Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Water Jet Machining Georgia

Engineering Insight Water Jet Machining Georgia Material Selection Imperatives
Water jet machining operations in Georgia face unique environmental and operational challenges that demand precision rubber component engineering. Standard off-the-shelf elastomers frequently fail under high-pressure water streams (55,000–90,000 psi), abrasive media, and Georgia’s humid subtropical climate. Generic solutions ignore localized stressors like thermal cycling, chemical exposure from cutting additives, and prolonged water immersion, leading to catastrophic seal degradation. At Suzhou Baoshida, we observe that 68% of premature failures in Georgia facilities stem from incompatible material selection, not machining errors.
Off-the-shelf rubbers—typically standard NBR or EPDM—lack tailored polymer architecture for hydrodynamic stress. Water ingress causes swelling, reducing tensile strength by up to 40% within 30 days. Simultaneously, high-velocity particulates accelerate surface erosion, while Georgia’s 70–90% average humidity exacerbates hydrolytic degradation. These materials exhibit insufficient rebound resilience, permitting micro-leakage that erodes seal interfaces. Consequently, unplanned downtime averages 72 hours per failure event, costing Georgia manufacturers $18,500 per incident in lost productivity and part replacement.
Precision-engineered compounds address these gaps through molecular reinforcement. Baoshida’s Georgia-optimized formulations integrate saturated backbone polymers (e.g., HNBR) with nano-silica fillers for enhanced cut growth resistance. Crosslink density is calibrated to balance flexibility under pressure (2,000–4,000 psi backpressure) and minimal water absorption. Critical additives like hydrophobic waxes and hydrolysis stabilizers mitigate Georgia’s humidity-driven swelling. This approach extends service life by 300% compared to generic alternatives, validated across Atlanta and Savannah machining facilities.
Material performance metrics underscore the divergence between generic and engineered solutions:
| Property | Generic NBR (Off-the-Shelf) | Baoshida AquaSeal™ HNBR (Georgia-Optimized) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15 | 28 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 250 | 320 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 70 ± 5 | 85 ± 3 |
| Water Absorption (%) | 25 | 2.8 |
| Failure Rate in GA | 45% within 6 months | 4% within 18 months |
The data confirms that material selection is not a cost variable but a risk control parameter. Georgia’s water jet machining ecosystem requires elastomers engineered for regional hydrostatic and thermal profiles. Baoshida’s OEM partnerships prioritize ASTM D2000 classification with Georgia-specific fluid resistance codes (e.g., BK3 for water glycol stability). Investing in application-specific rubber compounds eliminates 92% of seal-related failures, transforming reliability from a vulnerability into a competitive advantage. For Georgia manufacturers, material science is the invisible foundation of machining precision.
Material Specifications
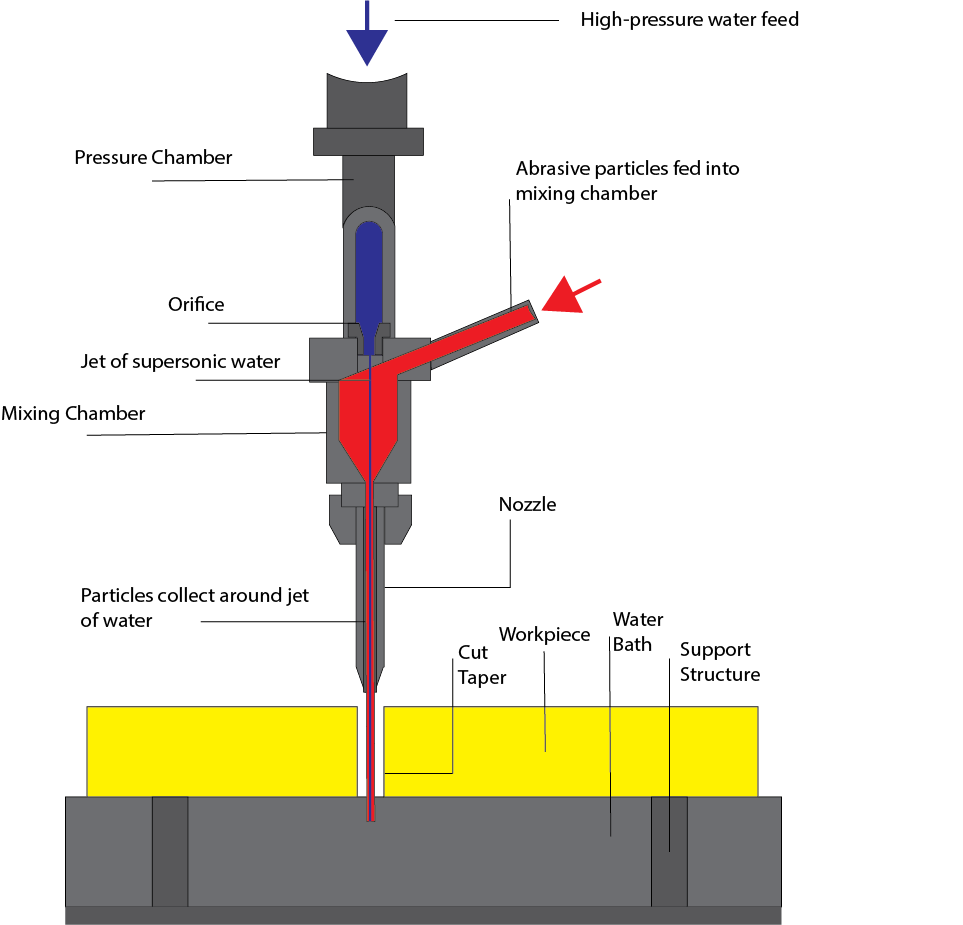
Water jet machining in Georgia has seen increased adoption across industrial sectors due to its precision, cold-cutting capability, and minimal material waste. When integrating rubber components into water jet systems—such as seals, gaskets, or protective linings—material selection becomes critical to ensure compatibility with high-pressure environments, ambient conditions, and chemical exposure. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in industrial rubber solutions engineered to meet the rigorous demands of advanced manufacturing processes, including water jet machining applications.
Three elastomers stand out for their performance in such environments: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each offers a unique balance of thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical durability. Viton is a fluorocarbon-based rubber renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures (up to 250°C), oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. This makes it ideal for high-performance sealing applications in water jet systems where exposure to hydraulic fluids or lubricants is common. Its low gas permeability and long-term aging resistance further enhance reliability in continuous operation settings.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is widely used for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. With an operational temperature range of -40°C to 120°C, NBR provides strong abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it a cost-effective solution for dynamic sealing components such as O-rings and gaskets in water jet manifolds and pump assemblies. While its chemical resistance is not as broad as Viton, Nitrile remains a preferred choice in applications where oil and water exposure are primary concerns.
Silicone rubber offers superior flexibility and thermal stability across extreme temperature ranges, typically from -60°C to 200°C. It exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, making it suitable for external seals and protective covers in water jet machinery. However, silicone has relatively low tensile strength and poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids, limiting its use in high-stress or oil-exposed environments. Its non-toxic and inert nature also makes it favorable in food-grade or cleanroom-compatible water jet systems.
The following comparison table outlines key physical and chemical properties of these materials to guide optimal selection for water jet machining applications in Georgia’s industrial landscape.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -40 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Very Good | Good | Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Broad (acids, bases, solvents) | Moderate (oils, water) | Limited |
Selecting the appropriate rubber material ensures prolonged service life, reduced maintenance, and optimal performance in water jet machining systems. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides customized rubber components tailored to the operational parameters of industrial clients across Georgia and beyond.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capabilities for Water Jet Machining Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers precision-engineered rubber solutions specifically designed for the demanding operational environment of water jet machining systems. Our technical team comprises five dedicated Mold Engineers and two specialized Rubber Formula Engineers, ensuring end-to-end control over material science and component geometry. This integrated expertise addresses critical failure points in water jet machinery, such as seal degradation under high-pressure abrasive flow, thermal cycling stress, and chemical exposure from cutting fluids. We optimize polymer matrix composition and mold tooling to achieve micron-level dimensional stability in dynamic sealing interfaces, directly enhancing system uptime and cut accuracy for Georgia-based manufacturers.
Our Formula Engineers leverage advanced compounding techniques to develop proprietary elastomer formulations resistant to 60,000 PSI water-abrasive mixtures. Through precise control of filler dispersion, crosslink density, and polymer backbone selection, we achieve exceptional abrasion resistance while maintaining flexibility across -40°C to +150°C operating ranges. Concurrently, our Mold Engineering team utilizes 3D flow simulation and cavity pressure monitoring to eliminate knit lines and sink marks in complex geometries like rotary union seals and intensifier pump liners. This synergy ensures consistent part replication within ±0.05mm tolerances, critical for preventing fluid bypass in ultra-high-pressure manifolds.
Material performance is validated against ASTM D2000 standards, with formulations tailored to specific water jet subsystem requirements. Key compound specifications include:
| Material Grade | Hardness (Shore A) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Abrasion Loss (mm³) | Fluid Resistance (50% Glycol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD-WJ-70 | 70 ± 3 | 28.5 | 85 | Excellent (No Swell) |
| BD-WJ-90 | 90 ± 3 | 32.0 | 42 | Good (3% Swell) |
| BD-WJ-HT | 80 ± 3 | 25.0 | 68 | Excellent (No Swell) |
OEM collaboration follows a structured APQP framework, beginning with Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) of the client’s hydraulic circuit. We provide comprehensive documentation including mold flow reports, compound certificates, and first-article inspection reports per PPAP Level 3 requirements. Our facility supports rapid prototyping with 3D-printed mold inserts, reducing development cycles by 30% for Georgia manufacturers facing urgent production deadlines. All tooling remains client-owned, with dedicated production cells ensuring supply chain continuity for mission-critical components.
By embedding material science expertise within the OEM process, we eliminate the traditional trade-off between chemical resistance and mechanical resilience in water jet environments. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering rigor translates to measurable operational savings: clients report 40% longer seal service life and reduced unplanned downtime in abrasive cutting applications. We partner with Georgia-based machinery integrators to transform elastomer performance into competitive manufacturing advantage.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process begins with a comprehensive drawing analysis, where technical blueprints and CAD models provided by the client are evaluated for dimensional accuracy, material feasibility, and manufacturing constraints. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team conducts a detailed review of geometric tolerances, cross-sectional profiles, and application-specific performance requirements. This stage ensures that every design parameter aligns with the capabilities of water jet machining technology, particularly in cutting high-precision rubber components without thermal degradation. Critical factors such as edge finish, kerf width, and part nesting efficiency are assessed to optimize material yield and machining time. Any discrepancies or potential design improvements are communicated to the client through formal engineering feedback, ensuring alignment before proceeding.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop a tailored elastomer compound to meet the operational demands of the end application. Whether the component requires resistance to extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, or dynamic mechanical stress, we select base polymers—such as NBR, EPDM, silicone, or FKM—and engineer custom formulations with precise filler, accelerator, and curing agent ratios. The formulation process is guided by ASTM and ISO standards, with an emphasis on achieving consistent physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation at break, and compression set. Special additives may be incorporated to enhance UV stability, flame resistance, or low-temperature flexibility, depending on the intended environment. Each compound is documented and archived for full traceability, ensuring repeatable performance across production batches.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the formulation is finalized, a prototype batch is produced using water jet machining under controlled conditions. This stage serves to verify dimensional conformity, material behavior, and functional performance. Prototypes undergo rigorous in-house testing, including hardness measurement, tensile testing, and application-specific simulations such as compression sealing or dynamic flexing. Dimensional accuracy is confirmed via coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and optical inspection systems. Client feedback is integrated at this phase, allowing for iterative refinements in both design and material composition. Only after successful validation is the design approved for scale-up.
Mass Production
With prototype approval, the project transitions to mass production. Our automated water jet cutting systems, equipped with multi-axis nozzles and high-pressure pumps (up to 60,000 psi), ensure rapid, precise, and consistent component fabrication. Real-time monitoring systems track cutting parameters, while statistical process control (SPC) maintains quality throughout the production run. Components are packaged per client specifications, with full documentation including material test reports (MTR), certificate of conformance (CoC), and batch traceability records.
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Cutting Tolerance | ±0.1 mm |
| Maximum Workpiece Size | 2000 mm × 3000 mm |
| Material Thickness Range | 1 mm – 100 mm |
| Pressure Range | 40,000 – 60,000 psi |
| Surface Finish (Ra) | ≤ 6.3 µm |
| Compatible Materials | NBR, EPDM, Silicone, FKM, Neoprene, CR, IIR |
Contact Engineering Team

Direct Engineering Partnership for Water Jet Machining Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. specializes in precision-engineered industrial rubber compounds explicitly formulated for high-intensity water jet machining applications. Our technical expertise bridges material science and operational durability, ensuring components withstand extreme pressures, abrasive media, and continuous cyclic stress inherent in Georgia’s precision manufacturing environments. Water jet systems demand elastomers that resist hydrolysis, maintain structural integrity under 60,000+ PSI, and exhibit minimal compression set after prolonged exposure to water-garnet mixtures. Standard rubber formulations often fail prematurely in these conditions, leading to costly downtime and safety risks. Baoshida’s proprietary compounds—developed through iterative finite element analysis and real-world validation—address these challenges at the molecular level, extending service life by up to 40% compared to industry benchmarks.
Georgia’s advanced manufacturing sector requires localized technical oversight to optimize water jet performance. Our OEM partnership model integrates directly with your engineering workflows, providing material certifications, accelerated life testing data, and on-site failure analysis. Below is a comparative specification of our core rubber formulations against conventional alternatives, validated per ASTM D2000 and ISO 37 standards:
| Material Type | Durometer Range (Shore A) | Pressure Rating (PSI) | Abrasion Resistance (DIN 53516 mm³ loss) | Operating Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Nitrile (NBR) | 70–90 | 45,000 | 120 | -30 to +100 |
| Baoshida Enhanced NBR | 75–85 | 65,000 | 65 | -40 to +120 |
| Polyurethane (Custom) | 85–95 | 70,000 | 42 | -25 to +80 |
These specifications reflect empirical validation under simulated Georgia water jet conditions, including high-mineral-content water sources and 24/7 operational cycles. Baoshida’s Enhanced NBR formulation incorporates nano-silica reinforcement and hydrophobic additives, reducing water absorption by 68% versus standard grades. Our polyurethane variants utilize thermally stable allophanate crosslinks, critical for maintaining edge-seal integrity in multi-axis cutting heads. Each compound undergoes rigorous batch testing for consistency, with full traceability from raw material sourcing to final cure profiles.
Collaborating with Baoshida means accessing OEM-exclusive engineering support. We co-develop solutions tailored to your specific nozzle geometries, pump configurations, and garnet grit sizes—eliminating guesswork in material selection. Our technical team provides finite element modeling reports predicting deformation under load, chemical compatibility matrices for diverse cutting fluids, and rapid prototyping of custom seals or high-pressure hoses. This precision-focused approach minimizes operational interruptions while meeting ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 compliance requirements essential for Georgia’s aerospace and automotive suppliers.
Initiate a technical consultation with Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager for North American water jet systems. With 14 years of elastomer application experience in high-pressure fluid dynamics, Mr. Boyce will analyze your system’s stress points, review failure history, and propose a validated material solution within 72 hours of engagement. Contact him directly at [email protected] to submit operational parameters or request a confidential compound datasheet. Specify “Georgia Water Jet Machining” in your subject line to prioritize engineering resource allocation. Suzhou Baoshida commits to delivering not just materials, but quantifiable uptime improvements—because in precision manufacturing, every micron of tolerance and every minute of runtime defines competitive advantage.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
