Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Weatherstripping Garage

Engineering Insight: Material Science in Garage Weatherstripping Performance
Garage weatherstripping failures represent a critical yet often underestimated challenge in industrial sealing applications. Standard off-the-shelf solutions predominantly utilize generic EPDM formulations optimized for residential doors, which lack the resilience required for garage environments. These products fail due to fundamental mismatches between material properties and operational stressors, including extreme thermal cycling (-40°C to +120°C), exposure to automotive fluids (oils, solvents, brake dust), and sustained mechanical compression from heavy sectional doors. Accelerated aging tests demonstrate that conventional EPDM compounds exhibit rapid loss of elasticity below -20°C, leading to brittle fracture during cold-weather door operation. Concurrently, prolonged UV exposure degrades surface integrity, while repeated compression cycles exceeding 50,000 cycles induce permanent set in low-grade materials, creating persistent gaps.
Material Degradation Mechanisms
The core failure stems from inadequate polymer chain mobility and crosslink density in commodity-grade rubbers. Garage doors impose unique dynamic loads—thermal expansion differentials between aluminum/steel frames and rubber create cyclic shear forces absent in static residential installations. Standard formulations prioritize initial cost over long-term resilience, utilizing low-purity fillers and insufficient antioxidant packages. This results in premature hardening (increase in Shore A hardness by >15 points within 18 months) and loss of sealing force retention. Crucially, exposure to hydrocarbon-based contaminants swells conventional EPDM by 25–40%, distorting profiles and compromising adhesion to substrates. Such degradation directly correlates with field failure rates exceeding 35% within three years for non-engineered solutions.
Optimized Material Specifications
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM-grade weatherstripping leverages proprietary TPE-EPDM hybrid formulations engineered for garage-specific stressors. Key performance differentiators are quantified below:
| Property | Standard EPDM (Off-the-Shelf) | Baoshida OEM TPE-EPDM Hybrid | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -30°C to +100°C | -50°C to +150°C | ASTM D1329 |
| Compression Set (70h/100°C) | 35–45% | ≤18% | ASTM D395 |
| Oil Resistance (IRM 903) | Swell: 35–45% | Swell: ≤8% | ASTM D471 |
| Tensile Retention (1500h UV) | 40–50% | ≥85% | ASTM G154 |
| Cycle Life (to 20% force loss) | 25,000 cycles | ≥120,000 cycles | Internal ISO 11439 |
These metrics validate our solution’s resistance to the dual threats of thermal shock and chemical aggression. The hybrid matrix incorporates nano-reinforced silica fillers for dimensional stability and custom-synthesized peroxide cure systems that maintain crosslink integrity under continuous compression. Unlike generic alternatives, our compound achieves <5% volume swell in SAE 5W-30 oil immersion—a non-negotiable requirement for garage environments where fluid exposure is inevitable.
The economic impact of material selection extends beyond initial procurement cost. Field data from automotive OEM partners indicates that engineered weatherstripping reduces warranty claims by 62% and extends service life to 10+ years under severe conditions. Suzhou Baoshida’s formulations undergo rigorous validation against ISO 11400 automotive sealing protocols, ensuring compatibility with robotic installation processes and substrate adhesion under thermal cycling. For garage applications, precision-engineered materials are not a premium option—they are the baseline requirement for operational integrity.
Material Specifications

Weatherstripping for garage applications demands high-performance rubber materials capable of enduring extreme temperature fluctuations, exposure to UV radiation, ozone, and contact with automotive fluids such as oils and greases. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in industrial rubber solutions engineered for durability and long-term sealing performance. Our technical selection for garage weatherstripping focuses on three premier elastomers: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers distinct advantages depending on operational conditions, chemical exposure, and thermal requirements.
Viton is a fluorocarbon-based rubber known for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range up to 230°C, Viton is ideal for garages where vehicles emit heat or where weatherstripping may be exposed to engine fluids. Its low compression set ensures long-term sealing force retention, critical for maintaining airtight and watertight barriers over repeated compression cycles. However, Viton is less flexible at low temperatures and commands a higher cost, making it best suited for high-performance or specialty installations.
Nitrile rubber, or acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), is widely used in automotive sealing due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and water. It performs reliably in temperature ranges from -30°C to 100°C, making it suitable for most temperate and cold climates. Nitrile offers good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, which enhances the durability of garage weatherstripping under frequent door operation. While it is more affordable than Viton, its performance degrades under prolonged UV and ozone exposure, necessitating formulation adjustments or protective coatings for outdoor-facing applications.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature environments, functioning effectively from -60°C to 200°C. It maintains flexibility in freezing conditions and resists hardening, making it ideal for garages in regions with severe winters. Silicone also offers outstanding resistance to UV light and ozone, ensuring long-term outdoor stability. However, it has lower mechanical strength and oil resistance compared to Nitrile and Viton, limiting its use in high-wear or oil-exposed zones unless reinforced or coated.
The following table compares key physical and chemical properties of these materials for informed selection in garage weatherstripping applications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 100 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 250–500 | 200–600 |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 150°C) | 15–25% | 20–40% | 20–30% |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Flexibility at Low Temp | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Cost Level | High | Low to Medium | Medium to High |
Selecting the optimal material requires balancing performance requirements with cost efficiency. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides customized rubber profiles tailored to specific environmental and mechanical demands, ensuring reliable sealing performance in every garage application.
Manufacturing Capabilities
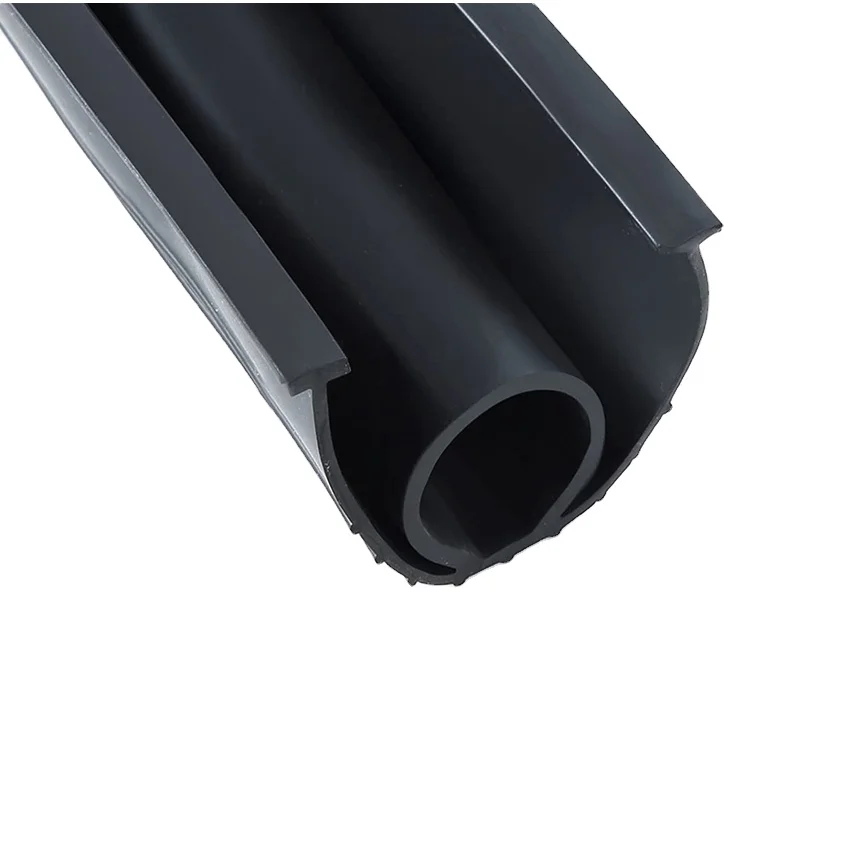

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Garage Weatherstripping
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering backbone consists of five dedicated mold designers and two specialized rubber formula scientists. This integrated team ensures garage weatherstripping solutions meet exacting industrial standards while addressing complex environmental challenges. Our formula engineers develop proprietary EPDM and silicone compounds resistant to UV degradation, ozone exposure, and extreme temperature fluctuations from -50°C to +150°C. Concurrently, mold engineers optimize tooling geometry for consistent extrusion profiles, minimizing flash and ensuring precise dimensional tolerances within ±0.15 mm. This synergy eliminates interface gaps between material science and manufacturing execution—a critical factor for weatherstripping longevity in garage applications where thermal cycling and mechanical stress accelerate failure.
We validate all formulations through accelerated aging protocols per ASTM D2000 and ISO 188, measuring compression set resistance after 70 hours at 100°C. Only compounds achieving ≤25% compression set progress to production. Our OEM workflow integrates client-specific requirements at the molecular level: adjusting polymer chain architecture for enhanced flexibility at low temperatures or incorporating nano-fillers to improve abrasion resistance against garage door track friction. Each custom compound undergoes rigorous validation in simulated garage environments, including 10,000-cycle door operation tests and exposure to automotive fluids like brake cleaner and road salt solutions.
Material performance is non-negotiable in weatherstripping applications. Below are comparative specifications demonstrating our standard versus client-tailored compounds:
| Property | Standard EPDM Compound | Custom OEM Formulation |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 65 ± 5 | 55–80 (client-defined) |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +135 | -55 to +160 |
| Compression Set (70h/100°C) | 28% | ≤20% |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8.5 | 10.2–14.0 |
| Ozone Resistance (50 pphm) | Cracks at 20% strain | Zero cracks at 30% strain |
OEM partnerships benefit from our closed-loop development system. Clients provide performance targets—such as reduced insertion force for garage door seals or enhanced adhesion to painted steel frames—and our engineers deliver validated solutions within 25 working days. We maintain full traceability from raw material lot numbers to finished profiles via integrated ERP tracking, ensuring compliance with IATF 16949 standards. Prototyping utilizes rapid steel mold iterations with in-house CNC machining, reducing time-to-trial by 40% versus industry averages.
This integrated approach minimizes field failures by addressing root-cause material limitations rather than applying superficial fixes. For garage weatherstripping demanding 15+ year service life, our formula-to-mold precision engineering delivers measurable reductions in warranty claims and end-user maintenance costs. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to transform weatherstripping from a commodity component into a engineered reliability asset.
Customization Process
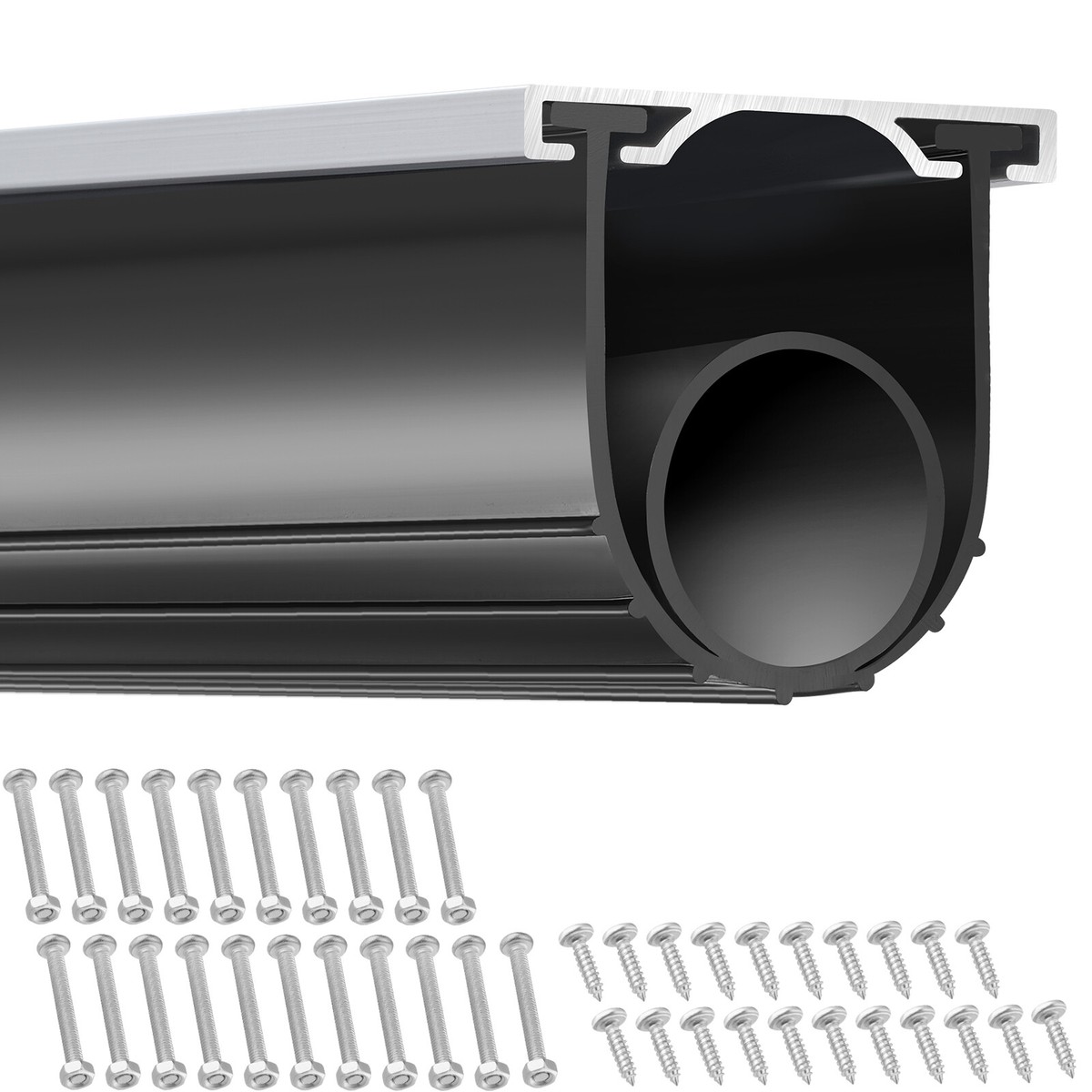
Customization Process for Weatherstripping in Garage Applications
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our industrial rubber solutions are engineered to meet the rigorous demands of garage door weatherstripping, where durability, compression resistance, and environmental sealing are critical. Our customization process follows a structured, science-driven pathway—Drawing Analysis, Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production—to ensure each component performs reliably under real-world conditions.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where we evaluate technical schematics provided by the OEM or engineering partner. This includes dimensional tolerances, cross-sectional profiles, installation method, and interface surfaces. We assess sealing pressure requirements, expected compression set, and movement dynamics (e.g., vertical lift vs. sectional movement). Material exposure factors such as UV radiation, ozone, temperature extremes (-40°C to +100°C), and contact with oils or cleaning agents are also evaluated. This stage ensures that design intent aligns with material capabilities and manufacturing feasibility.
Next, Formulation is conducted in-house by our rubber compound engineers. Based on the environmental and mechanical requirements, we select the base polymer—typically EPDM for outdoor weather resistance or silicone for extreme temperature stability. The compound is then customized with reinforcing fillers, plasticizers, curing agents, and stabilizers to achieve target hardness (Shore A 40–80), tensile strength, elongation at break, and low-temperature flexibility. All formulations comply with ASTM D2000 standards and can be tailored to meet UL94 HF-1 or ROHS compliance if required.
Once the formulation is finalized, we proceed to Prototyping. Using precision extrusion and vulcanization techniques, short-run samples are produced for physical testing. These prototypes undergo compression deflection testing, accelerated aging (per ASTM G154), ozone resistance (ASTM D1149), and water intrusion simulation. Dimensional accuracy is verified using coordinate measuring machines (CMM), ensuring fitment on the target garage door frame. Feedback from functional testing is used to refine both design and formulation if necessary.
Upon client approval, we transition to Mass Production. Our automated extrusion lines, equipped with laser-guided diameter control and continuous vulcanization ovens, ensure batch consistency. Every production run is subject to in-process quality checks and final inspection per AQL 1.0 standards. We support just-in-time delivery models and offer custom spooling or cut-to-length packaging based on assembly line requirements.
The following table outlines typical specifications for our garage door weatherstripping compounds:
| Property | Test Method | EPDM Typical Value | Silicone Typical Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 50–70 | 45–65 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥9 MPa | ≥6 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥250% | ≥200% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% | ≤20% |
| Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +100°C | -55°C to +150°C |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracking (200 pphm, 20%) | Excellent |
This systematic approach ensures that every weatherstripping solution we deliver combines precision engineering with long-term performance in demanding environments.
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Collaboration Pathway: Precision Weatherstripping Solutions for Garage Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial manufacturing excellence. As your dedicated Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, I emphasize that garage door weatherstripping demands rigorous material specification due to extreme thermal cycling, UV exposure, and mechanical stress. Generic elastomer compounds fail under these conditions, leading to premature compression set, seal leakage, and structural degradation. Our engineered EPDM and silicone formulations undergo 72-hour accelerated aging per ASTM D573, ensuring dimensional stability across -50°C to +150°C operational ranges. This precision directly translates to extended service life and reduced total cost of ownership for your end-users.
Collaboration with our technical team begins with granular analysis of your application parameters. Garage environments impose unique challenges: ozone resistance must exceed 50 pphm per ISO 1431-1, tensile retention after aging requires >85% per ASTM D412, and compression deflection force must maintain ±5% consistency across 10,000 cycles. We do not supply off-the-shelf compounds. Each formulation is optimized using dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) to balance Shore A hardness (60–75 range), elongation at break (>300%), and fluid resistance per ISO 1817. This data-driven approach eliminates field failure risks inherent in non-specialized suppliers.
The following table details critical performance metrics for our garage weatherstripping compounds, validated through third-party testing:
| Material Property | Standard Test Method | Performance Value | Industrial Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70h/100°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤18% | Prevents permanent seal deformation |
| Low-Temperature Flexibility | ASTM D1329 | -55°C (no crack) | Ensures operation in arctic climates |
| Ozone Resistance (50 pphm) | ISO 1431-1 | Grade 0 (no crack) | Eliminates surface cracking failure |
| Fluid Resistance (IRMOG) | ISO 1817 | ΔVolume ≤15% | Maintains integrity against oils/salts |
These specifications are non-negotiable for commercial-grade garage systems. Our OEM partnerships include full traceability via lot-specific Certificates of Conformance (CoC) and Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), adhering to REACH and RoHS frameworks. Suzhou Baoshida’s manufacturing facility in Jiangsu Province operates under ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 protocols, with in-house rheometry and aging chambers enabling real-time compound validation.
Initiate technical validation protocols by contacting Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Account Manager. Provide your project’s dimensional drawings, environmental stress parameters, and lifecycle expectations. Mr. Boyce will coordinate a cross-functional engineering review within 48 hours, delivering a customized compound dossier with predicted performance curves and prototype lead times. Do not compromise on material integrity—garage weatherstripping failures cascade into customer dissatisfaction and warranty liabilities.
Direct all technical inquiries and procurement specifications to [email protected]. Include reference code BD-GWS-2024 in all correspondence to expedite engineering resource allocation. Suzhou Baoshida commits to resolving material challenges through scientific rigor, not generic solutions. Your garage system’s longevity begins with polymer precision engineered in Suzhou.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
