Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Tpe Material Vs Pvc

Engineering Insight: TPE Material vs PVC – The Critical Role of Material Selection in Industrial Applications
In the field of industrial rubber solutions, the selection between thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is not merely a matter of cost or availability—it is a decisive engineering consideration that directly impacts product performance, longevity, and operational safety. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize that off-the-shelf material solutions often fail under real-world industrial conditions due to a lack of tailored formulation and application-specific testing. General-purpose materials may meet basic physical requirements on paper, but they frequently degrade prematurely when exposed to dynamic stress, temperature fluctuations, chemical exposure, or UV radiation.
PVC has long been a staple in flexible component manufacturing due to its low cost and ease of processing. However, its performance limitations become evident in demanding environments. Unplasticized or rigid PVC lacks elasticity, while plasticized PVC—commonly used for flexible parts—suffers from plasticizer migration over time. This leads to embrittlement, loss of flexibility, and potential failure in sealing or damping applications. Additionally, standard PVC formulations are not inherently suitable for high-temperature operations and may release hazardous compounds when exposed to fire, limiting their use in regulated or safety-critical industries.
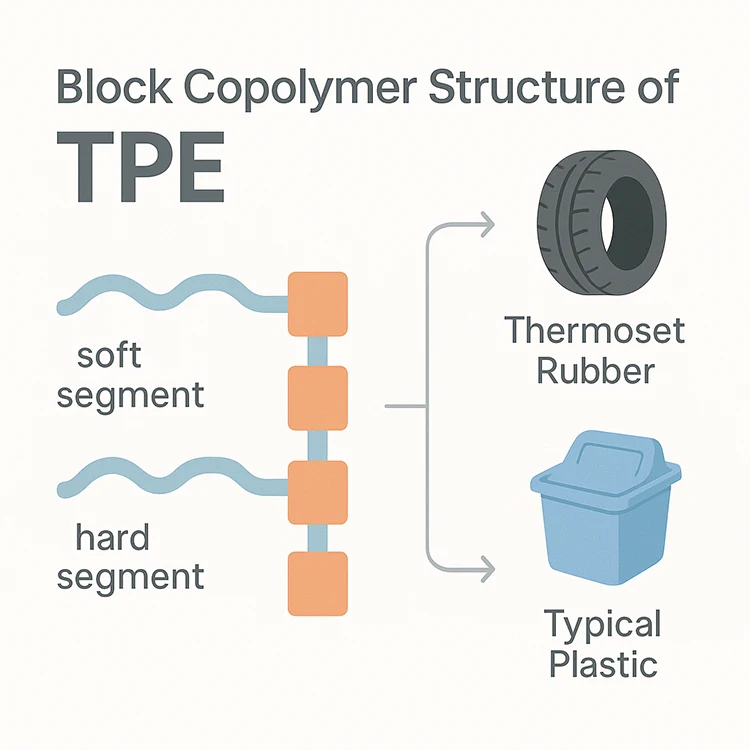
In contrast, TPE offers a superior balance of elasticity, durability, and chemical resistance. As a copolymer system, TPE can be precisely engineered to meet targeted mechanical and thermal properties. Unlike PVC, TPE does not rely on volatile plasticizers, ensuring long-term flexibility and resistance to environmental aging. Its thermoplastic nature allows for efficient processing and recyclability, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental and sustainability standards. TPE formulations can be customized for oil resistance, low-temperature flexibility, or enhanced tensile strength—critical attributes in automotive, industrial machinery, and fluid handling systems.
The failure of off-the-shelf materials often stems from a one-size-fits-all approach that ignores operational variables. For example, a standard PVC seal may function adequately in a controlled indoor environment but crack under thermal cycling in outdoor equipment. Similarly, an unmodified TPE may absorb oils or swell in chemical exposure scenarios if not properly formulated. This underscores the necessity of application-driven material development, where compound design is informed by real-world service conditions.
At Suzhou Baoshida, we specialize in engineered rubber solutions that bridge the gap between generic materials and high-performance requirements. Our technical team collaborates with OEMs to develop custom TPE and PVC formulations that address specific mechanical, thermal, and regulatory challenges.
The following table outlines key comparative properties of standard TPE and PVC formulations:
| Property | TPE (Typical) | PVC (Plasticized) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 30–95 | 50–90 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8–15 | 10–18 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 400–800 | 200–400 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -50°C to 120°C | -20°C to 60°C |
| UV Resistance | Good (formulation dependent) | Poor to Moderate |
| Plasticizer Migration | None | Significant over time |
| Recyclability | High | Limited |
| Flame Behavior | Self-extinguishing (customizable) | Releases HCl when burned |
Material selection is not a commodity decision—it is a foundational element of product integrity. Partnering with a technical supplier ensures that material performance aligns with engineering intent.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Critical Elastomer Selection
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides precision-engineered elastomer solutions for industrial applications. While the broader context references TPE versus PVC comparisons, this section details specifications for three high-performance materials essential in demanding OEM environments: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). These materials serve distinct roles in sealing, vibration damping, and fluid handling where thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical integrity are non-negotiable.
Viton fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits exceptional resistance to aggressive chemicals, including fuels, oils, and acids, due to its high fluorine content (66%). It operates continuously at -20°C to +230°C, with intermittent peaks up to 300°C. Its tensile strength ranges from 10 to 18 MPa (ASTM D412), and hardness spans 60–90 Shore A. Viton is the standard for aerospace fuel systems, chemical processing seals, and semiconductor manufacturing components where failure is unacceptable.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) balances cost efficiency with robust oil and fuel resistance, driven by acrylonitrile content (18–50%). Higher acrylonitrile percentages enhance oil resistance but reduce low-temperature flexibility. NBR functions reliably from -40°C to +120°C (up to 150°C intermittently), with tensile strength of 10–20 MPa and hardness of 40–90 Shore A. It dominates automotive O-rings, hydraulic seals, and printing roller applications requiring abrasion resistance and compression set stability below 10%.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) delivers unmatched thermal stability from -60°C to +200°C (special grades to 300°C) and superior biocompatibility. Its tensile strength is moderate (5–10 MPa), but elongation exceeds 300%, with hardness typically 30–80 Shore A. Silicone resists ozone, UV, and steam but exhibits poor tear strength and fuel resistance. It is critical in medical device gaskets, food-grade tubing, and high-temperature electrical insulation where purity and flexibility are paramount.
The comparative table below summarizes key specifications per ASTM/ISO standards for OEM design validation:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Temp Range | -20°C to +230°C | -40°C to +120°C | -60°C to +200°C |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 10–18 | 10–20 | 5–10 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 60–90 | 40–90 | 30–80 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.80–1.95 | 0.95–1.05 | 1.10–1.50 |
| Fuel Resistance | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Acid Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Poor |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Key Limitation | Cost; Low-temp flexibility | Poor heat/ozone resistance | Low tensile/tear strength |
Suzhou Baoshida emphasizes material selection based on application-specific stressors. Viton is optimal for extreme chemical exposure, NBR for cost-sensitive oil-handling systems, and Silicone for thermal-cycling or biocompatible requirements. All materials undergo rigorous batch testing per ISO 37 and ASTM D2000 standards to ensure dimensional stability and performance consistency in OEM production. Consult our engineering team for compound customization addressing compression set, fluid immersion, or regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, UL). Precision in material science drives reliability in your final product.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Excellence in TPE and PVC Material Development
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, particularly in the specialized domain of thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) material systems. With a dedicated team comprising five experienced mould engineers and two advanced formula engineers, we deliver precision-driven, application-specific solutions tailored to the demanding requirements of global OEMs. Our integrated approach ensures seamless alignment between material formulation, mould design, and production scalability, enabling us to meet exacting performance and regulatory standards across industries such as automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, and industrial sealing.
Our formula engineers specialize in the molecular-level tuning of TPE and PVC compounds, optimizing properties such as hardness, tensile strength, thermal stability, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility. This scientific approach enables us to develop custom formulations that outperform standard-grade materials, particularly in dynamic environments where flexibility, durability, and long-term aging resistance are critical. Unlike generic suppliers, we control the entire development cycle—from raw material selection and compounding to physical testing and batch consistency—ensuring repeatability and compliance with ISO and RoHS standards.
Complementing our formulation expertise, our five in-house mould engineers bring deep knowledge of injection moulding dynamics, flow analysis, and tooling optimization. They work in parallel with the formula team to ensure that material behavior is accurately predicted and fully leveraged during the manufacturing process. This synergy reduces trial iterations, accelerates time-to-market, and enhances part integrity, especially for complex geometries and multi-material overmoulding applications where TPE is bonded to rigid substrates such as ABS or PC.
Our OEM capabilities are built on a foundation of technical transparency and collaborative engineering. Clients receive full material data sheets, mould flow reports, and DFM (Design for Manufacturability) feedback before production launch. We support low-volume prototyping through to high-volume automated production, with full traceability and quality control protocols in place.
The following table highlights key comparative specifications of our engineered TPE and PVC formulations, reflecting our ability to tailor performance characteristics to application demands.
| Property | Engineered TPE (Custom Formulation) | Rigid PVC (Plasticized) | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40–95 | 50–85 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8–15 | 10–14 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 400–800 | 200–350 | ASTM D412 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -50°C to +120°C | -20°C to +70°C | ASTM D1239 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ≤40% | ASTM D395 |
| Flame Rating (UL94) | HB to V-0 | HB | UL 94 |
| RoHS/REACH Compliance | Full | Conditional | IEC 62321 |
This level of technical control and customization underscores our position as a trusted engineering partner in advanced elastomer solutions. At Suzhou Baoshida, we don’t just supply materials—we engineer performance.
Customization Process

TPE Material vs PVC: Customization Process for Industrial Applications
Material selection between thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) initiates our precision-driven customization workflow at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. This decision directly impacts downstream engineering parameters, regulatory compliance, and lifecycle performance. Our four-phase process ensures optimal material integration for industrial rubber solutions, beginning with rigorous Drawing Analysis. Engineers dissect client technical drawings to identify critical dimensions, durometer requirements, and environmental exposure conditions. For TPE applications demanding high elasticity and low-temperature resilience, tighter tolerances are allocated to accommodate material memory recovery. PVC projects prioritize dimensional stability in static-load scenarios but require explicit validation of plasticizer migration risks in fluid-contact environments.
Formulation follows drawing validation, where our rubber compound specialists adjust base polymers to meet exact performance targets. TPE formulations undergo dynamic vulcanization tuning to enhance oil resistance and tensile strength, while PVC compounds focus on plasticizer selection to balance flexibility versus volatility. All formulations adhere to REACH and RoHS standards, with PVC requiring additional scrutiny for restricted phthalates. This phase includes accelerated aging simulations to predict 10,000-hour performance under operational stressors like ozone exposure or thermal cycling.
Prototyping transforms validated formulations into physical samples for functional testing. We employ multi-cavity molds to produce 50–100 units per iteration, subjecting them to ASTM D2000-standard compression set tests, Shore A hardness verification, and dynamic flex fatigue analysis. TPE prototypes undergo cold-bend testing to -40°C, whereas PVC units are evaluated for plasticizer bleed at 70°C. Client feedback on prototype performance triggers micro-adjustments to filler ratios or processing temperatures before final sign-off.
Mass Production deployment leverages our ISO 13485-certified manufacturing lines with real-time SPC monitoring. TPE runs utilize precision extrusion at 180–220°C with closed-loop cooling to prevent stickiness, while PVC requires lower processing temperatures (150–180°C) and dedicated ventilation for HCl emission control. Each batch undergoes inline spectrometry for composition verification and post-cure dimensional audits. Yield consistency is maintained through automated scrap reclamation systems, with TPE enabling 95%+ recyclability versus PVC’s 60% mechanical recycling limit.
Critical Performance Comparison: TPE vs PVC
| Property | TPE | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Shore Hardness Range | 20A–95A | 50A–90A |
| Continuous Use Temp | -50°C to +135°C | -20°C to +60°C |
| Recyclability | >95% (Mechanical) | ≤60% (Limited by additives) |
| Oil/Fuel Resistance | Excellent (Customizable) | Poor (Requires plasticizers) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Phthalate-free formulations | Restricted additives (e.g., DEHP) |
This structured approach ensures material properties align with functional demands while minimizing production risks. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering rigor transforms specification sheets into field-proven components, with TPE excelling in dynamic sealing applications and PVC serving cost-sensitive static assemblies where temperature exposure remains moderate. Final validation always includes client-site performance trials before full-scale rollout.
Contact Engineering Team

For industrial manufacturers seeking high-performance elastomeric materials, the choice between TPE and PVC is critical to product functionality, durability, and compliance. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering engineered rubber and polymer solutions tailored to the rigorous demands of automotive, construction, consumer goods, and medical device industries. Our technical expertise ensures that clients receive not only materials but comprehensive formulation guidance to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) represent two distinct classes of polymers with divergent physical, chemical, and processing characteristics. Understanding these differences is essential when selecting materials for sealing, insulation, or flexible components. TPEs offer superior elasticity, UV resistance, and recyclability, making them ideal for dynamic applications requiring repeated flexing and exposure to environmental stressors. In contrast, PVC provides excellent flame retardancy, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, often at a lower initial cost, which benefits static or indoor applications.
To assist engineers and procurement managers in making informed decisions, we provide detailed comparative analysis based on application-specific requirements. Below is a technical comparison highlighting key performance metrics:
| Property | TPE | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Shore Hardness Range | 20A – 80D | 30A – 85D |
| Tensile Strength | 8 – 30 MPa | 10 – 25 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 300% – 1000% | 150% – 400% |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120°C (short term) | Up to 60°C (continuous) |
| Low-Temperature Flexibility | Excellent (down to -60°C) | Limited (brittle below -20°C) |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | High | Moderate to Low |
| Flame Retardancy | Moderate (requires additives) | High (inherent in formulations) |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable | Limited recyclability |
| Density | 0.9 – 1.1 g/cm³ | 1.3 – 1.45 g/cm³ |
| Common Applications | Seals, grips, automotive trims | Cable sheathing, flooring, profiles |
At Suzhou Baoshida, we go beyond material supply. Our team of rubber formulation engineers works directly with clients to customize compounds that meet exact mechanical, regulatory, and processing needs. Whether you are transitioning from PVC to more sustainable TPE alternatives or require dual-material co-extrusion solutions, our technical support ensures seamless integration into your production workflow.
For immediate assistance with material selection, sample requests, or custom formulation development, contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager. With over 15 years of experience in industrial elastomer applications, Mr. Boyce provides precise, data-driven recommendations that align with your project timelines and performance targets. Reach out via email at [email protected] to schedule a technical consultation. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we are committed to advancing industrial performance through precision rubber solutions—partner with us to engineer smarter, more resilient products.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
