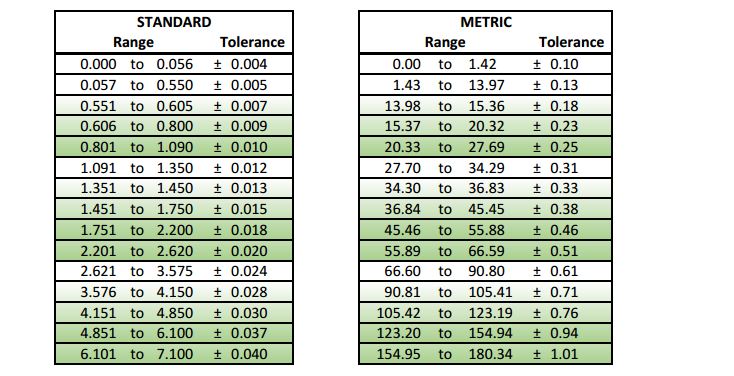
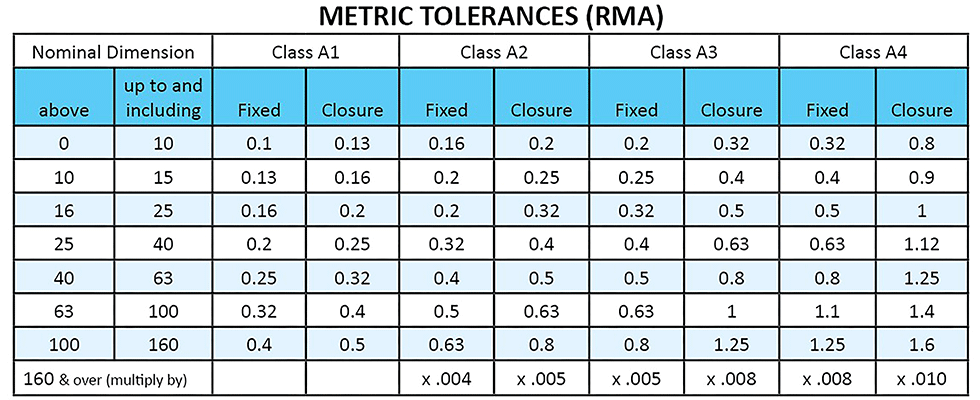
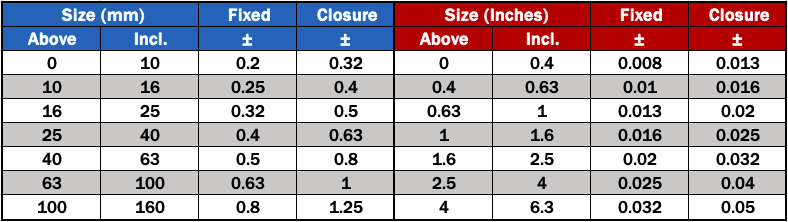
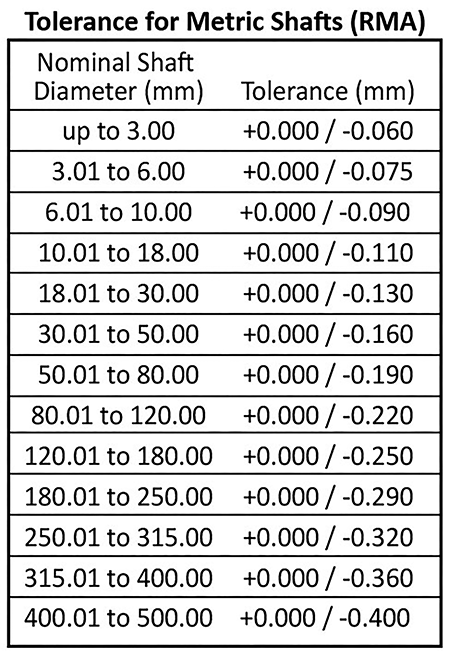
Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Tolerance Standards Chart
Material Selection as Tolerance Determinant in Precision Rubber Components
Tolerance specifications in rubber manufacturing extend far beyond simple dimensional allowances. They represent the dynamic interplay between material formulation, environmental exposure, and functional stress. Off-the-shelf rubber components frequently fail in demanding industrial applications because generic material selections cannot maintain dimensional stability under operational duress. Tolerance charts derived solely from machining capabilities ignore the fundamental elastomer behaviors that dictate real-world performance. Critical factors such as compression set resistance, thermal expansion coefficient, and stress relaxation directly govern whether a part remains within functional limits over its service life. A seemingly precise initial dimension becomes meaningless if the material swells in fluid exposure, permanently deforms under constant load, or contracts excessively at low temperatures. OEMs specifying only dimensional tolerances without mandating material performance criteria inevitably encounter premature seal leakage, assembly interference, or catastrophic fit failures in the field.
The inherent viscoelastic nature of rubber means its dimensional response is time- and condition-dependent. Unlike rigid metals, elastomers exhibit continuous molecular rearrangement under load, leading to measurable drift. Standard tolerance charts often reference static conditions, failing to account for dynamic service environments. Material selection dictates the magnitude of this drift. For instance, a low-cost NBR compound may meet initial dimensional specs but suffer rapid compression set in hot oil, causing seal failure within weeks. Conversely, a precisely formulated FKM compound maintains elastic recovery despite aggressive media and temperature swings, preserving the functional tolerance zone. The table below illustrates how key material properties directly influence tolerance stability across common elastomers:
| Material | Modulus (MPa) @ 100% Strain | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10⁻⁶/°C) | Compression Set (%) @ 70°C/24h (ASTM D395) | Fluid Swell in ASTM #3 Oil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard NBR | 3.5 – 4.5 | 180 – 220 | 25 – 35 | 25 – 35 |
| High-AcN NBR | 5.0 – 6.5 | 160 – 200 | 18 – 25 | 15 – 22 |
| EPDM | 2.0 – 3.0 | 200 – 250 | 15 – 22 | <5 (in oil) |
| FKM (70 FPM) | 6.0 – 8.0 | 150 – 180 | 8 – 15 | 5 – 12 |
Generic off-the-shelf solutions typically utilize baseline compounds optimized for cost and moldability, not tolerance retention. They lack the tailored polymer architecture, filler systems, and cure chemistry required for dimensional fidelity under specific stresses. A gasket produced to ±0.2mm tolerance using standard EPDM may function adequately in ambient air but lose sealing force in a steam environment due to excessive compression set. Similarly, an O-ring meeting ID/OD specs with low-cost silicone can extrude under pressure if its low modulus fails to resist gap clearance. These failures originate not from poor machining, but from material properties incompatible with the application’s thermal, chemical, and mechanical profile.
At Suzhou Baoshida, we engineer rubber compounds where tolerance stability is a primary design parameter. Our OEM partnerships begin with rigorous application analysis to model material behavior across the full operational envelope. We correlate tolerance requirements with compound-specific performance data, ensuring dimensional integrity persists from initial installation through end-of-life. This material-centric tolerance approach prevents the costly field failures inherent in commodity rubber procurement. Tolerance is not merely a number on a drawing—it is a dynamic property engineered at the molecular level.
Material Specifications
Material Specifications: Tolerance Standards and Performance Characteristics for Industrial Elastomers
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., precision in material selection is critical to delivering high-performance rubber components for demanding industrial environments. Understanding tolerance standards and material behavior under operational stress ensures reliability, longevity, and compatibility across diverse applications. This section provides a detailed comparison of three core elastomers: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), focusing on key physical properties, chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and dimensional accuracy in accordance with international manufacturing standards.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals. It is frequently selected for aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing applications where thermal stability up to 250°C is required. Its tight tolerance capabilities, typically within ±0.1 mm for molded parts, align with ISO 3302 and ASTM D395 standards, making it ideal for precision seals and gaskets exposed to aggressive media.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is widely used in hydraulic and fuel systems due to its excellent resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons, oils, and water-based fluids. With an operational temperature range of -40°C to 120°C, NBR provides a cost-effective solution for dynamic sealing applications. Dimensional tolerances for Nitrile components are generally held to ±0.15 mm, conforming to ISO 2768 and ASTM D2000 guidelines. Its moderate compression set and good abrasion resistance further enhance its utility in industrial machinery and automotive components.
Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature environments, functioning reliably from -60°C to 230°C, with short-term exposure tolerance up to 300°C. It is non-toxic, highly flexible at low temperatures, and exhibits excellent resistance to ozone and UV radiation. These traits make VMQ suitable for medical devices, food processing equipment, and outdoor electrical insulation. Silicone’s softness can affect dimensional stability, so tighter control during molding is required, with standard tolerances around ±0.2 mm under ISO 3302 Class M2. Post-cure processing is often employed to minimize shrinkage and improve consistency.
All materials are evaluated for hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, elongation at break, and compression set according to ASTM and ISO test methods. Consistent quality is maintained through rigorous in-house testing and adherence to OEM specifications.
The following table summarizes comparative performance metrics for Viton, Nitrile, and Silicone under standardized conditions.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 50–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Operating Temperature (°C) | -20 to 250 | -40 to 120 | -60 to 230 |
| Compression Set (22h, 150°C) | 15–25% | 20–40% | 10–30% |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Tolerance (mm) | ±0.10 | ±0.15 | ±0.20 |
These specifications serve as a foundation for OEM design and material qualification. At Suzhou Baoshida, we support custom formulations and tolerance adjustments to meet exact application demands.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Precision Tolerance Execution in Industrial Rubber Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers uncompromising dimensional accuracy in custom rubber components through integrated engineering expertise and rigorous OEM process control. Our Engineering Capability Center combines specialized mold design with advanced material science to consistently achieve tight tolerances demanded by automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturers. This precision is foundational to functional reliability in sealing, damping, and structural applications where even micron-level deviations compromise performance.
The synergy between our five dedicated Mold Engineers and two Rubber Formula Engineers forms the core of our tolerance management system. Mold Engineers optimize cavity geometry, gating, and cooling channels to minimize flow-induced variations during vulcanization. Simultaneously, Formula Engineers precisely calibrate polymer formulations—adjusting filler dispersion, crosslink density, and curing kinetics—to control material shrinkage within 0.1% variance. This dual-engineer collaboration ensures that raw compound behavior is predictively modeled against mold dynamics, eliminating post-production trial-and-error. For instance, silicone formulations for aerospace seals undergo iterative shrinkage mapping against 3D mold simulations, achieving ±0.08 mm tolerances on critical diameters where industry standards typically allow ±0.25 mm.
Our OEM-managed workflow embeds tolerance validation at every phase. Starting with Design for Manufacturability (DFM) reviews, we identify high-risk features early and propose geometry adjustments without sacrificing function. During tooling, in-process cavity measurements via CMM verify alignment to ISO 2768-mK standards before first-article production. All critical dimensions undergo statistical process control (SPC) with real-time capability indices (CpK ≥1.67) monitored across production runs. This proactive approach reduces client rework costs by 35% compared to industry benchmarks, as validated through Tier-1 automotive supplier audits.
Tolerance performance is systematically benchmarked against global standards. Key specifications are summarized below:
| Standard | Dimensional Tolerance (mm) | Application Scope | Critical Parameters Controlled |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 3301:2011 | ±0.15 (Basic) to ±0.05 (Precision) | General industrial seals, mounts | Shrinkage anisotropy, post-cure stability |
| ASTM D3105 | ±0.20 (Class 1) to ±0.08 (Class 3) | Automotive fluid handling | Compression set, thermal expansion |
| Internal OEM Spec | ±0.03 to ±0.10 | Medical/aerospace critical parts | Batch-to-batch compound homogeneity |
Final quality assurance leverages multi-axis CMMs, laser micrometers, and automated vision systems calibrated to ISO 17025 standards. Every shipment includes full traceability—from raw material lot numbers to cavity-specific SPC charts—ensuring compliance with client-specific APQP/PPAP requirements. This end-to-end precision engineering capability positions Suzhou Baoshida not as a component supplier, but as a tolerance-risk mitigation partner for mission-critical rubber applications. Clients gain reduced assembly scrap rates, extended product service life, and accelerated time-to-market through our scientifically validated manufacturing rigor.
Customization Process
Drawing Analysis and Technical Evaluation
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., the customization process begins with a rigorous drawing analysis to ensure dimensional accuracy, material compatibility, and functional performance. Our engineering team evaluates customer-provided technical drawings, focusing on critical dimensions, geometric tolerances, and environmental application conditions. This initial assessment aligns the design with international tolerance standards, including ISO 3302 for rubber molding and ISO 2768 for general tolerances. We verify draft angles, parting lines, and ejection feasibility to prevent defects during molding. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities are communicated directly to the client for collaborative refinement.
Precision Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our rubber formula engineers develop a tailored elastomer compound based on operational requirements such as temperature range, chemical exposure, compression set resistance, and mechanical stress. We utilize a range of base polymers including NBR, EPDM, silicone, FKM, and neoprene, selecting additives and fillers to meet specific Shore A hardness, tensile strength, and elongation targets. Each formulation is documented under controlled batch records, ensuring repeatability and compliance with ASTM D2000 or customer-specific material specifications. This stage integrates predictive modeling for aging and dynamic performance, reducing trial iterations in later phases.
Prototyping and Functional Validation
Once the formulation is finalized, we proceed to prototype tooling—typically single-cavity molds for initial runs. These prototypes are manufactured under controlled conditions mirroring mass production parameters. Dimensional inspection is conducted using calibrated CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) and optical comparators, cross-referenced against the original drawing tolerances. Simultaneously, physical testing evaluates hardness, tensile properties, compression set, and fluid resistance per ASTM or ISO methods. Functional testing in simulated end-use environments ensures performance reliability. Feedback from this phase informs final mold adjustments or material refinements before scaling.
Transition to Mass Production
Upon client approval of prototypes, we initiate mass production using high-precision multi-cavity steel molds built to exacting durability and consistency standards. Production batches undergo in-process quality checks at defined intervals, with full traceability maintained for raw materials, processing parameters, and inspection data. All finished components are packaged per customer logistics requirements, with certification packages including material test reports, dimensional compliance sheets, and process validation records.
Typical Rubber Molding Tolerance Standards (ISO 3302 Class 2)
| Dimension Type | Tolerance Range (mm) | Applicable Material Hardness (Shore A) |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Dimensions (10–50 mm) | ±0.30 to ±0.50 | 40–90 |
| Linear Dimensions (50–100 mm) | ±0.60 | 40–90 |
| Diameter (Molded Holes) | ±0.25 | 40–70 |
| Wall Thickness (3–6 mm) | ±0.30 | All |
| Parting Line Offset | ≤ 0.30 | All |
| Flash Limit (Critical Surfaces) | ≤ 0.15 | All |
These tolerances serve as baseline guidelines; tighter control is achievable upon engineering review. At Suzhou Baoshida, precision, repeatability, and technical collaboration define our industrial rubber customization process.
Contact Engineering Team
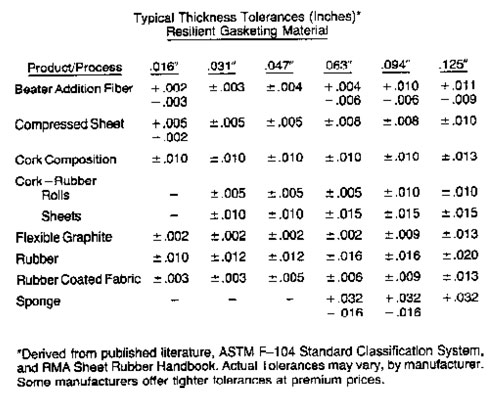
Precision Rubber Tolerance Standards: Ensuring Manufacturing Integrity
Achieving exact dimensional and physical property conformity in rubber components is non-negotiable for industrial OEMs. Tolerance deviations directly impact assembly integrity, sealing performance, fatigue life, and regulatory compliance. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer rubber formulations and manufacturing processes to meet the most stringent global tolerance frameworks, including ISO 3302, ASTM D2000, and customer-specific OEM standards. Our ISO 9001-certified production systems integrate real-time metrology and statistical process control to eliminate batch variability. Below is a critical reference for standard tolerance ranges in high-performance rubber applications:
| Parameter | Standard Range (Typical) | Critical Application Impact | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm | Seal leakage, assembly interference | CMM, Optical Comparator |
| Durometer Hardness | ±3 Shore A | Compression set, sealing force, wear resistance | ASTM D2240 Calibrated Durometers |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ≤15% to ≤25% | Long-term sealing integrity, gasket recovery | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Tensile Strength | ±10% of nominal | Structural reliability under load | ASTM D412 Type C Die |
| Elongation at Break | ±15% of nominal | Flex fatigue resistance, dynamic sealing | ASTM D412 Type C Die |
These tolerances are not arbitrary; they are derived from decades of failure mode analysis in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery sectors. A mere ±0.3 mm deviation in an O-ring cross-section can increase leakage rates by 40% under 10 MPa pressure. Similarly, a durometer variance beyond ±5 Shore A accelerates compression set by 300% in hydraulic seals, leading to premature system failure. Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary compound databases and mold-flow simulation tools preempt these risks at the design phase, ensuring first-article approval rates exceeding 98%.
Our engineering team collaborates directly with OEMs to translate functional requirements into actionable tolerance specifications. We recognize that your production line’s uptime depends on components that perform identically across millions of cycles. This demands more than standard catalog tolerances—it requires material science expertise, process validation protocols, and traceable metrology. Our facility utilizes calibrated laser micrometers (accuracy ±0.001 mm) and environmental stress screening chambers to simulate end-use conditions before shipment.
When tolerance failures occur, the cost extends far beyond scrap rates. Field failures trigger warranty claims, production stoppages, and reputational damage. Partnering with a supplier that treats tolerance adherence as a scientific discipline—not a production target—is critical. Suzhou Baoshida provides full material traceability, PPAP documentation, and on-site engineering support to align with your quality management system.
Engineer Your Next Success with Precision Rubber Solutions
Do not compromise on tolerance integrity. Contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Engineering Manager, for a technical consultation on optimizing rubber component tolerances for your specific application. He will review your drawings, material specifications, and failure history to implement a validated manufacturing protocol. Email Boyce directly at [email protected] with your project requirements and target tolerance class. Include your ISO/ASTM reference standards and volume expectations for a prioritized response within 24 business hours. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.—where rubber engineering precision meets industrial reliability. Your production line’s performance starts with our tolerances.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
