Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Steel Edge Protectors
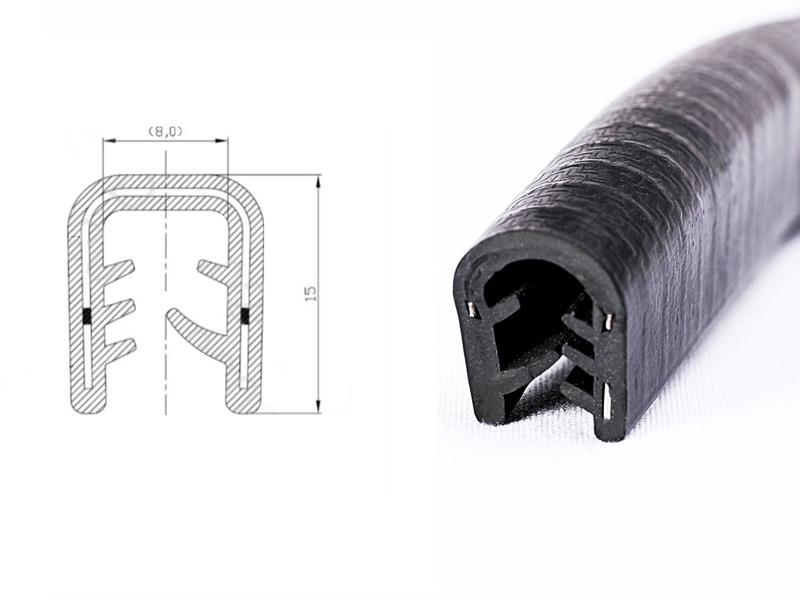
Engineering Insight: Material Selection as the Foundation of Steel Edge Protector Performance
In the demanding environment of industrial material handling and transport, steel edge protectors serve as the critical interface between structural integrity and catastrophic damage. While often perceived as simple commodity items, their functional efficacy is fundamentally dictated by precise elastomer formulation. Off-the-shelf solutions frequently fail to meet operational requirements due to a critical oversight: the absence of engineered material science tailored to specific load profiles, environmental exposure, and dynamic stress conditions. Generic rubber compounds, typically formulated for broad applicability and lowest cost, lack the targeted resilience necessary for protecting high-value steel edges during handling, shipping, and storage. This results in premature failure modes such as excessive compression set, surface tearing, chemical degradation, and loss of grip – directly compromising the protector’s core function and potentially causing significant damage to the protected asset.
The primary failure mechanism of standard protectors stems from inadequate resistance to permanent deformation under sustained load. Low-cost compounds often utilize fillers and polymers optimized for initial cost, not long-term durometer stability. When subjected to the concentrated pressure of steel edges over extended periods, these materials exhibit high compression set. The protector loses its original shape and rebound characteristics, creating gaps that allow the steel edge to bite through the deformed rubber, leading to direct metal-on-metal contact and edge damage. Furthermore, exposure to common industrial contaminants – hydraulic oils, greases, ozone, UV radiation, and temperature extremes – rapidly degrades non-engineered elastomers. Poor resistance to these agents causes surface cracking, hardening, or softening, accelerating functional failure and creating safety hazards from dislodged fragments.
Material selection must therefore address the specific operational triad: mechanical stress, chemical environment, and thermal profile. A successful formulation balances tensile strength, elongation at break, tear resistance, and compression set within narrow, application-defined parameters. Crucially, the compound must maintain these properties across the expected service life, resisting specification drift under real-world conditions. Off-the-shelf products inherently lack this precision, employing one-size-fits-all recipes that sacrifice critical performance attributes for manufacturability and price point. The consequence is a false economy, where initial savings are vastly outweighed by costs from damaged goods, rework, delays, and potential safety incidents.
The following table contrasts key performance parameters between generic off-the-shelf protectors and engineered solutions developed for demanding industrial applications:
| Performance Parameter | Typical Off-the-Shelf Protector | Engineered Industrial Solution (Suzhou Baoshida) |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | 45-60% | ≤ 25% |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8-12 | 15-20 |
| Tear Resistance (kN/m) | 25-35 | 45-60 |
| Oil Resistance (IRMOG 1#) | Volume Swell > 50% | Volume Swell < 15% |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +70 | -40 to +120 |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep expertise in rubber compounding to eliminate these failure points. Our OEM engineering process begins with rigorous analysis of the client’s specific steel grade, handling equipment, transport conditions, and environmental exposures. We formulate proprietary elastomer blends using high-purity polymers, optimized filler systems, and advanced protective additives. This ensures dimensional stability under load, exceptional resistance to industrial contaminants, and consistent performance across extreme temperature ranges. The result is a protector that maintains its integrity and protective function throughout the supply chain, safeguarding your steel products and operational efficiency – a precision engineered solution where generic alternatives inevitably fall short. Material selection is not a cost line item; it is the cornerstone of reliable asset protection.
Material Specifications
Steel edge protectors are critical components in industrial handling, transportation, and material protection applications. These protectors serve to prevent damage to sharp or protruding metal edges, safeguarding both the structural integrity of the materials and the safety of personnel and equipment. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our steel edge protectors are engineered using high-performance rubber compounds to ensure durability, resistance to environmental stressors, and long-term operational reliability. The selection of the appropriate elastomer is fundamental to achieving optimal performance under specific service conditions. We offer steel edge protectors fabricated from three primary rubber materials: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each offering distinct advantages based on chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical requirements.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. This makes it ideal for use in demanding industrial environments such as petrochemical plants, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace applications where exposure to hydrocarbons and elevated temperatures is common. Viton edge protectors maintain structural integrity from -20°C to +200°C, with intermittent resistance up to 250°C, ensuring reliable performance in extreme thermal cycles.
Nitrile rubber, also known as Buna-N, is widely used for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and hydraulic fluids. It offers good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it a cost-effective solution for general industrial applications. Nitrile edge protectors are particularly suited for use in machinery, logistics, and manufacturing settings where contact with lubricants and fuels is frequent. Operating effectively within a temperature range of -30°C to +100°C, NBR provides a balanced combination of performance and economy.
Silicone rubber is selected for applications requiring extreme temperature stability and flexibility. With an operational range from -60°C to +200°C, silicone outperforms many elastomers in both cryogenic and high-heat environments. While it exhibits lower tensile strength compared to Viton and Nitrile, its outstanding UV and ozone resistance, coupled with excellent electrical insulation properties, makes it ideal for outdoor installations, electrical enclosures, and food-grade or medical-adjacent environments where purity and compliance are essential.
The following table provides a comparative overview of the key material properties to assist in the selection process based on application-specific demands.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +200 (up to 250 intermittent) | -30 to +100 | -60 to +200 |
| Oil and Fuel Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding | Good | Fair |
| Ozone and UV Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | High | High | Moderate |
| Flexibility at Low Temp | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
| Common Applications | Petrochemical, aerospace, high-temp seals | Automotive, hydraulics, general industry | Outdoor, medical, electrical, food-grade |
Material selection directly impacts the service life and functional efficacy of steel edge protectors. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides expert consultation to match material properties with operational requirements, ensuring optimal protection and performance across diverse industrial sectors.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Steel Edge Protection
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber solutions where material science meets exacting industrial application demands. Our core strength in manufacturing high-performance steel edge protectors stems from a dedicated, cross-functional engineering team operating at the intersection of advanced polymer chemistry and precision tooling design. This integrated approach ensures every component meets the rigorous mechanical, environmental, and safety requirements inherent in protecting structural steel during handling, transport, and storage.
Our team comprises five specialized Mould Engineers with extensive experience in complex rubber injection and compression moulding. These engineers focus on optimizing cavity design, gating systems, venting, and cooling channels to achieve exceptional dimensional stability, consistent part geometry, and minimal flash – critical factors for edge protectors requiring precise fitment on diverse steel profiles. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM software and finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate flow dynamics and predict potential defects, significantly reducing time-to-market and ensuring first-article conformance. Concurrently, our two dedicated Rubber Formula Engineers possess deep expertise in elastomer compounding. They develop and refine proprietary formulations specifically tailored for the demanding conditions edge protectors face, including impact resistance, abrasion resistance, UV stability, and performance across wide temperature excursions. Material selection and formulation are never generic; they are systematically engineered based on the specific load, environmental exposure, and longevity requirements provided by the OEM partner.
This dual-engineering capability forms the backbone of our robust OEM service model. We engage deeply during the initial specification phase, translating client performance criteria into actionable material and tooling parameters. Our process includes rigorous prototyping, iterative testing against defined failure modes, and comprehensive documentation for full traceability. We manage the entire lifecycle from concept validation through sustained production, implementing stringent process controls and statistical process monitoring (SPC) to guarantee batch-to-batch consistency essential for industrial safety components. Baoshida does not merely manufacture to drawings; we co-engineer solutions that enhance product reliability and reduce total cost of ownership for our OEM partners.
Key performance characteristics of our standard OEM steel edge protector formulations are validated through controlled testing protocols, as summarized below:
| Property | Typical Value Range | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 65 – 75 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 15 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥ 300% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤ 25% | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temp Range | -40°C to +100°C | Internal Method |
| Abrasion Resistance (DIN) | ≤ 120 mm³ | DIN 53516 |
This engineering-led methodology, combining advanced mould design with scientifically formulated rubber compounds, ensures Suzhou Baoshida delivers steel edge protectors that consistently exceed industry expectations for durability and protective performance. Our commitment to precision engineering at every stage provides OEMs with a reliable, technically superior manufacturing partner.
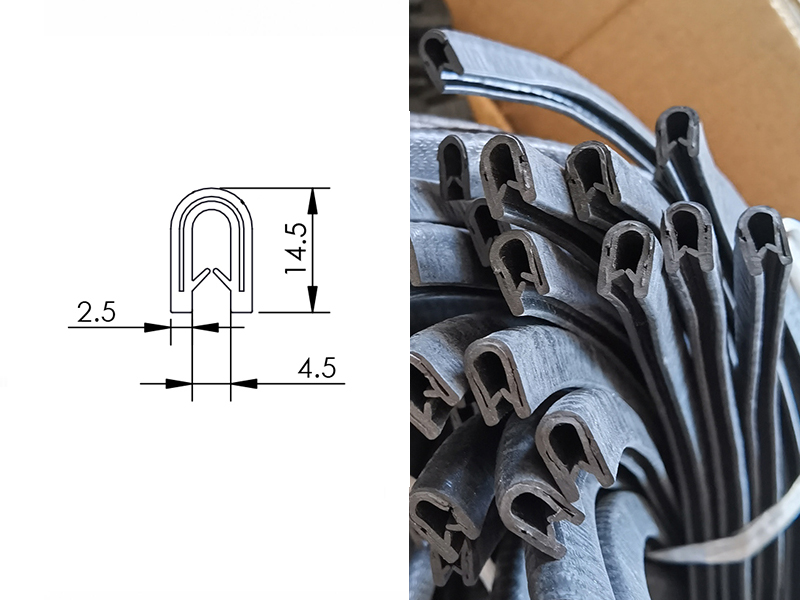
Customization Process
Customization Process for Steel Edge Protectors at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering high-performance industrial rubber solutions tailored to the precise mechanical and environmental demands of modern logistics and material handling. Our customization process for steel edge protectors follows a rigorous four-phase methodology: Drawing Analysis, Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production. This systematic approach ensures dimensional accuracy, material resilience, and long-term functional reliability.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, during which our engineering team evaluates the client-provided technical drawings or CAD models. We assess critical parameters such as edge radius, flange dimensions, mounting configuration, and tolerance specifications. This phase includes a thorough review of application conditions—load exposure, surface contact type, and installation environment—to determine optimal design adjustments. Our engineers collaborate directly with OEMs and logistics equipment manufacturers to ensure compatibility with existing steel structures, such as container corners, pallet edges, or racking systems.
Following design validation, we proceed to Formulation. Our rubber compounding laboratory develops a proprietary elastomer blend based on the operational stress profile. Key considerations include abrasion resistance, compression set, UV and ozone stability, and temperature range. Common base polymers include natural rubber (NR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), selected for their balance of elasticity and durability. Additives such as carbon black, sulfur vulcanizing agents, and anti-aging compounds are precisely metered to meet industry-specific performance benchmarks.
Once the compound is finalized, we initiate the Prototyping stage. Using CNC-machined molds or 3D-printed tooling, we produce small-batch samples for client evaluation. Each prototype undergoes dimensional inspection via coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and functional testing under simulated service conditions. Clients receive a comprehensive test report including hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, elongation at break, and tear resistance. Iterative refinements are implemented until full compliance with technical and operational requirements is achieved.
Upon client approval, we transition to Mass Production. Our manufacturing facility employs high-pressure hydraulic presses and automated curing systems to ensure batch consistency and dimensional repeatability. In-line quality control checks are conducted at every stage, from raw material inspection to final packaging. Production cycles are optimized for scalability, supporting order volumes from 10,000 to over 500,000 units annually, with lead times typically ranging from 15 to 30 days.
Below are typical material and performance specifications for our standard steel edge protector formulations:
| Property | Test Method | NR Compound | SBR Compound | EPDM Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60 ± 5 | 65 ± 5 | 70 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ASTM D412 | ≥18 | ≥15 | ≥12 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ASTM D412 | ≥450 | ≥350 | ≥300 |
| Tear Resistance (kN/m) | ASTM D624 | ≥45 | ≥38 | ≥32 |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -20°C to +80°C | -30°C to +90°C | -40°C to +120°C |
| Compression Set (24h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤20% | ≤25% | ≤30% |
This structured customization pathway enables Suzhou Baoshida to deliver steel edge protectors that meet exacting industrial standards while ensuring longevity, safety, and cost-efficiency across diverse operational environments.
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Engagement for Precision Industrial Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of polymer science and industrial logistics, delivering engineered rubber components that mitigate material degradation in high-stakes manufacturing environments. Our steel edge protectors exemplify this commitment, utilizing proprietary elastomer formulations to absorb impact energy while maintaining dimensional stability under dynamic load conditions. For OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, the selection of edge protection transcends mere cost considerations—it directly influences scrap rates, shipping integrity, and end-product quality. Industry data indicates that substandard protectors contribute to 18–22% of surface defects in coiled steel shipments, translating to significant rework expenses. Our solutions counteract this through molecular cross-linking precision that balances Shore A hardness with elongation resilience, ensuring consistent performance across temperature extremes and abrasive handling cycles.
The technical specifications below detail our standard EPDM-based protector formulation, validated through ASTM D2000 and ISO 188 testing protocols. These parameters reflect our adherence to automotive and heavy machinery sector requirements where micron-level tolerances dictate operational success.
| Property | Test Method | Value | Industrial Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 70 ± 3 | Optimal balance: prevents deformation without damaging steel coatings |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥18 MPa | Resists tearing during high-tension strapping applications |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥350% | Accommodates thermal expansion in outdoor storage |
| Temperature Range | ISO 188 | -40°C to +120°C | Stable performance in Arctic logistics to tropical ports |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤22% | Maintains sealing integrity after prolonged load exposure |
| Abrasion Resistance | DIN 53516 | ≤120 mm³ | Extends service life in repetitive handling environments |
These metrics are not static targets but dynamic outcomes of our closed-loop R&D process. Each batch undergoes real-time rheometer analysis during vulcanization, with adjustments made to sulfur accelerator ratios based on raw material lot variations. This granular control ensures repeatability across 500,000+ units—a non-negotiable standard for clients in wind energy tower fabrication and automotive body-in-white assembly lines.
Initiate technical collaboration by contacting Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Relationship Manager, who possesses 14 years of experience in rubber compounding for structural metal protection. Mr. Boyce will facilitate a precision-engineered solution pathway, beginning with your specific load profile, steel grade, and environmental exposure data. His team will provide:
Material compatibility reports against ASTM A1008/A1011 substrates
3D-printed prototype validation within 72 hours of requirement submission
Custom durometer adjustments (60–85 Shore A) without minimum order penalties
Direct all technical inquiries and production schedule discussions to [email protected]. Include your current edge protector failure mode analysis or ISO shipping specifications to accelerate solution development. Responses are guaranteed within 24 business hours, with priority scheduling for urgent line-down scenarios. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering team operates under IATF 16949 frameworks, ensuring every interaction translates into quantifiable risk reduction for your supply chain. Partner with us to transform edge protection from a cost center into a certified value driver.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
