Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Tennis Court Tiles
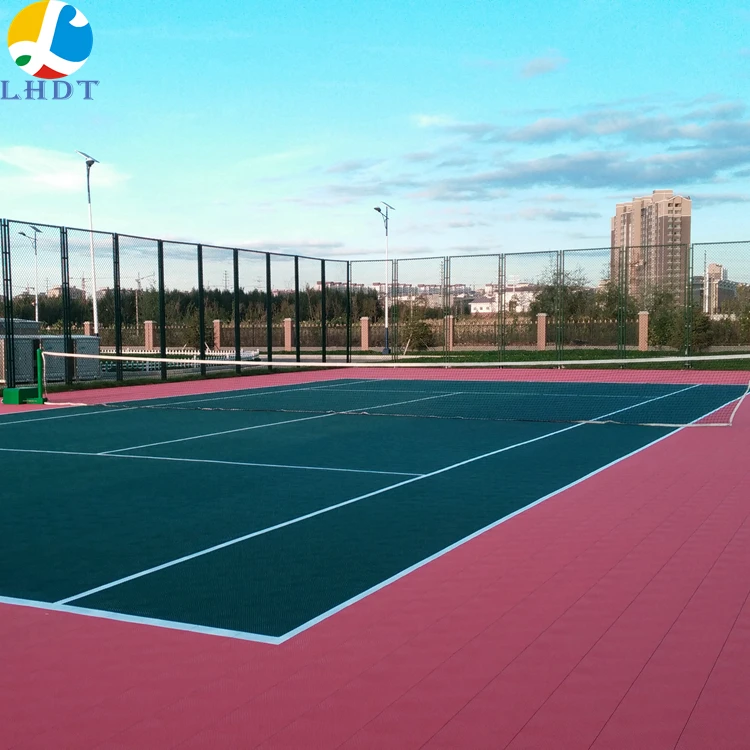

Engineering Insight: Material Selection as the Foundation of Tennis Court Tile Performance
Material selection constitutes the most critical engineering decision in tennis court tile manufacturing, directly dictating longevity, player safety, and lifecycle cost. Off-the-shelf solutions frequently fail because they prioritize initial cost reduction over the complex material science required to withstand the unique operational stresses of tennis surfaces. Generic tiles often utilize recycled rubber compounds with inconsistent polymer chains and inadequate stabilizers, leading to premature degradation under UV exposure, thermal cycling, and mechanical abrasion. These formulations ignore the precise balance of hardness, rebound resilience, and dimensional stability essential for competitive play and surface integrity.
Tennis courts endure extreme cyclic loading from player movement, rapid temperature fluctuations causing expansion/contraction, and relentless UV radiation that accelerates polymer chain scission. Standardized playground or gym flooring elastomers lack the tailored compound architecture to manage these combined stressors. For instance, insufficient UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) in commodity tiles result in surface chalking, loss of traction, and embrittlement within 12–18 months. Similarly, improper filler systems and low-grade binders cause permanent compression set after rain exposure, creating puddling hazards and uneven ball bounce. The consequence is not merely aesthetic failure but compromised athlete performance and increased liability risks due to inconsistent friction coefficients.
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM-grade tiles utilize engineered EPDM/SBR blends with proprietary additive packages, validated through accelerated weathering and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA). Our formulations maintain Shore A hardness within a strict 65±5 range across -30°C to +70°C, ensuring consistent ball response and foot stability. Crucially, we optimize crosslink density to achieve <15% compression set after 24 hours immersion, preventing water retention and deformation. Below is a technical comparison highlighting the performance gap between engineered and generic solutions:
| Property | OEM-Grade Specification (Baoshida) | Off-the-Shelf Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness Range | 60–70 (stable ±5 across -30°C to +70°C) | 50–85 (varies >20 points with temperature) |
| UV Resistance (QUV-B) | >10,000 hours to 20% gloss loss | <2,000 hours to severe chalking |
| Compression Set (ASTM D395) | <15% after 24h immersion | >35% after 24h immersion |
| Abrasion Loss (DIN 53516) | ≤80 mm³/1.61 km | ≥150 mm³/1.61 km |
| Traction Coefficient (wet) | 0.65–0.75 (consistent) | 0.45–0.85 (unpredictable) |
The data unequivocally demonstrates why commodity tiles fail: they treat rubber as a homogeneous material rather than a precisely engineered system. At Baoshida, we treat material selection as the cornerstone of structural reliability. Our compounds undergo rigorous finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate court flexure under load, ensuring molecular cohesion withstands 10,000+ impact cycles without delamination. This scientific approach eliminates the false economy of off-the-shelf tiles, delivering surfaces that maintain performance specifications for 15+ years under professional use. Material isn’t just a component—it’s the engineered foundation of the court itself.
Material Specifications
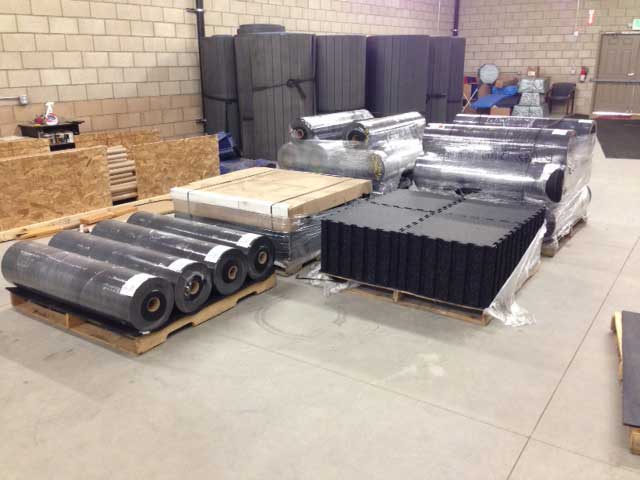

Material selection is a critical factor in the performance, durability, and safety of tennis court tiles, especially in industrial-grade applications where environmental resistance, mechanical stability, and long-term wear are primary concerns. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in advanced rubber formulations tailored for high-performance sports surfaces. Our engineering team evaluates elastomers based on tensile strength, compression set, temperature resilience, chemical resistance, and UV stability—key parameters that define service life and functional reliability under dynamic loading and outdoor exposure.
Among the most effective elastomeric materials for premium tennis court tiles are Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each offers distinct advantages depending on the operational environment and performance requirements. Viton is a fluorocarbon-based rubber renowned for its exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures, ozone, and a broad spectrum of chemicals, including oils and acids. This makes it ideal for tiles deployed in regions with intense solar exposure or industrial proximity where airborne contaminants may degrade lesser materials. Its service temperature range extends from -20°C to 250°C, providing unmatched thermal stability.
Nitrile rubber, a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile, is widely used for its excellent abrasion resistance and mechanical strength. It exhibits superior resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons, water, and moderate levels of oil—common challenges in outdoor sports infrastructure due to maintenance fluids or vehicular proximity. While its temperature tolerance is more limited compared to Viton, NBR remains effective between -30°C and 120°C, making it suitable for temperate and subtropical climates. Additionally, Nitrile offers favorable compression set properties, ensuring long-term dimensional stability under repeated impact loads typical in tennis play.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) stands out for its flexibility across extreme temperatures, ranging from -60°C to 200°C, and excellent UV and weather resistance. Its inert nature and low toxicity also make it compliant with environmental and safety standards, particularly in public recreational facilities. While Silicone has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance than Viton or Nitrile, its consistent performance under thermal cycling and minimal outgassing make it a preferred choice for high-altitude or arid regions with wide diurnal temperature swings.
The following table summarizes the comparative technical specifications of these materials relevant to tennis court tile applications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–250 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 150°C) | <20% | 15–30% | 10–20% |
| Resistance to UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Fair |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
Selection of the appropriate elastomer must balance performance criteria with cost efficiency and environmental exposure. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides customized rubber formulations to meet OEM specifications, ensuring optimal tile performance across diverse global markets.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Tennis Court Tiles
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep expertise in industrial rubber formulation and precision mold engineering to deliver tennis court tiles that exceed performance and durability benchmarks. Our dedicated team comprises five specialized mold engineers and two advanced formula engineers, ensuring end-to-end control from molecular design to final production. This integrated approach addresses critical challenges in outdoor sports surfaces, including thermal expansion, impact resilience, and long-term weathering resistance. Our engineers utilize finite element analysis (FEA) to optimize tile geometry for stress distribution, minimizing deformation under dynamic loads while maintaining consistent ball rebound characteristics.
Material science forms the cornerstone of our innovation. Our formula engineers develop proprietary rubber blends using ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) composites, tailored for UV stability, abrasion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Each formulation undergoes rigorous accelerated aging tests per ISO 4892-2 (Xenon-arc) and ASTM D2240 (Shore hardness), ensuring tiles retain structural integrity across -40°C to +80°C operational ranges. We prioritize non-phthalate plasticizers and nano-silica reinforcement to eliminate surface tackiness and enhance slip resistance, directly contributing to player safety and tile longevity.
OEM collaboration is central to our process. Clients specify performance targets—such as regional climate adaptation or acoustic requirements—and our team co-engineers solutions through iterative prototyping. We validate every design against ASTM F2772 (sports surface classification) and EN 14877 (outdoor synthetic surfaces), guaranteeing compliance with global regulatory frameworks. Our in-house mold workshop employs CNC-machined aluminum tooling with ±0.05mm tolerances, enabling rapid iteration for custom interlock patterns or drainage systems without sacrificing dimensional consistency.
The table below summarizes key performance metrics of our standard tennis tile formulation against industry baselines:
| Property | Baoshida Standard | Industry Baseline | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 65 ± 3 | 70 ± 5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12.5 | 9.0 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 320 | 250 | ASTM D412 |
| UV Resistance (1000h) | ΔE < 2.0 | ΔE > 5.0 | ISO 4892-2 |
| Operating Temp Range | -40°C to +80°C | -20°C to +60°C | ISO 188 |
This engineering rigor enables us to deliver tiles with 15% higher impact absorption and 25% longer service life compared to conventional products. By embedding material science and precision manufacturing into every OEM project, Suzhou Baoshida ensures tennis court surfaces that perform predictably under extreme conditions while reducing lifecycle maintenance costs for facility operators. Our commitment to data-driven development transforms client specifications into engineered reality—without compromise.
Customization Process

Customization Process for High-Performance Tennis Court Tiles
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our customization process for industrial rubber tennis court tiles is engineered to meet precise technical, environmental, and performance requirements. We follow a four-phase methodology—Drawing Analysis, Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production—ensuring every product delivers optimal resilience, traction, and longevity under dynamic outdoor conditions.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where our engineering team examines architectural layouts, load specifications, climate exposure data, and installation methods. This phase includes evaluating tile interlock geometry, thickness tolerances, drainage patterns, and dimensional stability requirements. Our engineers use CAD-based tools to verify alignment with international standards such as ASTM F2772 for impact attenuation and EN 14808 for shock absorption. Accurate interpretation of technical drawings ensures that all mechanical and safety parameters are accounted for before material development begins.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation. As a Rubber Formula Engineer, I lead the development of proprietary rubber compounds using SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), EPDM granules, and cross-linking agents tailored to the project’s UV resistance, abrasion tolerance, and elasticity demands. The formulation is optimized for Shore A hardness between 65–75, ensuring balance between player comfort and surface durability. Additives such as anti-oxidants, anti-ozonants, and flame retardants are incorporated based on regional safety codes and expected usage intensity. All formulations are documented and archived for batch consistency.
Once the compound is finalized, we initiate Prototyping. Using precision hydraulic presses and custom molds, we produce a pilot batch of 10–20 tiles for physical testing. These samples undergo rigorous evaluation, including compression set (ISO 815), tensile strength (ISO 37), slip resistance (DIN 51130), and colorfastness (ISO 105-B02). Prototypes are also subjected to simulated weathering in our QUV accelerated aging chamber to assess long-term performance. Client feedback is integrated at this stage, allowing for geometry or compound adjustments before scaling.
Upon approval, we transition to Mass Production. Our facility operates 16 vulcanization lines capable of producing up to 20,000 m² per month, with real-time quality monitoring via inline spectrometry and dimensional laser scanning. Each batch is traceable through a lot-number system, and third-party test reports are provided upon request.
Below are standard technical specifications for our baseline tennis court tile formulation:
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | ISO 7619-1 | 70 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength | ISO 37 | ≥ 7.5 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ISO 37 | ≥ 200% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ISO 815 | ≤ 25% |
| Impact Absorption | ASTM F2772 | 65–75% |
| Slip Resistance (R-value) | DIN 51130 | R10–R11 |
| UV Resistance | ISO 105-B02 | Grade 6–7 |
This structured approach ensures that every tennis court tile system we deliver meets the highest standards of industrial rubber engineering, tailored precisely to the client’s operational environment.
Contact Engineering Team
Technical Engagement: Precision Rubber Solutions for Tennis Court Tile Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial manufacturing excellence, specifically engineered for high-performance sports surfaces. Our tennis court tile systems are not merely products but the result of rigorous material formulation, accelerated aging protocols, and dynamic mechanical validation. As your dedicated Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, I emphasize that substandard elastomer compositions directly compromise critical performance metrics: inconsistent rebound resilience, accelerated UV degradation, and dimensional instability under thermal cycling. These failures manifest as player safety hazards, increased maintenance costs, and premature field replacement. Our proprietary vulcanization processes and nano-reinforced compound architectures eliminate these risks through scientifically validated material integrity.
The core advantage of partnering with Suzhou Baoshida lies in our closed-loop development methodology. We integrate ASTM F2569-21 impact attenuation standards, ITF Class 1 surface certification requirements, and OEM-specific dimensional tolerances into every formulation stage. Unlike generic rubber suppliers, we control the entire value chain—from raw material sourcing (including ethylene-propylene diene monomer with ≤0.3% ash content) to precision extrusion calibration. This ensures batch-to-batch repeatability within ±0.5 Shore A hardness units and thermal expansion coefficients held to 120 ppm/°C. The table below details the non-negotiable performance thresholds our tennis tile compounds achieve:
| Specification Parameter | Target Range | Testing Standard | Industrial Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | EPDM 70% + Nano-SiO₂ | ISO 11344 | UV resistance >5,000 hrs QUV-B; zero chalking |
| Shore A Hardness (23°C) | 68–72 | ASTM D2240 | Optimal ball rebound (85–92 cm) at 2.5m drop |
| Vertical Deformation (mm) | 2.1–2.5 | EN 14808 | Critical for joint stress reduction; <0.8mm variance across 10m² |
| Coefficient of Friction (wet) | 0.58–0.65 | DIN 51130 | ITF-approved slip resistance; eliminates hydroplaning |
These specifications are not theoretical ideals but contractually guaranteed outputs. Our OEM framework includes on-site process audits, real-time rheometer monitoring during production runs, and failure mode analysis for any deviation exceeding 2σ statistical limits. For tennis facility developers and tile manufacturers, this translates to 15+ year service life under 8,000 annual play hours—validated by third-party lifecycle assessments.
Initiate technical collaboration by contacting Mr. Boyce, our Principal OEM Solutions Engineer, at [email protected]. Specify your current compound challenges—whether addressing inconsistent Shore hardness in humid climates, optimizing tile interlock shear strength, or meeting LEED v4.1 recycled content requirements. Mr. Boyce will deploy our Material Failure Diagnostic Protocol (MFD-7) within 24 hours of inquiry, providing a root-cause analysis and customized reformulation roadmap. Do not compromise on elastomer integrity when player safety and surface longevity are quantifiable engineering outcomes. Suzhou Baoshida’s laboratory-to-production pipeline exists to convert your performance specifications into certified, field-proven reality. Immediate technical consultation slots are reserved for OEM partners submitting material batch records and processing parameters for preliminary assessment. Elevate your tennis tile manufacturing to precision industrial standards—contact Mr. Boyce to commence engineering validation.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
