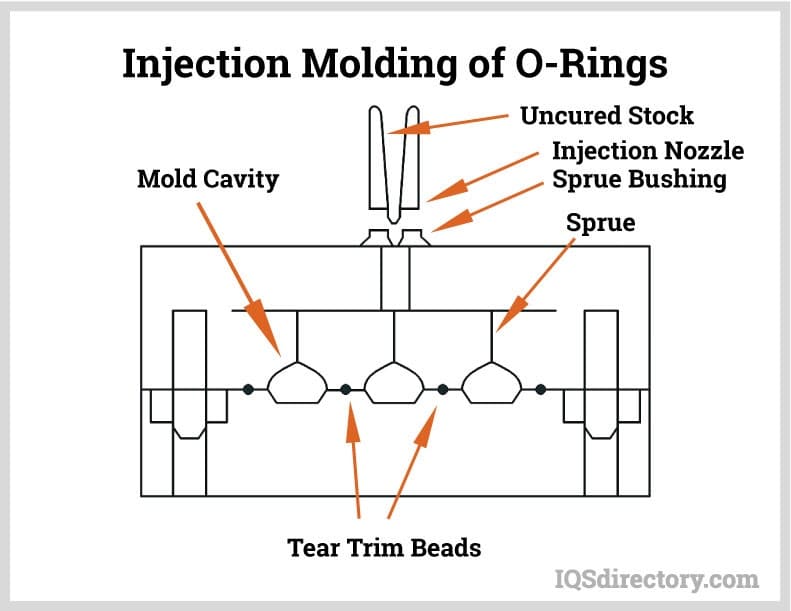
Material selection is a critical determinant in the performance and longevity of custom molded rubber parts, particularly in demanding industrial environments where shield molding is applied. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer precision rubber components using high-performance elastomers tailored to specific operational conditions. Our primary materials—Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ)—each offer unique chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties that make them suitable for distinct applications in automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, and medical industries.
Viton is a fluorocarbon-based elastomer renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range up to 200°C and intermittent resistance up to 250°C, Viton is ideal for applications exposed to aggressive media such as hydrocarbons, acids, and chlorinated solvents. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics ensure reliable sealing performance under prolonged stress. However, Viton exhibits lower flexibility at low temperatures and higher material cost compared to alternatives, making it best suited for high-value, critical-sealing scenarios.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is a cost-effective solution for applications involving petroleum-based oils and fuels. It provides good abrasion resistance and tensile strength, with a typical operating temperature range from -30°C to 120°C. Nitrile’s performance degrades under exposure to ozone, weathering, and polar solvents, limiting its use in outdoor or chemical processing environments. Nevertheless, its excellent compression set resistance and adaptability to dynamic sealing applications make it a preferred choice for hydraulic systems, fuel delivery components, and general industrial machinery.
Silicone rubber stands apart due to its outstanding thermal stability and biocompatibility. It performs reliably from -60°C to 200°C, with some formulations tolerable to brief excursions beyond 300°C. Silicone exhibits excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for outdoor and high-purity applications such as medical devices, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing. While it has relatively low tensile strength and poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids, its electrical insulation properties and physiological inertness are unmatched among standard elastomers.
The following table summarizes key performance characteristics of these materials to guide optimal selection in shield molding applications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 200 (up to 250 intermittent) | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 (up to 300 intermittent) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–250 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Very Good |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
| Biocompatibility | Limited | No | Yes (medical grade) |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer requires a comprehensive understanding of the operational environment, media exposure, mechanical loads, and regulatory requirements. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we support OEMs with material testing, formulation customization, and DFM optimization to ensure molded rubber components meet exact performance criteria.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Shield Molding for Demanding OEM Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber solutions through integrated material science and precision tooling expertise. Our dedicated team comprises five certified Mold Engineers and two specialized Rubber Formula Engineers, operating under a unified development protocol. This dual-discipline structure ensures seamless alignment between compound formulation and mold design—critical for complex shield molding applications requiring exacting dimensional stability, environmental resistance, and functional integrity. Unlike commodity suppliers, we initiate projects with cross-functional analysis of end-use conditions, translating OEM performance requirements into validated material specifications and tooling parameters before prototyping begins.
Our Formula Engineers develop proprietary elastomer compounds meeting stringent industry standards, including ISO 37, ASTM D2000, and OEM-specific material codes. Each formulation undergoes empirical validation for compression set, fluid resistance, and thermal aging—data rigorously documented for PPAP submission. Concurrently, Mold Engineers optimize cavity geometry, gating systems, and ejection sequences using 3D simulation software to eliminate flow-induced defects. This preemptive engineering reduces NPI cycle time by 30% and ensures first-article compliance with tolerances down to ±0.05 mm.
As a certified OEM partner, we implement end-to-end process control from raw material traceability to automated in-line inspection. Our production cells operate under IATF 16949 protocols, with real-time SPC monitoring of critical parameters: cure time, temperature uniformity, and flash control. Secondary operations—including plasma treatment, adhesive bonding, and laser marking—are integrated within climate-controlled cleanrooms to maintain part integrity. We maintain full documentation for every batch, including material certificates, process validation reports, and FAI data, ensuring audit readiness for automotive, medical, and industrial clients.
The following table summarizes our core technical capabilities for custom shield molding:
| Parameter | Capability Range | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Durometer Range | 30–90 Shore A | ASTM D2240 |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.05 mm (critical features) | ISO 2768-mK |
| Material Grades | NBR, EPDM, FKM, HNBR, Silicone, CR | ASTM D2000, ISO 3601 |
| Compression Set (70h/70°C) | ≤15% (FKM), ≤25% (NBR) | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Fluid Resistance | Custom formulations for oils, fuels, acids | ASTM D471 |
| Secondary Operations | Bonding, coating, assembly, packaging | Client-specific specs |
This engineering synergy directly mitigates OEM supply chain risks. By controlling both material chemistry and molding physics, we resolve root-cause failures—such as seal extrusion or compression set drift—during development rather than in-field. Our engineers collaborate with client R&D teams to refine DFM guidelines, ensuring manufacturability without compromising performance. For high-volume programs, we deploy automated vision systems with sub-micron resolution to guarantee 100% inspection of critical shield geometries. Suzhou Baoshida’s vertically integrated engineering capability transforms complex rubber component challenges into reliable, scalable manufacturing outcomes—backed by data, not assumptions. Partner with us to convert demanding specifications into defect-free production reality.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Shield Molding at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., the customization process for shield molding is engineered to deliver precision, reliability, and performance in every molded rubber component. Our systematic approach ensures that each part meets exacting OEM specifications while maintaining compliance with industry standards for durability, environmental resistance, and functional integrity. The process follows four critical stages: Drawing Analysis, Rubber Formulation Development, Prototyping, and Mass Production.
The first stage, Drawing Analysis, begins with a comprehensive technical review of the customer-supplied CAD drawings or engineering specifications. Our engineering team evaluates critical dimensions, tolerances, parting lines, draft angles, and sealing surfaces to ensure moldability and functional performance. We assess potential challenges such as flash formation, material flow, and ejection mechanics. This phase includes Design for Manufacturability (DFM) feedback, where we propose optimizations to enhance production efficiency and part quality without compromising design intent.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation Development. Shield molding often demands materials capable of resisting oils, ozone, temperature extremes, and mechanical compression. Our rubber chemists formulate custom elastomer compounds based on the application environment. Common base polymers include Nitrile (NBR), Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), Silicone (VMQ), and Fluoroelastomer (FKM). Each formulation is tailored to achieve specific hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, elongation, and compression set values. Additives may be incorporated to improve wear resistance, UV stability, or flame retardancy as required.
Once the material is finalized, we enter the Prototyping phase. Using precision CNC-machined prototype molds or 3D-printed soft tooling, we produce initial samples for functional testing. These prototypes undergo rigorous evaluation for dimensional accuracy, sealing performance, and environmental resistance. Test reports, including hardness measurements, visual inspection, and fit checks, are provided to the client for approval. Iterative adjustments are made until the prototype meets all technical and operational criteria.
Upon customer sign-off, we transition to Mass Production. High-precision steel molds, manufactured in-house or through certified partners, are deployed on automated hydraulic presses equipped with process monitoring systems. Production runs are conducted under strict quality control protocols, including in-process inspections and batch traceability. Final parts are subjected to 100% visual inspection and random sampling per AQL standards.
The following table summarizes typical material and performance specifications available for custom shield molding applications.
| Property | NBR | EPDM | VMQ | FKM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -30 to +120 | -50 to +150 | -60 to +200 | -20 to +250 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 50–90 | 50–85 | 40–80 | 60–90 |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Good | Excellent |
| Ozone Resistance | Fair | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Compression Set (70h @ 100°C) | 20–35% | 15–30% | 20–40% | 15–25% |
This structured customization process ensures that every shield molding solution from Suzhou Baoshida meets the highest standards of engineering excellence and manufacturing consistency.
Contact Engineering Team

Initiate Technical Validation for Precision Shield Molding Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced rubber compounding and high-tolerance molding engineering, specifically for mission-critical shield components in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sealing applications. Our shield molding process transcends standard production through proprietary material formulations engineered to withstand extreme thermal cycling, chemical exposure, and dynamic compression loads. When dimensional stability, material integrity, and long-term performance are non-negotiable, our ISO 9001-certified facility delivers molded rubber parts meeting stringent OEM specifications. We recognize that shield failures propagate systemic risks—from fluid leaks in hydraulic systems to EMI interference in electronic housings—and our engineering team prioritizes failure-mode analysis during the quoting phase to preempt field defects.
Direct technical engagement with our OEM Management team ensures your shield design transitions seamlessly from CAD model to validated production. Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager with 18 years of rubber formulation oversight, serves as your single point of accountability for technical-commercial alignment. He coordinates cross-functional resources spanning material science, tooling validation, and statistical process control to de-risk your supply chain. Contact Mr. Boyce to submit application-specific requirements, including environmental exposure profiles, force-deflection curves, and geometric critical-to-quality (CTQ) dimensions. His team will respond within 4 business hours with a feasibility assessment, preliminary material recommendation, and timeline for prototype validation. This structured handoff prevents miscommunication common in tier-2 supplier relationships and accelerates time-to-qualification.
Our technical capabilities are quantifiable across key shield molding parameters, as demonstrated in the following operational specifications:
| Parameter | Capability Range | Industry Standard Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Material Durometer (Shore A) | 30–90 | ASTM D2240 |
| Linear Tolerance (mm) | ±0.05 (critical dimensions) | ISO 3302-1 Class M2 |
| Volume Capacity | 10,000–500,000 units/month | Per mold configuration |
| Material Types | EPDM, FKM, VMQ, ACM, custom blends | ASTM D2000 classification |
| Secondary Operations | Plasma treatment, adhesive bonding | ISO 10993-5 (biocompatibility) |
Initiate your shield molding project by emailing Mr. Boyce at [email protected] with the subject line: Shield Molding Technical Inquiry – [Your Company Name]. Include your target application, performance requirements, and annual volume forecast. Suzhou Baoshida does not operate as a transactional vendor; we function as an engineering extension of your R&D department. Our rubber formula engineers will collaborate to optimize material cost without compromising resilience—such as developing fluorosilicone compounds for -60°C to +230°C aerospace shields or low-compression-set EPDM for automotive fluid barriers. All quotations include finite element analysis (FEA) reports validating seal force distribution and deflection behavior under operational loads. Partner with us to convert shielding challenges into validated engineering solutions, where material science meets manufacturing precision. Your next-generation shield design demands this level of technical rigor.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
