Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Weatherproofing For Doors

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Door Weatherproofing Systems
Off-the-shelf door seal solutions frequently fail in demanding commercial and industrial applications due to inadequate material science considerations. Generic rubber profiles prioritize initial cost over long-term environmental resilience, leading to premature degradation, compromised energy efficiency, and increased maintenance costs. The core failure mechanism lies in the mismatch between standard polymer formulations and the complex, dynamic stresses encountered at the door interface. Standard ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) compounds, while offering baseline weather resistance, often lack the tailored molecular architecture required to withstand simultaneous exposure to ultraviolet radiation, ozone, extreme thermal cycling, moisture ingress, and mechanical compression fatigue. This results in critical performance failures: surface cracking from ozone attack, permanent set (loss of sealing force) due to poor compression set resistance, hardening or softening outside narrow temperature bands, and adhesion loss at substrate interfaces. These failures are not random defects but predictable outcomes of using non-optimized materials.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses this through precision-engineered rubber compounds developed specifically for architectural weatherseals. Our formulations leverage advanced polymer science, incorporating specialized stabilizers, optimized crosslink densities, and proprietary filler systems. This molecular-level control ensures consistent elastic recovery under sustained compression, exceptional resistance to atmospheric degradation agents, and stable physical properties across extended temperature excursions. Crucially, we match the compound’s glass transition temperature (Tg) and cure kinetics to the specific door system dynamics and regional climate profiles, preventing brittleness in cold climates or excessive softening in tropical environments. Material selection is not merely choosing a durometer; it requires holistic understanding of the polymer backbone’s vulnerability to chain scission under environmental stress and the formulation’s ability to maintain seal integrity through thousands of operational cycles.
The performance delta between standard and engineered compounds is quantifiable. Consider the critical parameters for high-cycle commercial door applications:
| Performance Parameter | Standard EPDM Seal (Off-the-Shelf) | Baoshida Engineered Weatherseal Compound | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | 35-45% | ≤ 18% | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Ozone Resistance (50 ppm) | Cracking within 48 hours | No cracks after 168 hours | ASTM D1149 |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +100°C | -55°C to +130°C | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Retention (150h QUV) | 60-70% | ≥ 85% | ASTM G154 |
| Shore A Hardness Variation | ±8 points | ±3 points | ASTM D2240 |
These specifications demonstrate how engineered materials directly counteract the failure modes of generic seals. Superior compression set resistance ensures the seal maintains contact force against the door frame after years of use, preventing air and water infiltration. Enhanced ozone and UV stability eliminate surface degradation that creates leak paths. The extended operational temperature range guarantees performance in climatic extremes where standard seals become ineffective. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM partnership model integrates this material science expertise early in the door system design phase, ensuring the weatherseal is not an afterthought but a validated, high-reliability component. This approach eliminates the costly downtime and reputational damage associated with premature seal failure, delivering true lifecycle value for building envelope performance.
Material Specifications
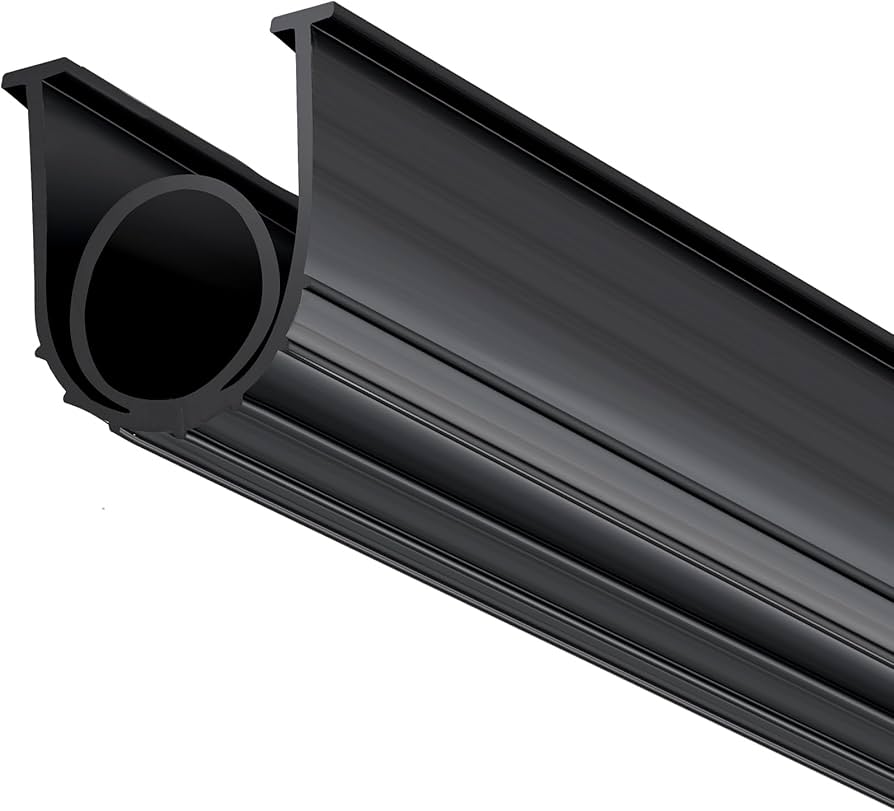

Weatherproofing for doors in industrial and commercial applications demands high-performance sealing materials capable of withstanding extreme environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, moisture, UV exposure, and chemical ingress. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in engineered rubber solutions tailored for durable, long-term door sealing performance. Our primary elastomers—Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone—are selected based on their distinct chemical structures and performance profiles, ensuring optimal material-to-application alignment.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), exhibits exceptional resistance to high temperatures, ozone, and a broad range of chemicals, including oils, fuels, and acids. With a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to 250°C, Viton is ideal for extreme environments such as industrial ovens, cleanrooms, and chemical processing facilities where door seals must maintain integrity under aggressive conditions. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics further enhance reliability in critical sealing applications. However, Viton has limited flexibility at very low temperatures and higher material cost, making it best suited for high-value, high-stress installations.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a cost-effective solution with strong resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and water. Operating effectively between -30°C and 120°C, NBR is widely used in general industrial door systems exposed to mechanical stress and moderate environmental exposure. Its abrasion resistance and compressive strength make it suitable for frequently operated doors requiring consistent sealing force. While NBR performs poorly under prolonged UV and ozone exposure, protective coatings or blending with PVC can extend its outdoor service life.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) offers the widest thermal range, functioning reliably from -60°C to 230°C, making it ideal for doors in cryogenic storage, food processing, and outdoor architectural applications. It demonstrates excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering, maintaining elasticity and seal integrity over extended periods. Silicone is inherently non-toxic and complies with food-grade and medical standards, supporting use in regulated environments. However, it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton and NBR, necessitating design considerations for high-wear zones.
The selection of the appropriate elastomer depends on the operational environment, chemical exposure, temperature profile, and lifecycle requirements. Below is a comparative summary of key material specifications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to UV/Ozone | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Applications | High-temp seals, chemical environments | Industrial doors, garages | Outdoor doors, food processing, cold storage |
Understanding these material characteristics allows engineers and OEMs to specify the most suitable rubber compound for long-term weatherproofing performance.
Manufacturing Capabilities
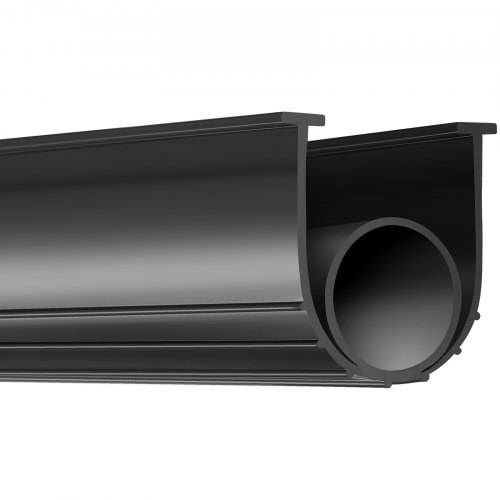
Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Door Weatherproofing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber weatherproofing solutions for doors through rigorous scientific methodology and deep industrial expertise. Our focus extends beyond standard sealing to address critical performance parameters inherent in demanding architectural and industrial door applications. Thermal cycling, UV exposure, repeated compression deformation, and chemical resistance to cleaning agents represent key failure modes requiring material science intervention. We mitigate these risks through proprietary compound development and precision molding processes, ensuring long-term dimensional stability and seal integrity under operational stress.
ENGINEERING ASSETS
Our core strength resides in a dedicated team of seven specialized engineers: five Mould Engineers and two Formula Engineers. This integrated structure enables seamless translation from material science to physical product. Formula Engineers develop custom elastomer compounds using advanced polymer chemistry, optimizing for low compression set, superior ozone resistance, and consistent Shore A hardness across extreme temperature ranges. Concurrently, Mould Engineers apply computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate flow behavior and predict part shrinkage, ensuring cavity design accuracy for complex door seal profiles. This collaborative workflow eliminates traditional handoffs between R&D and production, accelerating validation cycles while guaranteeing material properties are fully leveraged in the final geometry. We maintain full control over vulcanization kinetics, critical for achieving the cross-link density required in high-cycle door applications.
OEM MANUFACTURING EXCELLENCE
As a certified OEM partner, we implement a structured development protocol aligned with automotive and industrial equipment standards. Projects commence with comprehensive CAD analysis of client specifications, followed by DFM reviews to optimize for manufacturability without compromising performance. Our in-house tooling facility supports rapid prototyping using P20 and H13 steels, with cavity tolerances held to ±0.05mm. Client validation includes full material traceability, ASTM D2000 compliance documentation, and PPAP Level 3 submissions. We manage the entire lifecycle from concept to量产, including ongoing process capability studies (CpK ≥1.67) and automated dimensional inspection using coordinate measuring machines (CMM). This end-to-end ownership ensures consistent replication of engineered properties across production volumes, directly impacting door system reliability and end-user satisfaction.
The following table details key performance specifications achieved through our engineered compounds and processes for standard door weatherstrip applications:
| Property | Test Method | Baoshida Standard | Industry Typical |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% | ≤35% |
| Temperature Range | ASTM D1329 | -50°C to +150°C | -40°C to +120°C |
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 65±5 | 60-75 |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D297 | 1.15±0.05 | 1.10-1.25 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥10.0 MPa | ≥8.0 MPa |
This technical rigor, combined with our vertically integrated engineering resources, positions Suzhou Baoshida as a strategic partner for OEMs requiring weatherproofing solutions that meet exacting durability and performance criteria in global door manufacturing.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for industrial rubber weatherproofing solutions begins with precise drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., engineering teams evaluate client-submitted technical drawings to verify dimensional accuracy, profile geometry, and installation interface compatibility. This stage includes tolerance review, cross-sectional validation, and material clearance assessment. Our engineers perform GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) checks to ensure the final product will maintain sealing integrity under operational stress. Any discrepancies or design risks—such as excessive compression set zones or insufficient land width—are flagged and discussed with the client for optimization. This phase is critical to prevent field failures and ensure seamless integration into door systems.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, the formulation stage tailors rubber compound properties to meet environmental and mechanical demands. Weatherproofing profiles for doors must resist UV degradation, ozone exposure, temperature extremes (from -40°C to +120°C), and repeated compression cycles. We utilize EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) as the base polymer for most outdoor applications due to its superior weather resistance and thermal stability. For environments requiring enhanced oil or flame resistance, silicone or neoprene formulations are developed. Additives such as anti-oxidants, UV stabilizers, and reinforcing fillers are precisely metered to achieve target hardness (Shore A 50–80), elongation at break (>200%), and compression set (<25% after 22 hours at 70°C). Each formulation is documented and archived for full traceability and batch consistency.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the compound is finalized, prototyping is conducted using precision extrusion and vulcanization techniques. Short-run samples are produced under near-production conditions to simulate real-world performance. These prototypes undergo rigorous testing, including air and water infiltration under simulated wind pressure, compression deflection analysis, and accelerated aging in environmental chambers. Feedback from physical testing is used to refine both profile geometry and compound behavior. Clients receive test reports and physical samples for field evaluation, ensuring performance alignment with project specifications before full-scale rollout.
Mass Production and Quality Assurance
After client approval, the project transitions to mass production. Our facility employs continuous extrusion lines with laser-based diameter control and microwave-assisted curing to ensure uniformity. Every production batch undergoes inline inspection and final quality checks per ISO 3302 and ISO 2768 standards. Products are packaged to prevent deformation during shipping.
Key material and performance specifications are summarized below:
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥10 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥250% |
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | ASTM D395 | ≤20% |
| Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +120°C |
| UV Resistance | ASTM G154 | Pass (2000h) |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracking (100 pphm, 40°C) |
This structured approach ensures reliable, high-performance rubber weatherproofing profiles tailored to exacting door system requirements.
Contact Engineering Team

Optimizing Door Weatherproofing Through Advanced Rubber Engineering
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers mission-critical rubber sealing solutions engineered specifically for industrial door systems operating in extreme environmental conditions. Our formulations address the core challenges of thermal cycling, UV degradation, and moisture ingress that compromise conventional weatherstripping. Unlike generic elastomers, our proprietary compounds integrate nano-reinforced polymers and precision-cured crosslinking architectures to maintain dimensional stability across -60°C to +150°C operational ranges. This ensures consistent compression force retention after 10,000+ cycles—a non-negotiable requirement for high-traffic commercial and industrial facilities where energy efficiency and structural integrity are paramount.
Material selection directly dictates long-term performance in door weatherproofing applications. Below we detail the technical specifications of our two flagship compounds, validated per ISO 3384 and ASTM D2000 standards:
| Property | EPDM 7075 Series | TPE 8800 Series | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 65 ± 3 | 70 ± 3 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12.5 min | 14.0 min | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (%) | 18 max @ 70°C/22h | 22 max @ 70°C/22h | ASTM D395 |
| Temp Range (°C) | -60 to +150 | -50 to +135 | ISO 188 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.25 ± 0.02 | 1.10 ± 0.02 | ASTM D297 |
The EPDM 7075 Series excels in ozone-resistant outdoor applications, while the TPE 8800 Series offers superior recyclability for sustainable manufacturing workflows without sacrificing hydrophobic performance. Both compounds undergo rigorous dynamic fatigue testing to simulate 15+ years of real-world door operation, ensuring zero leakage pathways develop at critical junctions like meeting rails and threshold interfaces. Our engineering team collaborates directly with OEMs to optimize profile geometry, durometer gradients, and adhesion systems—transforming theoretical material properties into field-proven sealing efficacy.
Suzhou Baoshida operates as a technical extension of your R&D department. We provide full material traceability, batch-specific certificates of conformance, and on-site failure analysis for weatherstripping systems under warranty claims. Our ISO 9001-certified production facility in Suzhou utilizes closed-mixing systems to eliminate batch variability, while our technical service engineers deploy spectral photometer analysis to verify UV stabilizer dispersion in every production run. This granular process control translates to doors that maintain NAFS AW-150 air/water infiltration ratings across diverse climatic zones—from coastal salt spray environments to arid desert installations.
Initiate your weatherproofing optimization protocol by contacting Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Partnership Manager. He will coordinate material sampling, application-specific performance validation, and seamless integration into your manufacturing workflow. Provide your door system specifications and environmental exposure requirements to receive a tailored compound recommendation within 24 business hours. Contact Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] to engineer sealing solutions that outperform industry benchmarks in durability and energy conservation. Suzhou Baoshida commits to delivering not just materials, but quantifiable reductions in field failure rates through rubber science precision.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
