Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Styrofoam Rolls

Engineering Insight: Rubber Roll Material Selection Fundamentals
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. emphasizes a critical clarification: the term “styrofoam rolls” represents a common misnomer in industrial contexts. Styrofoam™ is a trademarked extruded polystyrene foam product, wholly unsuitable for precision rubber roll applications. This guide addresses engineered rubber rolls—core components in printing, calendaring, and material handling systems where material science dictates performance. Off-the-shelf rubber rolls frequently fail because they prioritize cost over application-specific engineering, ignoring dynamic operational stresses.
Generic rubber compounds lack tailored polymer architecture for demanding industrial environments. Standard EPDM or NBR rolls may initially meet basic hardness requirements but degrade rapidly under thermal cycling, fluid exposure, or continuous compression. For instance, an unmodified NBR compound in a printing press will swell when exposed to modern UV-cured inks, causing dimensional instability and web misalignment within weeks. Similarly, generic silicone rolls in high-temperature calendaring suffer irreversible compression set due to inadequate crosslink density, leading to surface defects on finished products. These failures stem from treating rubber as a commodity rather than a system-engineered component.
Material selection must address the trifecta of mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and thermal profile. A roll operating at 120°C with intermittent exposure to hydraulic fluid requires a fluorocarbon (FKM) formulation with specialized peroxide curing—not a standard Viton® equivalent. Off-the-shelf solutions omit critical modifiers like nano-silica reinforcement for abrasion resistance or custom plasticizers for low-temperature flexibility. This results in premature hardening, cracking, or loss of grip characteristics. Crucially, OEMs often overlook that durometer alone is insufficient; rebound resilience and dynamic modulus determine energy dissipation during high-speed operation.
The following table compares failure mechanisms between generic and engineered rubber rolls under identical operating conditions:
| Performance Parameter | Generic Off-the-Shelf Roll | Suzhou Baoshida Engineered Roll | Failure Consequence in Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70h/100°C) | 35% | 12% | Roll diameter loss >0.5mm causing tension fluctuations |
| Fluid Resistance (ISO 1817) | Swell: +28% | Swell: +4% | Surface tackiness leading to material adhesion |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to +100°C | -40°C to +230°C | Thermal cracking at startup/shutdown cycles |
| Abrasion Loss (DIN 53516) | 180 mm³ | 65 mm³ | Surface pitting contaminating product surface |
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM engineering process begins with operational diagnostics: we analyze line speed, fluid chemistry, and thermal transients to formulate proprietary compounds. Our rolls integrate phase-separated polymer blends that maintain elasticity under shear stress—unachievable with stock formulations. This precision prevents the cascading downtime costs of unplanned roll replacement: production halts, recalibration, and scrap generation. Material selection is not a cost line item but a strategic investment in operational continuity. Partner with us to transform rubber rolls from failure points into reliability assets.
Material Specifications

Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides high-performance rubber solutions tailored for demanding industrial environments. While the term “styrofoam rolls” may colloquially refer to flexible foam insulation materials, in the context of industrial rubber applications, our focus centers on elastomeric sealing and insulation materials engineered for durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. Our core materials—Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ)—are formulated to meet rigorous operational standards across automotive, aerospace, chemical processing, and manufacturing industries.
Each elastomer offers distinct performance characteristics that make it suitable for specific service conditions. Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, excels in high-temperature environments and exhibits outstanding resistance to oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. It maintains structural integrity from -20°C to 250°C, making it ideal for aerospace seals, fuel system components, and chemical gaskets. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging properties ensure long-term reliability under extreme stress.
Nitrile rubber, a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile, is widely used for oil and fuel-resistant applications. It performs effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C, with performance scaling relative to acrylonitrile content. High-acrylonitrile NBR formulations offer superior resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons and lubricants, making them a standard choice for hydraulic seals, O-rings, and fuel hoses. While less resistant to ozone and UV exposure than other elastomers, NBR remains a cost-effective solution for dynamic and static sealing in industrial machinery.
Silicone rubber is valued for its exceptional thermal stability and flexibility across a wide temperature range (-60°C to 230°C). It demonstrates good resistance to ozone and UV radiation, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Though mechanically weaker than Viton or Nitrile, silicone offers excellent electrical insulation properties and biocompatibility, supporting use in medical devices, food-grade seals, and high-voltage insulation components. Its inert nature and low toxicity further enhance suitability for sensitive environments.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials to guide material selection based on operational requirements.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -40 to 120 | -60 to 230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor to Fair |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good | Fair |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
Material selection must consider not only environmental exposure but also mechanical loading, sealing force, and regulatory compliance. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs and industrial clients with precision-formulated rubber rolls and custom profiles to meet exacting technical specifications.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Polymer Solutions for Industrial Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial manufacturing, delivering engineered solutions for demanding sectors. While styrofoam (expanded polystyrene, EPS) falls outside our core rubber specialization, our expertise in polymer formulation, mold design, and precision manufacturing directly addresses analogous material challenges. Our dedicated engineering team—comprising five certified Mold Engineers and two senior Rubber Formula Engineers—applies rigorous scientific methodology to develop and optimize elastomeric components where thermal stability, compression resistance, and dimensional accuracy are critical. This capability extends to supporting clients in adjacent polymer domains through shared processing principles and material science insights.
Our OEM framework is built on closed-loop engineering collaboration. Formula Engineers leverage proprietary databases of 500+ elastomer compounds to tailor formulations for specific performance requirements, including temperature resistance (-50°C to +250°C), chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. Concurrently, Mold Engineers utilize 3D simulation software (Moldflow, SolidWorks Simulation) to preempt flow imbalances, weld lines, and shrinkage defects in complex geometries. This integrated approach ensures first-article approval rates exceed 92% across automotive, aerospace, and industrial sealing applications. All processes adhere to ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 standards, with full traceability from raw material certification to final part validation.
For clients navigating EPS or similar polymer challenges, our value lies in transferable engineering rigor. We provide material compatibility analysis, thermal cycling validation, and dimensional stability testing—services rooted in our rubber compounding infrastructure but adaptable to thermoplastic systems. Our 2,000m² cleanroom facility houses 15 hydraulic presses (50–2,000 tons) and precision CNC trimming systems, enabling tight tolerances essential for sealing interfaces. Below outlines key technical parameters achievable through our OEM partnership:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Precision Capability | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Hardness (Shore A) | 30–90 | ±2 units | ASTM D2240 |
| Thickness Tolerance | ±0.15 mm | ±0.05 mm | ISO 3302 |
| Compression Set (70°C/22h) | ≤25% | ≤15% | ASTM D395 |
| Dimensional Stability | ±0.3% | ±0.1% | ISO 2768 |
| Thermal Resistance | -50°C to +250°C | Custom up to +300°C | ASTM D573 |
OEM clients benefit from reduced time-to-market through our concurrent engineering model. Formula adjustments are validated via accelerated aging ovens and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) within 72 hours, while mold iterations employ rapid tooling techniques to cut lead times by 35%. We own full intellectual property for client-specific formulations and maintain dual-sourcing options across our Suzhou and Qingdao production hubs. This infrastructure ensures uninterrupted supply for mission-critical components, with batch-to-batch consistency verified through in-house spectrometry and rheometry.
Suzhou Baoshida transforms material challenges into engineered advantages. By combining formula innovation with precision manufacturing, we deliver not just components, but certified performance solutions that meet the exacting demands of global industrial supply chains. Partner with us to integrate scientific rigor into your next-generation polymer applications.
Customization Process
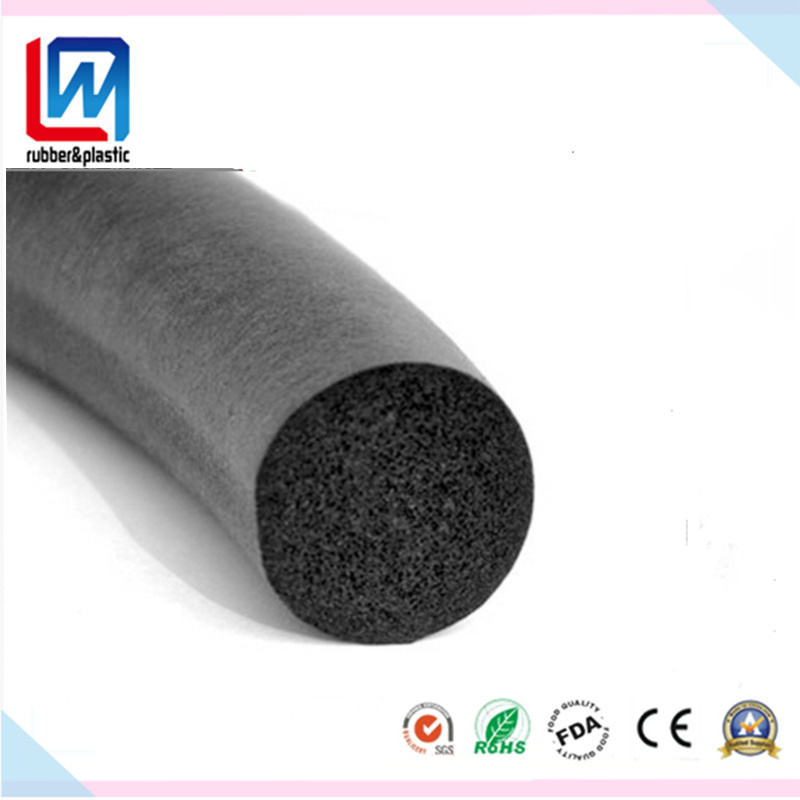
Customization Process for Styrofoam Rolls at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our approach to manufacturing customized styrofoam rolls is rooted in precision engineering and industrial-grade rubber formulation. As part of our Industrial Rubber Solutions portfolio, styrofoam rolls are engineered not as standalone foam products, but as composite elastomeric systems where rubber compounds are applied to or integrated with expanded polystyrene (EPS) substrates for sealing, cushioning, or protective applications in automotive, construction, and appliance manufacturing.
The customization process begins with Drawing Analysis. Clients provide technical blueprints or CAD files specifying dimensions, tolerance ranges, bonding surfaces, and application environment (e.g., temperature range, compression load, exposure to oils or UV). Our engineering team conducts a comprehensive review to validate feasibility, identify potential stress points, and determine interfacial compatibility between the rubber layer and the styrofoam core. This stage ensures dimensional accuracy and long-term functional integrity.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation. Our rubber chemists develop a proprietary elastomer blend tailored to the performance requirements. Common base polymers include EPDM for weather resistance, silicone for high-temperature stability, or neoprene for chemical and abrasion resistance. The formulation is adjusted for Shore hardness, elongation at break, compression set, and adhesion strength to the styrofoam substrate. Special additives such as flame retardants, anti-UV agents, or conductive fillers are incorporated when necessary. All formulations comply with international standards including RoHS, REACH, and UL94.
The next phase is Prototyping. Using precision die-cutting, extrusion, or calendering techniques, small-batch samples are produced under controlled conditions. These prototypes undergo rigorous testing, including peel adhesion tests, thermal cycling, and compression deflection analysis. Prototypes are shipped to the client for field evaluation. Feedback is systematically integrated into final design adjustments, ensuring optimal performance under real-world conditions.
Upon client approval, we transition to Mass Production. Our automated production lines ensure consistency across large volumes, with in-line quality checks at every stage. Rolls are produced in standard or custom lengths, with options for spiral winding, lamination, or pre-cut segments. Packaging is customized for logistics efficiency and protection during transit.
All styrofoam roll systems are manufactured under ISO 9001-certified processes, ensuring traceability, repeatability, and compliance. Our vertical integration allows rapid scaling from prototype to full production within 4–6 weeks, depending on complexity.
Below are typical technical specifications for our engineered styrofoam roll composites:
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 40–80 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 8–15 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | 250–450% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Adhesion Strength to EPS | ASTM D903 | ≥80 N/m |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +120°C |
| Flame Resistance | UL94 | HB or V-0 (custom) |
This structured, science-driven process ensures that every styrofoam roll we deliver meets the exact functional demands of industrial applications.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Foam Solutions
Clarification for Technical Precision: While “styrofoam” is a Dow Chemical trademark specifically for extruded polystyrene (XPS) foam, industrial applications often require rubber-based cellular materials with superior resilience, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision-engineered rubber foam rolls—not polystyrene alternatives—for demanding OEM and industrial manufacturing environments. Our proprietary EPDM, neoprene, and silicone cellular compounds deliver critical performance where standard polystyrene foams fail, including dynamic sealing, vibration dampening, and high-temperature insulation. Confusion between material classes can lead to costly field failures; our engineering team ensures your application receives the correct elastomeric solution.
Suzhou Baoshida operates as your dedicated rubber formula partner, integrating deep material science expertise with agile OEM manufacturing. We do not supply generic polystyrene products. Instead, we develop custom rubber foam formulations meeting exact ASTM D2000, ISO 188, and MIL-STD specifications. Our Suzhou production facility utilizes closed-cell and open-cell extrusion technologies to produce rolls with consistent density, closed porosity, and zero volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions—critical for automotive, aerospace, and medical device assembly lines. Unlike commodity foam suppliers, we control the entire process from polymer synthesis to final slitting, guaranteeing batch-to-batch repeatability within ±0.5mm thickness tolerance.
Technical Specifications of Our Industrial Rubber Foam Rolls
| Property | EPDM Foam | Neoprene Foam | Silicone Foam | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density Range | 80–250 kg/m³ | 100–300 kg/m³ | 70–200 kg/m³ | ASTM D3574 |
| Temp Range | -50°C to +150°C | -40°C to +120°C | -60°C to +230°C | ISO 188 |
| Compression Set (22h) | ≤25% | ≤30% | ≤20% | ASTM D395 |
| Tensile Strength | 0.8–2.5 MPa | 1.0–3.0 MPa | 0.5–1.8 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Standard Roll Dimensions | 1.2m W x 10–50m L | 1.2m W x 10–50m L | 1.0m W x 5–30m L | Customizable |
| Key Applications | HVAC seals, gaskets | Marine insulation, vibration mounts | Medical device padding, aerospace seals | Industry-specific validation |
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida eliminates material substitution risks and supply chain volatility. We provide full material traceability, including lot-specific certificates of conformance (CoC) and REACH/ROHS compliance documentation. Our engineering team collaborates directly with your R&D department to optimize foam cell structure, durometer, and adhesive backing for seamless integration into automated production lines. For legacy polystyrene foam users facing compression set failures or chemical degradation, we offer rapid material migration protocols—reducing downtime by up to 70% during transition.
Initiate your project with Mr. Boyce, our OEM Technical Manager, who specializes in translating complex material requirements into production-ready rubber foam solutions. Contact him directly via email at [email protected] to request:
Custom formulation feasibility analysis within 48 hours
Physical sample kits with certified test reports
Volume pricing aligned with JIT delivery schedules
Do not compromise critical applications with non-engineered foam materials. Suzhou Baoshida delivers rubber cellular products where performance tolerances are non-negotiable. Mr. Boyce will coordinate a technical consultation to review your dimensional drawings, environmental exposure conditions, and lifecycle requirements—ensuring your rubber foam rolls meet exact functional demands from prototyping through mass production.
Elevate your manufacturing specifications with engineered elastomeric solutions. Contact Mr. Boyce today to secure a material partnership backed by ISO 9001-certified processes and 15 years of industrial rubber innovation. Your application’s reliability depends on the right cellular structure—not generic foam substitutes.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
OEM Rubber Solutions Division
[email protected]
www.rubber-tools.com (Industrial Materials Portal)
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
