Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Types Of Door Seals
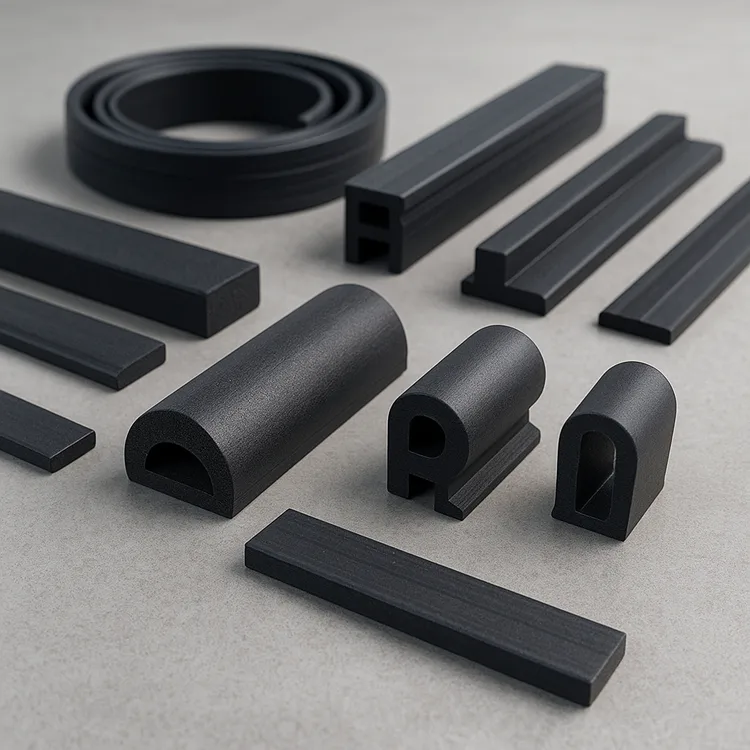

Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Door Seal Performance
In precision rubber sealing applications, the performance and longevity of door seals are directly tied to material selection. While off-the-shelf solutions may appear cost-effective and readily available, they frequently fail to meet the rigorous demands of industrial, automotive, and architectural environments. These failures stem from an oversimplified approach to seal design—one that neglects the complex interplay between environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and chemical compatibility.
Door seals are subjected to dynamic conditions including compression, shear, temperature fluctuations, UV radiation, moisture, and contact with oils, solvents, or cleaning agents. A generic EPDM seal, for example, may perform adequately in a mild climate but degrade rapidly in an environment with frequent ozone exposure or chemical splashes. Similarly, a silicone-based seal might offer excellent thermal stability but lack the tensile strength required for high-cycle door mechanisms.
Material selection must begin with a thorough analysis of the operational environment. For instance, fluorocarbon (FKM) compounds provide exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, and high temperatures, making them ideal for automotive engine compartments or industrial ovens. However, their higher cost and limited flexibility at low temperatures render them unsuitable for general-purpose applications. Conversely, thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer ease of processing and good flexibility but may compress permanently under sustained load, leading to seal leakage over time.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize engineered material solutions tailored to specific use cases. Our precision rubber seals are formulated using advanced compounding techniques that balance hardness, elongation, compression set, and chemical resistance. This ensures optimal sealing force retention over the product lifecycle, even under extreme conditions.
Off-the-shelf seals often fail because they are designed for average conditions, not worst-case scenarios. They typically use standardized durometer ratings and base polymers without reinforcement or specialty additives. In contrast, custom-engineered seals incorporate fillers, stabilizers, and cross-linking agents to enhance durability and performance consistency.
The table below outlines key material properties for common rubber compounds used in door seal applications.
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Compression Set (22h, 100°C) | Hardness (Shore A) | Key Resistance Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | ≤25% | 50–80 | Ozone, UV, water, steam |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to +200 | ≤20% | 40–80 | Extreme temperatures, UV |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -30 to +120 | ≤30% | 50–90 | Oils, fuels, aliphatic hydrocarbons |
| FKM | -20 to +200 | ≤15% | 60–80 | Aromatic hydrocarbons, acids, fuels |
| TPE | -40 to +135 | ≤40% | 50–95 | Abrasion, flexibility, low-temperature performance |
Understanding these material characteristics allows engineers to move beyond generic solutions and implement seals that deliver reliable, long-term performance. At Baoshida, we partner with OEMs to develop application-specific formulations—ensuring that every door seal not only fits but functions with industrial precision.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Precision Door Seals: Viton, Nitrile, and Silicone
Selecting the optimal elastomer for door seals is critical for ensuring long-term sealing integrity, environmental resistance, and performance consistency across demanding industrial and automotive applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our OEM-focused engineering team rigorously evaluates material properties against specific operational parameters. This section details the core specifications of three dominant compounds: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), providing the technical foundation for informed selection.
Viton fluoroelastomers represent the pinnacle of chemical and thermal resistance for extreme environments. Formulated with high fluorine content, Viton seals maintain structural integrity within a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to 230°C, with brief excursions up to 300°C. They exhibit exceptional resistance to automotive fuels, oils, lubricants, and aggressive industrial chemicals, including many solvents and acids. Standard formulations typically achieve a Shore A hardness of 70-90, tensile strength of 10-15 MPa, and elongation at break of 150-250%. Viton’s primary limitation is higher material cost and reduced low-temperature flexibility compared to NBR or Silicone, making it ideal for under-hood automotive seals, aerospace applications, and chemical processing equipment where chemical exposure is severe.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) remains the most widely specified material for general-purpose door seals due to its excellent balance of performance and cost-effectiveness. NBR demonstrates superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and water, with a standard continuous service range of -30°C to 120°C (special formulations extend to 150°C). Its Shore A hardness typically spans 50-90, offering versatility in compression force requirements. Standard tensile strength ranges from 10-20 MPa with elongation of 200-400%. While NBR provides good abrasion resistance and mechanical properties, it exhibits limited resistance to ozone, weathering, and polar solvents like ketones or esters. It is the preferred choice for automotive door/window seals, appliance gaskets, and general industrial enclosures where fuel/oil exposure is moderate.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in applications demanding extreme temperature stability and consistent flexibility. VMQ seals operate reliably from -60°C to 200°C continuously, with short-term peaks near 230°C. They offer outstanding resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, maintaining elastic properties over wide temperature swings. Standard hardness ranges from 30-80 Shore A, with tensile strength of 5-10 MPa and high elongation (300-700%). Silicone’s key limitations include lower tensile strength and tear resistance compared to NBR or Viton, and poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids. Its exceptional biocompatibility and electrical insulation properties make it indispensable for medical equipment doors, high-end electronics enclosures, and architectural glazing systems requiring long-term outdoor exposure.
The following table summarizes critical comparative specifications based on standard ASTM test methods (D2000, D395, D412):
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Temp Range | -20°C to 230°C | -30°C to 120°C | -60°C to 200°C |
| Shore A Hardness Range | 70 – 90 | 50 – 90 | 30 – 80 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 10 – 15 | 10 – 20 | 5 – 10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150 – 250 | 200 – 400 | 300 – 700 |
| Compression Set (22h, 150°C) | 15% – 25% | 20% – 40% | 25% – 35% |
| Primary Chemical Resistance | Fuels, Oils, Acids, Solvents | Petroleum Oils, Greases, Water | Ozone, UV, Weathering |
| Key Application Focus | Extreme Chemical/Temp Environments | General Purpose Automotive/Industrial | Extreme Temp Flexibility, Weathering |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages this material science expertise to provide OEMs with tailored door seal solutions. Our engineering team collaborates closely with clients to match compound properties precisely to environmental stressors, regulatory requirements, and lifecycle cost targets, ensuring optimal sealing performance and durability in your specific application. Material selection is not generic; it is a precision engineering decision fundamental to product success.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Excellence in Precision Rubber Seal Development
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our reputation in the precision rubber seals industry. With a dedicated team of five certified mould engineers and two specialized rubber formulation engineers, we deliver technically advanced, application-specific door seal solutions tailored to the exacting demands of global OEMs. Our integrated engineering approach ensures seamless development from concept to mass production, combining material science with precision tooling expertise.
Our two in-house rubber formula engineers possess extensive experience in polymer chemistry and elastomer compounding. They are responsible for developing custom rubber formulations that meet specific performance criteria such as compression set resistance, temperature stability, UV and ozone resistance, and sealing integrity under dynamic loads. Whether the application requires EPDM for weather resistance, silicone for extreme temperatures, or NBR for oil resistance, our formulation team optimizes compound performance while maintaining cost-efficiency and process compatibility. This level of material control is critical for OEMs requiring long-term reliability in automotive, construction, and industrial equipment applications.
Complementing our formulation expertise are five professional mould engineers who specialize in the design and validation of high-precision rubber compression, transfer, and injection moulds. These engineers utilize advanced CAD/CAM software and finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate material flow, predict part deformation, and optimize gate design and venting. This precision-driven methodology reduces prototyping cycles and ensures consistent dimensional accuracy across production runs. Our moulds are built to withstand high-cycle operations while maintaining tight tolerances—essential for door seals that must perform reliably over thousands of opening and closing cycles.
We operate as a full-service OEM partner, offering end-to-end development support including design for manufacturability (DFM) reviews, rapid prototyping, material qualification, and process validation. Our engineering team collaborates directly with client R&D departments to refine seal geometry, optimize durometer profiles, and ensure compliance with international standards such as ISO 3302 and ISO 2768. This collaborative model accelerates time-to-market and reduces development risk.
The synergy between our formulation and mould engineering disciplines enables us to solve complex sealing challenges—such as multi-material bonding, low-temperature flexibility, and acoustic insulation—through integrated design and material innovation. Our technical team maintains rigorous documentation and traceability protocols, supporting clients in regulated industries requiring full material and process audits.
Below is a summary of our core engineering capabilities and technical parameters:
| Parameter | Specification / Capability |
|---|---|
| Mould Engineers | 5 certified professionals |
| Rubber Formula Engineers | 2 specialized in elastomer development |
| Mould Design Software | AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Moldflow |
| Standard Elastomers | EPDM, NBR, Silicone, CR, SBR, ACM |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 40–90 ±5 |
| Tolerance Compliance | ISO 3302 (Class M2), ISO 2768 (Fine) |
| Prototyping Lead Time | 15–25 days (including tooling and sample validation) |
| OEM Collaboration Model | Joint design, DFM, material selection, PPAP support |
This engineering foundation positions Suzhou Baoshida as a trusted technical partner for OEMs demanding precision, reliability, and innovation in door seal manufacturing.
Customization Process
Customization Process for Precision Door Seals
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our OEM customization process for rubber door seals integrates material science with precision manufacturing to meet exacting industrial specifications. This structured workflow ensures seamless transition from client drawings to high-volume production while mitigating performance risks.
Drawing Analysis
Initial engagement begins with rigorous technical review of client CAD files and dimensional schematics. Our engineering team validates critical parameters including cross-sectional tolerances, compression deflection requirements, and installation groove compatibility. We identify potential stress concentrations or material flow challenges during molding, providing actionable feedback within 72 hours. This phase ensures geometric feasibility aligns with ISO 3302-1 tolerances and application-specific functional demands.
Material Formulation
Based on operational environment data—temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and dynamic compression cycles—our rubber chemists develop proprietary compound formulations. We prioritize optimizing durometer stability, compression set resistance, and low-temperature flexibility. Key material properties are validated against ASTM D2000 standards before prototyping. The table below outlines common formulations for door seal applications.
| Material Type | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 55–75 | -50 to +135 | Automotive weatherstripping, exterior building seals |
| SBR | 60–80 | -30 to +100 | Industrial equipment doors, cost-sensitive applications |
| NBR | 50–70 | -20 to +105 | Fuel/oil-resistant seals in machinery enclosures |
Prototyping Validation
Pre-production samples are manufactured using client-specified tooling or our rapid prototyping molds. Each prototype undergoes accelerated life testing: 10,000+ compression cycles per SAE J1488, ozone resistance per ASTM D1149, and adhesion strength verification. Dimensional reports with GD&T callouts are provided alongside material test certificates. Client approval requires ≤0.1mm deviation on critical dimensions and <15% compression set at 70°C after 24 hours.
Mass Production Deployment
Upon prototype sign-off, we initiate series production with embedded quality gates. Every production run includes real-time cavity pressure monitoring and automated vision inspection for flash control. Statistical process control (SPC) tracks key variables like cure time and compound viscosity. Final lots undergo batch traceability auditing per IATF 16949, with material certificates and dimensional reports shipped with each container. Our lean manufacturing cells maintain ±0.15mm tolerance consistency at volumes exceeding 500,000 units monthly.
This end-to-end process eliminates iteration delays through concurrent engineering, ensuring your door seals achieve 15+ year service life in demanding environments. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM partnership guarantees material-performance alignment from drawing board to assembly line integration.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Door Seal Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in the engineering and supply of high-performance rubber door seals tailored to meet the rigorous demands of industrial, automotive, architectural, and transportation applications. As a trusted OEM partner, we combine material science expertise with advanced manufacturing capabilities to deliver sealing solutions that ensure durability, environmental resistance, and optimal performance under dynamic conditions. Our portfolio spans a wide range of elastomeric compounds, including EPDM, silicone, neoprene, and thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV), each formulated to address specific operational challenges such as temperature extremes, UV exposure, compression set resistance, and chemical compatibility.
Our door seals are precision-engineered using state-of-the-art extrusion, splicing, and molding technologies, ensuring consistent dimensional accuracy and seamless integration into your assembly process. Whether you require custom profiles, co-extruded multi-material seals, or application-specific durometer formulations, our engineering team works closely with clients to develop solutions that exceed functional and regulatory requirements. We support low-volume prototyping through high-volume production, backed by stringent quality control protocols and ISO-compliant documentation.
To ensure long-term reliability, our seals undergo comprehensive performance validation, including compression deflection testing, accelerated aging, ozone resistance, and weathering cycles. This technical rigor, combined with our responsive supply chain, positions Suzhou Baoshida as a strategic partner for global manufacturers seeking consistent quality and technical depth in their sealing components.
Below is a representative specification table for a standard EPDM door seal profile commonly used in commercial vehicle and enclosure applications:
| Property | Specification | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material | EPDM 70±5 Shore A | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥10 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395B |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +135°C | Internal |
| Weathering Resistance | 1500h no cracking | ASTM G154 |
| Flame Rating | UL94 HB | UL94 |
For technical collaboration, custom formulation development, or sample requests, we invite you to contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. Mr. Boyce brings over 12 years of experience in elastomer formulation and industrial sealing applications, providing direct technical oversight for client-specific projects. Reach him via email at [email protected] to discuss your door seal requirements, request material data sheets, or initiate a design review. Our team responds to all inquiries within 24 business hours and supports communication in English, Mandarin, and technical German. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for engineered rubber solutions where performance, precision, and reliability matter.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
